1st century facts for kids
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 1st century BC · 1st century · 2nd century |
| Decades: | 0s 10s 20s 30s 40s 50s 60s 70s 80s 90s |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
The 1st century was a period of 100 years, lasting from the year 1 to the year 100. During this time, the Roman Empire grew much larger, especially in Europe, North Africa, and the Near East.
The Roman Empire kept expanding under Emperor Claudius in 43 AD. The changes made by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, helped make the empire stable. Later in the century, the family of emperors started by Augustus, called the Julio-Claudian dynasty, ended when Nero died in 68 AD. After Nero, there was a short period of civil war called the Year of the Four Emperors. This time of trouble ended when Vespasian became the 9th Roman emperor and started a new family of rulers, the Flavian Dynasty.
In China, the Han dynasty continued to rule. There was a short break for 14 years when Wang Mang took over and started the Xin dynasty. But Han rule was brought back in 23 AD. Wang Mang's time separated the Western Han and Eastern Han periods. The capital city was also moved from Chang'an to Luoyang.
Contents
Regions of the World
- Western Europe: Controlled by the Roman Empire.
- Southern Europe: Also controlled by Rome.
- North Africa: Under Roman control.
- West Africa: Many different tribal groups lived here.
- Central Africa: Home to Bantu tribes, and the Nok civilization was ending.
- East Africa: Important kingdoms like Meroe, Blemmyes, and the Axum Empire existed.
- Southern Africa: Inhabited by Bantu tribes and Khoisan people.
- Western Asia: Shared by the Roman and Parthian empires, along with smaller tribes.
- Central Asia: Home to Sarmatian tribes.
- South-central Asia: Ruled by the Kushan empire, Western Satraps, Satavahana, and Tibetans.
- Southeast Asia: Included city-states and kingdoms like Khmer, Mon kingdoms, and Funan.
- East Asia: The Eastern Han Dynasty ruled China, and Korea had three kingdoms: Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla.
Key Events
- Early 1st century – The famous statue of Augustus of Primaporta was made.
- Early 1st century – The beautiful Gemma Augustea was created.
- Early 1st century – The House of the Silver Wedding was built in Pompeii.
- 1 AD: Lions disappeared from Western Europe.
- c. 6 AD: A census (counting of people) happened in Judea.
- 8–23 AD: Wang Mang took control of China from the Han dynasty for a short time.
- 9 AD: Three Roman armies were defeated by German tribes led by Arminius at Teutoberg Forest.
- 14 AD: Augustus, the first Roman emperor, died. His nephew Tiberius became the next emperor.
- 28–75 AD: During the time of Emperor Ming of Han, Buddhism arrived in China.
- 26 AD: According to the Bible, Jesus began his public work.
- 30 AD: Jesus died on the cross. This marked the start of the Christian Church.
- 34 AD: Saint Paul became a Christian.
- 41–54 AD: An Ambassador from Sri Lanka visited the court of Emperor Claudius in Rome.
- Masoretes added special marks to the Hebrew Bible to show how words should be pronounced.
- Buddhist monks in Sri Lanka wrote down Buddha's teachings for the first time.
- The Kushan Empire, a group of nomadic people, took control of parts of Afghanistan, Pakistan, and North India.
- The Goths settled in northern Poland and created the Wielbark culture.
- c. 50 AD: The first Christian meeting, the Council of Jerusalem, took place.
- c. 52 AD: Apostle Thomas arrived in India, starting Christianity there.
- July 19, 64 AD: The Great Fire of Rome happened. Emperor Nero blamed Christians, leading to their first major persecution in Rome.
- 66–73 AD: The First Jewish–Roman War took place.
- August 70 AD: The Second Temple in Jerusalem was destroyed by the Romans under Titus.
- August 79 AD: The cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum were buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius.
- The Jewish Council of Jamnia was held.
- The Roman Empire continued to grow, reaching its largest size later under Trajan.
- The Arena (colosseum) was built, giving us the word "arena."
Important People
- Apollonius of Tyana
- Arminius
- Augustus
- Boudica
- Caligula
- Claudius
- Domitian
- Du Shi
- Galba
- Hero of Alexandria
- Jesus of Nazareth
- John the Baptist
- Josephus
- Liu Xin
- Livia
- Livy
- Nero
- Nerva
- Paul of Tarsus
- Pliny the Elder
- Pontius Pilate
- Seneca the Younger
- Simon Peter
- Strabo
- Tacitus
- Tiberius
- Titus
- Trajan
- Vespasian
- Vitruvius
- Wang Mang
New Inventions and Discoveries
- The codex, which is the first version of a modern book, appeared in the Roman Empire.
- The year 78 AD marked the start of the Saka Era, used in some South Asian calendars.
- Bookbinding was developed.
- Hero of Alexandria invented many things, including an early steam turbine (called an aeolipile) and machines powered by water.
- In 31 AD, the Chinese engineer Du Shi invented the first known hydraulic-powered bellows. These bellows used a waterwheel to heat blast furnaces for making cast iron.
- The square-pallet chain pump was invented in China during this century.
- The Chinese astronomer Liu Xin documented 1080 different stars.
- By the end of the 1st century, the codex started to replace the scroll for writing.
Christianity
According to the New Testament, during the rule of Tiberius, Jesus, a Jewish religious leader from Galilee, was put to death in Jerusalem by crucifixion. His followers believed that "God raised him from the dead" three days later. Over the next few decades, his followers, including the apostle Paul, spread his message throughout the Greek-speaking areas of Asia Minor and eventually to Rome.
Roman rulers soon began to persecute Christians. For example, Emperor Nero blamed Christians for the Great Fire of Rome in 64 AD. This persecution continued for centuries. Christian stories say that almost all of Jesus's apostles died for their beliefs, except for John the Evangelist.
Later, in the 4th century, Christianity was accepted by Emperor Constantine. By the end of the 4th century, Emperor Theodosius I made Christianity the official religion of the Roman Empire.
Decades and years
Note: years before or after the 1st century are in italics.
| 0s BC | 10 BC | 9 BC | 8 BC | 7 BC | 6 BC | 5 BC | 4 BC | 3 BC | 2 BC | 1 BC |
| 0s | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10s | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20s | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30s | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 |
| 40s | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 |
| 50s | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 |
| 60s | 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 |
| 70s | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76
77 |
78 | 79 | |
| 80s | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 |
| 90s | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 |
| 100s | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 |
| Millennium | Century | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Christ / Before Common Era (BC/BCE) | ||||||||||
| 4th: | 40th | 39th | 38th | 37th | 36th | 35th | 34th | 33rd | 32nd | 31st |
| 3rd: | 30th | 29th | 28th | 27th | 26th | 25th | 24th | 23rd | 22nd | 21st |
| 2nd: | 20th | 19th | 18th | 17th | 16th | 15th | 14th | 13th | 12th | 11th |
| 1st: | 10th | 9th | 8th | 7th | 6th | 5th | 4th | 3rd | 2nd | 1st |
| Anno Domini / Common Era (AD/CE) | ||||||||||
| 1st: | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th |
| 2nd: | 11th | 12th | 13th | 14th | 15th | 16th | 17th | 18th | 19th | 20th |
| 3rd: | 21st | 22nd | 23rd | 24th | 25th | 26th | 27th | 28th | 29th | 30th |
| 4th: | 31st | |||||||||
Related pages
Images for kids
-
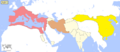
A map of the world in 1 AD, showing the Roman Empire (red) and the Chinese Han dynasty (yellow).
-
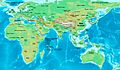
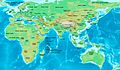
The Eastern Hemisphere in 50 AD, halfway through the 1st century.
-
A bronze statue of Augustus, the first Roman emperor.
-
A bust (sculpture of the head and shoulders) of Caligula, another Roman emperor.
-
A depiction of the crucifixion of Jesus by Diego Velázquez.
See also
 In Spanish: Siglo I para niños
In Spanish: Siglo I para niños