1st millennium BC facts for kids
| Millennia: | 2nd millennium BC · 1st millennium BC · 1st millennium AD |
| Centuries: | 10th century BC · 9th century BC · 8th century BC · 7th century BC · 6th century BC · 5th century BC · 4th century BC · 3rd century BC · 2nd century BC · 1st century BC |
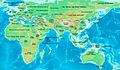
The 1st millennium BC was a long period of time. It started in the year 1000 BC and ended in 1 BC. This means it covered the 10th through the 1st centuries BC. During this time, the Iron Age happened in many parts of the world. It was also a time when ancient civilizations in the Ancient Near East began to change into the classical world.
The number of people on Earth roughly doubled during this millennium. It grew from about 100 million to around 200–250 million people.
Contents
Major Civilizations and Changes
- Further information: Ancient history and World history
In the early part of this millennium, the Neo-Assyrian Empire was very powerful in the Near East. But by the 6th century BC, the Achaemenid Empire took its place. Ancient Egypt was getting weaker and eventually fell to the Achaemenids in 525 BC.
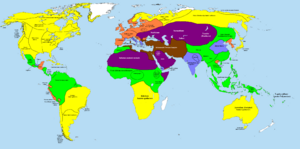
In Greece, the Classical Age began. Greek people started to set up colonies in places like Magna Graecia (southern Italy). This period reached its peak with the conquests of Alexander the Great. After his victories, Hellenistic civilization spread, lasting from the 4th to the 2nd centuries BC.
The Roman Republic grew stronger in Italy. It took over from the Etruscans and later defeated the Carthaginians between the 5th and 3rd centuries BC. By the end of the millennium, the mighty Roman Empire was rising. In Central Europe, the early Celts were important. Northern Europe was in its Pre-Roman Iron Age.
In East Africa, new kingdoms appeared. These included the Nubian Empire and Aksum.
In South Asia, the Vedic civilization developed into the Maurya Empire. The Scythians were powerful in Central Asia. In China, the Spring and Autumn period saw the start of Confucianism. Later, the Han Dynasty expanded China's influence towards Central Asia. There, it met with Indo-Greek and Iranian states. Japan was in the Yayoi period. The Maya civilization also began to rise in Mesoamerica.
This millennium was a very important time for the world's major religions. Early Judaism and Zoroastrianism developed in the Near East. In India, Vedic religion and Vedanta, Jainism, and Buddhism all grew. Early writing became important in Greek, Latin, Hebrew, Sanskrit, Tamil, and Chinese. This period, especially from the 8th to 2nd centuries BC, is sometimes called the "Axial Age" because of these big changes.
The world's population more than doubled during this time. It went from about 50–100 million people to an estimated 170–300 million. By the end of the millennium, almost 90% of people lived in the large Iron Age civilizations. These included the Roman Empire, the Parthian Empire, the Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian kingdoms, the Hindu kingdoms, and Han China. The Americas had less than 20 million people, mostly in Mesoamerica. Sub-Saharan Africa likely had less than 10 million. Oceania had less than one million people.
Ancient History Timeline
- Further information: Iron Age, Classical Antiquity, and Axial Age
This timeline shows some important events that happened during the 1st millennium BC.
10th Century BC
- Neo-Assyrian Empire becomes strong in the Near East.
- Shoshenq I of Egypt invades Canaan.
9th Century BC
- Egypt: The Nile River floods the Temple of Luxor in 872 BC.
- Egypt: A civil war happens in Egypt in 836 BC.
- North Africa: The city of Carthage is founded in 814 BC.
- China: The Gonghe Regency rules from 841 BC to 828 BC.
8th Century BC
- 727 BC: Kushite forces invade Egypt, starting the 25th dynasty.
- 771 BC: China enters the Spring and Autumn period.
- Near East: Babylonia breaks away from Assyria after the death of Tiglath-Pileser III.
- Near East: Sargon II takes Samaria in 722 BC. Many Israelites are taken captive by Assyria.
- Greece: The Archaic period begins. The Greek alphabet is developed.
- Greece: The poet Homer lives.
- 776 BC: The first Olympiad (Olympic Games) is held in Greece.
- 753 BC: The city of Rome is founded in Europe.
7th Century BC
- 671 BC: Assyria conquers Egypt.
- Near East: The Assyrian Empire begins to decline after the death of Ashurbanipal in 631 BC.
6th Century BC
- Egypt: Psamtik II attacks Napata in 592 BC.
- Sudan: Aspelta moves the Kushite capital to Meroe.
- Near East: Cyrus the Great leads the Achaemenids to conquer Babylon in 539 BC.
- South Asia: The "second urbanization" begins, and the Śramaṇa movement starts.
- South Asia: Early Buddhism begins.
- Europe: The Roman Republic is founded in 509 BC.
5th Century BC
- China: Confucius dies in 479 BC.
- China: The Warring States period begins in 476 BC.
- China: Construction of the Grand Canal starts in 486 BC.
- Near East: Second Temple Judaism develops, and the Hebrew Bible is put together.
- Greece: The classical period begins.
- Greece: The Greco-Persian Wars take place, including famous battles like Marathon and Thermopylae.
- Greece: Herodotus writes his Histories around 440 BC.
- Greece: The Peloponnesian War begins in 431 BC.
- Oceania: People from Austronesia reach Western Polynesia.
4th Century BC
- Greece: The Corinthian War begins in 395 BC.
- Egypt: The Achaemenid conquest of Egypt happens in 343 BC.
- Greece/Asia/Egypt: In the 330s BC, Alexander the Great conquers many lands, ending the Achaemenid Empire. This leads to the Macedonian Empire and the start of the Hellenistic period.
- South Asia: The Mauryan Empire rises.
3rd Century BC
- China: The Qin Dynasty unites China.
- China: The Han Dynasty begins in 206 BC.
- South Asia: The Kalinga war takes place in 261 BC.
- Rome: Rome expands its power in Italy.
- Rome/Carthage: The Punic Wars begin.
- 264 BC: The First Punic War starts.
- 218 BC: The Second Punic War starts.
2nd Century BC
- Rome/Carthage: The Third Punic War begins in 149 BC. Rome creates the Roman province of Africa.
- Rome/Greece: The Battle of Corinth in 146 BC marks the beginning of the Roman era in Greece.
- South Asia: The Maurya Empire falls in 185 BC.
- China: Confucianism becomes the main way of thinking for the state.
1st Century BC
- China: The Records of the Grand Historian are finished in 91 BC.
- Rome/Europe: The Gallic Wars take place from 58-50 BC.
- Rome: The Final War of the Roman Republic happens, including the Battle of Actium.
- Rome/Egypt: Rome conquers Egypt in 31 BC.
- Rome: The Roman Empire is founded in 27 BC.
Important People
Many important people lived during this time. Some, like Solomon or Zoroaster, are known from ancient stories, but we don't have records from their exact time.
- Rulers
- China: Many different dynasties and monarchs.
- Egypt: Rulers during the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt.
- Carthage: Kings of Carthage.
- Assyrian Empire: Kings of Assyria.
- Babylonia: Rulers of the Neo-Babylonian dynasty.
- Canaan/Israel: Kings of Israel and Judah.
- Achaemenid Persia: Kings of Persia.
- Kingdom of Kush: Kings of Kush.
- Classical Greece: Leaders like Pericles in Athens.
- Macedon: Alexander the Great and other kings.
- Hellenistic period: Rulers from the Ptolemaic, Antigonid dynasty, and Seleucid families.
- Rome: Kings of Rome and later consuls.
- Parthian Empire: Kings of Parthia.
- India: Many monarchs.
- Japan: Emperors of Japan.
- Thinkers and Scholars
- Elijah: A prophet from the 9th century BC.
- Isaiah: A prophet from the 8th century BC.
- Parshvanatha: An important figure in Jainism, possibly from the 8th or 7th century BC.
- Jeremiah: A prophet around 628 BC.
- Thales of Miletus (c. 624–545 BC): An early Greek philosopher.
- Solon (c. 638–558 BC): A wise Athenian lawmaker.
- Zoroaster: A prophet who founded Zoroastrianism.
- Mahavira: The last important teacher of Jainism, around the 6th century BC.
- Pythagoras: A Greek mathematician and philosopher from the 6th century BC.
- Heraclitus (c. 535–475 BC): A Greek philosopher.
- Confucius: A famous Chinese teacher and philosopher from the 6th to 5th century BC.
- Laozi: A Chinese philosopher, founder of Taoism.
- Parmenides: A Greek philosopher from the late 6th or early 5th century BC.
- Gautama Buddha: The founder of Buddhism, from the 5th century BC.
- Socrates (469–399 BC): A very famous Greek philosopher.
- Thucydides (c. 460–400 BC): A Greek historian.
- Aristophanes (446–386 BC): A Greek playwright.
- Plato (428–348 BC): A famous Greek philosopher, student of Socrates.
- Aristotle (384–322 BC): A famous Greek philosopher, student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great.
- Zhuang Zhou: A Chinese philosopher from the 4th century BC.
- Panini: An Indian grammarian from the 4th century BC.
- Mencius (372–289 BC): A Chinese philosopher, follower of Confucius.
- Pingala: An Indian mathematician from the 3rd century BC.
- Qin Shi Huang (259–210 BC): The first emperor of unified China.
- Euclid: A Greek mathematician, around 300 BC, known for geometry.
- Archimedes (287–212 BC): A Greek mathematician and inventor.
- Sima Qian: A Chinese historian from the 2nd century BC.
- Varro (116–27 BC): A Roman scholar.
- Cicero (106–43 BC): A Roman statesman and writer.
Inventions and Discoveries
- Further information: Ancient technology
- 8th century BC: The Greek alphabet is created. It is the first alphabet to include vowels.
- 7th century BC: The Trireme, a type of ancient warship, is developed.
- 6th century BC: A paved trackway is built in Greece to move ships over land. The Pythagorean theorem in mathematics is developed. The idea of Monotheism (worshiping one God) becomes more common.
- 5th century BC: The Blast furnace is used in China. The idea of Atomism (that everything is made of tiny particles) is proposed. The crossbow and siege engines are invented.
- 4th century BC: Formal grammar is developed in India. The Kyrenia ship, an ancient Greek merchant ship, sinks.
- 3rd century BC: The Lighthouse of Alexandria is built. Cast iron that can be shaped is made in China. Archimedes discovers the principle of buoyancy. Eratosthenes calculates that the Earth is spherical. The water clock is used. The Qin builds and connects parts of the Great Wall of China. The Qin Shi Huang's Mausoleum is built, guarded by life-sized Terracotta soldiers.
- 2nd century BC: The Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek computer, is created.
Literature
Many important books and writings were created during this millennium.
- Greco-Roman Literature
- Homer (late 8th or early 7th century BC): Wrote the epic poems Iliad and Odyssey.
- Hesiod (8th to 7th century BC): Wrote Theogony and Works and Days.
- Sappho (late 7th to early 6th century BC): A famous Greek poet.
- Aesop's Fables: A collection of short stories with morals.
- Aeschylus (c. 525–455 BC): A Greek playwright.
- Herodotus (484–425 BC): Wrote Histories, often called the "Father of History."
- Euripides (c. 480–406 BC): A Greek playwright.
- Aristotle (384–322 BC): Wrote many books on philosophy, science, and logic.
- Euclid: Wrote Elements, a famous book on geometry.
- Cicero: A Roman statesman and writer.
- Virgil: A Roman poet.
- Chinese Literature
- I Ching (date unknown): A classic Chinese text about change.
- Classic of Poetry (Shījīng): A collection of ancient Chinese poems.
- Spring and Autumn Annals (Chūnqiū): Records of the state of Lu from 722–481 BC.
- Confucius: His teachings are found in the Analects (Lúnyǔ).
- Classic of Rites (Lǐjì): A book about ancient Chinese rituals and customs.
- Laozi (or Lao Tzu): Wrote the Tao Te Ching.
- Zhuangzi: Wrote the Zhuangzi (book).
- Mencius: His teachings are in the Mencius book.
- Sanskrit Literature (India)
- Vedas and Brahmanas: Ancient Hindu sacred texts.
- Mukhya Upanishads: Important philosophical texts.
- Early parts of the Sanskrit epics (like the Mahabharata and Ramayana).
- Hebrew Literature
- Around 8th to 7th century BC: Books like Nahum, Hosea, Amos, and Isaiah are written.
- Around 6th century BC: Many Psalms are written.
- Around 5th century BC: The Torah is put together.
- Later books like Ecclesiastes and Wisdom are written.
- Other Literature
- Pali literature: The Tipitaka, important Buddhist texts.
- Tamil: Sangam literature, early Tamil writings.
- Aramaic: The Book of Daniel.
Archaeology
- Further information: Iron Age
This table shows different cultures and archaeological periods from around the world during this millennium.
| Culture | Region | Period | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urnfield culture | Central Europe | 1300–750 BC | Part of the Bronze Age |
| Atlantic Bronze Age | Western Europe | 1300–700 BC | Part of the Bronze Age |
| Painted Grey Ware culture | South Asia | 1200–600 BC | Linked to the Indo-Aryan migration |
| Late Nordic Bronze Age | Northern Europe | 1100–550 BC | Part of the Bronze Age |
| Villanovan culture | Italy, Europe | 1100–700 BC | Early Iron Age in Italy |
| Greek Dark Ages | Greece | 1100–800 BC | A time of decline after the Bronze Age |
| Iron Age II | Near East | 1000–586 BC | Part of the Ancient Near East |
| Sa Huỳnh culture | Vietnam, Southeast Asia | 1000 BC–AD 200 | |
| Woodland period | North America | 1000 BC – AD 1000 | |
| Bantu expansion | Sub-Saharan Africa | 1000 BC–AD 500 | Spread of Bantu-speaking peoples |
| Middle Nok Period | West Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa | 900–300 BC | Known for iron smelting |
| Novocherkassk culture | Eastern Europe | 900–650 BC | |
| Chavín de Huántar | Peru, South America | 1200–500 BC | An important early culture in Peru |
| Poverty Point earthworks | Louisiana, North America | 1650–700 BC | Large earth mounds |
| Olmecs | Mesoamerica | 1500–400 BC | An early major civilization in Mesoamerica |
| Adena culture | Ohio, North America | 1000–200 BC | Known for mound building |
| Liaoning bronze dagger culture | East Asia | 800–600 BC | Known for bronze daggers |
| Middle Mumun | Korea, East Asia | 800–300 BC | |
| Etruscan civilization | Italy, Europe | 800–264 BC | An ancient Italian civilization |
| Paracas culture | Peru, South America | 800–100 BC | Known for textiles |
| Hallstatt culture | Central Europe | 800 BC–500 BC | Early Iron Age culture, linked to the Celts |
| British Iron Age | Britain, Europe | 700–50 BC | The Iron Age in Britain |
| Zapotec civilization | Mesoamerica | 700 BC – AD 700 | An important civilization in Mesoamerica |
| Pazyryk culture | Central Asia | 600–300 BC | Linked to the Scythians |
| Aldy-Bel culture | Central Asia | 600–300 BC | Also linked to the Scythians |
| La Tène culture | Central/Western Europe | 500–50 BC | A major Iron Age culture, linked to the Gauls |
| Pre-Roman Iron Age | Northern Europe | 500–50 BC | The Iron Age before Roman influence |
| Northern Black Polished Ware | South Asia | 500–300 BC | Pottery from the Vedic period |
| Late Mumun | Korea, East Asia | 550–300 BC | |
| Urewe | Sub-Saharan Africa | 400 BC–AD 500 | Known for iron working |
| Late Nok Period | West Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa | 300–1 BC | |
| Nasca culture | Peru, South America | 100 BC–800 AD | Known for Nazca Lines |
| Calima culture | Colombia, South America | 200 BC–400 AD | |
| Hopewell tradition | North America | 100 BC–AD 400 | Known for large earthworks |
| Teotihuacan | Mesoamerica | 100 BC –AD 550 | A large ancient city |
| Ipiutak Site | Alaska, North America | 100 BC –AD 800 | An archaeological site |
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: I milenio a. C. para niños
In Spanish: I milenio a. C. para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |