Yayoi period facts for kids
 |
|---|
|
The Yayoi period (pronounced Yah-yoy) was an important time in the history of Japan. It lasted for about 600 years, from around 300 BC to 300 AD. During this period, many new things came to Japan, like farming and metal tools.
A New Way of Life
The first signs of the Yayoi culture were found on the island of Kyūshū. From there, this new way of life slowly spread to the larger island of Honshū.
People in Japan started using two new metals around the same time: iron and bronze.
- Iron was used to make useful tools and strong weapons.
- Bronze was used for special objects like mirrors, daggers, and spears. These were often used in ceremonies or for important rituals.
Yayoi tools included things like axes and hoes, which helped with agriculture. They also made weapons such as arrowheads and swords.
The Yayoi People
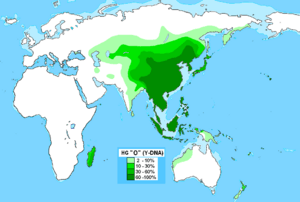
The Yayoi people were ancient people who moved to Japan from areas like southeastern China. This happened during the Yayoi period, between 300 BC and 300 AD.
Today, most Japanese people are direct descendants of the Yayoi people. About 97% of their DNA comes from the Yayoi. This shows a very strong connection between the ancient Yayoi and modern Japanese people.
The Yayoi people were closely related to other groups in East Asia, such as Chinese and Vietnamese people. Scientists believe they spoke early forms of the Japonic languages. Most experts think they came from southeastern China and then traveled to Japan.
Images for kids
-
The golden seal said to have been granted to the "King of Wo" by Emperor Guangwu of Han in 57 AD. It is inscribed King of Na of Wo in Han Dynasty (漢委奴國王)
-
Hashihaka kofun, Sakurai, Nara
See also
 In Spanish: Período Yayoi para niños
In Spanish: Período Yayoi para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |