Classical Greece facts for kids
Classical Greece was a special time in ancient Greek history, lasting from about 500 BC to 323 BC. During this period, Greek civilization developed an amazing style and way of life. Many people later looked back at this time as a golden age.
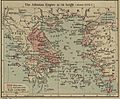
Politically, the 5th century BC was mostly led by Athens and its group of allies, the Delian League. This era began with the Greco-Persian Wars and ended with the Peloponnesian War in 404 BC.
This 200-year period greatly influenced the culture of ancient Rome. It still has a big impact on Western civilization today. A lot of our modern politics, art, science, literature, and philosophy comes from this ancient society.
Contents
Athens Rises to Power
The Persian Wars helped Athens become the most powerful city in Greece for about 100 years. Athens was the strongest at sea and also a major trading center. The most important leader during this time was Pericles. He used money paid by the cities in the Delian League to build the amazing Parthenon and other grand buildings in Athens.
The wealth of Athens attracted many talented and skilled people from all over Greece. It also created a rich group of people who supported artists and thinkers. The Athenian government encouraged learning and the arts, especially architecture. Athens became the center for Greek literature, philosophy, and theater.
Famous Thinkers and Artists
Some of the most important people in Western culture lived in Athens during this time. These included playwrights like Aeschylus, Aristophanes, Euripides, and Sophocles. Famous philosophers were Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates. Historians like Herodotus, Thucydides, and Xenophon also lived there. The poet Simonides and the sculptor Pheidias were also from this period. Pericles famously called Athens "the school of Hellas," meaning it was the learning center of Greece.
Changes in the 4th Century BC
After the Peloponnesian War ended, Sparta became the main power in Greece. However, the Spartan leaders were mostly warriors and not very good at ruling all of Greece. Within a few years, the people who supported democracy regained power in Athens and other cities.
The Peloponnesian War was a big turning point for the Greek world. After 403 BC, things became more complicated. Many cities tried to create their own empires, but these usually did not last long.
The Corinthian War showed how power was shifting in Greece. While Athens and Sparta fought and became weaker, the city of Thebes started to become very strong among the Greek city-states.
Sparta's Short Rule
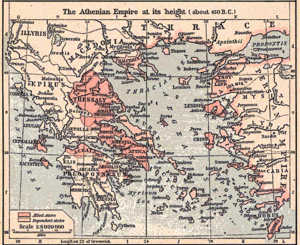
Sparta's control over Greece was powerful but short-lived. In 405 BC, the Spartans ruled over Athens' allies and Athens itself, and their power was complete. But by the end of the century, they couldn't even protect their own city.
The Athenians decided they would not return to how things were in the 5th century. According to a rule by Aristotle, Athens aimed to stop Sparta from controlling everything. The Spartans were clearly called "warmongers" (people who like to start wars).
Why Classical Greece Still Matters
Even though we have a lot of new technology today, people in Europe after the Renaissance felt a strong connection to ancient Greece. They saw themselves as the cultural followers of Greece. As late as 1939, the writer Will Durant said that "except for machines, almost everything in our culture comes from Greece." He also said that "there is nothing in Greek civilization that doesn't help us understand our own." This shows how important Classical Greece still is to our world.
Images for kids
-
Construction of the Parthenon began in the 5th century BC
-
A Kylix (drinking cup) from Attica showing a goddess performing a libation, 470 BC, white ground technique pottery
-
The Temple of Hephaestus at the Agora of Athens, built 449–415 BC
-
Thessalian cavalryman on the Alexander Sarcophagus, late 4th century BC (Istanbul Archaeological Museum)
-
A wall mural of a charioteer from the Macedonian royal tombs at Vergina, late 6th century BC
See also
 In Spanish: Grecia clásica para niños
In Spanish: Grecia clásica para niños