Classical antiquity facts for kids

Classical antiquity is a long and important time in history, mostly around the Mediterranean Sea. It includes the amazing civilizations of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. This period is also called the classical era or classical period.
During this time, many famous writers and thinkers lived. Great works of Greek and Roman literature were created by people like Homer, Aeschylus, and Ovid. Their stories and ideas still influence us today!
Contents
- The Beginning: Archaic Period (8th to 6th centuries BC)
- Golden Age: Classical Greece (5th to 4th centuries BC)
- Spreading Greek Culture: Hellenistic Period (330 to 146 BC)
- The Roman Republic (5th to 1st centuries BC)
- The Mighty Roman Empire (1st century BC to 5th century AD)
- The End of an Era: Late Antiquity (4th to 6th centuries AD)
- Lasting Influence: Revivalism
- Other Important Topics
- Other Pages to Explore
- Images for kids
- See also
The Beginning: Archaic Period (8th to 6th centuries BC)
The earliest part of classical antiquity began after a time called the Bronze Age collapse. We know it started when people began writing again using the Greek alphabet, around the 8th century BC.
Many people believe the famous poet Homer, who wrote the Iliad and Odyssey, lived around this time. His life is often seen as the start of this period. The first Ancient Olympic Games are traditionally said to have happened in 776 BC. Also, the city of Rome was supposedly founded in 753 BC, and early settlements appeared in the Roman Forum.
Phoenicians: Great Traders of the Sea
The Phoenicians were skilled sailors and traders. They started from ports in the Levant (modern-day Middle East). By the 8th century BC, they controlled much of the trade across the Mediterranean Sea.
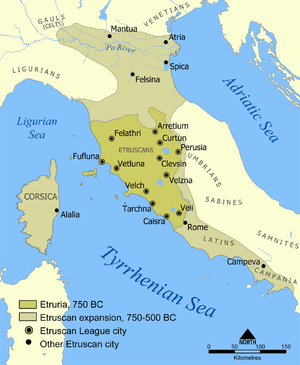
A very important Phoenician city was Carthage, founded in 814 BC. By 700 BC, the Carthaginians had set up strong trading posts in Sicily, Italy, and Sardinia. This led to some disagreements with the Etruscans, another powerful group in Italy.
Greece: Birthplace of New Ideas
After a quiet time known as the Greek Dark Ages, the Archaic period in Greece brought many new ideas. This was when democracy (rule by the people) began to develop. Important ideas in philosophy and theatre also started here. People began writing poetry again, and the written language, which had been lost, was brought back to life.
Golden Age: Classical Greece (5th to 4th centuries BC)
The classical period of Ancient Greece was a very important time. It started around 510 BC and ended with the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC.
During this era, there were long struggles between two powerful Greek city-states: Sparta and Athens. The Greeks also fought major wars against the Persians, a huge empire from the east. Later, the rise of Macedon in the 4th century BC changed the political landscape of Greece, at least for a while.
Spreading Greek Culture: Hellenistic Period (330 to 146 BC)
The Hellenistic period began with Alexander the Great. After his conquests, the Greek language became a common language spoken far beyond Greece. This meant that Greek culture mixed with the cultures of Persia, Central Asia, India, and Egypt.
This period ended when the Roman Republic became a very powerful force in the 2nd century BC. The Romans eventually conquered Greece in 146 BC.
The Roman Republic (5th to 1st centuries BC)
The Roman Forum was the main public area where ancient Rome grew. The Roman Republic began around 509 BC when the Roman Monarchy (rule by kings) was overthrown. It lasted for over 450 years.
This period saw many civil wars and eventually led to the Roman Empire. Even though it was called a "Republic," Rome was already acting like an empire as it conquered lands like Gaul, Illyria, Greece, and Hispania (modern-day Spain and Portugal).
The Mighty Roman Empire (1st century BC to 5th century AD)
It's hard to say exactly when the Roman Republic officially ended and the Roman Empire began. People living at the time didn't even realize the Republic was gone!
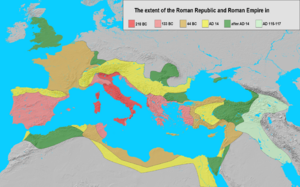
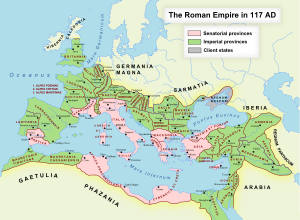
The Roman Empire grew to be one of the largest and most powerful empires in history. It controlled vast territories across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
The End of an Era: Late Antiquity (4th to 6th centuries AD)
During Late Antiquity, Christianity became very important. Under Emperor Constantine I, Christianity grew, and by 393 AD, it became the official religion of the Roman Empire.
Later, many invasions by Germanic tribes led to the end of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. However, the Eastern Roman Empire continued to thrive for many more centuries, lasting throughout the Middle Ages.
Lasting Influence: Revivalism
The ideas and achievements of ancient Greece and Rome continued to be admired and copied long after their time. This respect for the ancients influenced many areas of life, including politics, philosophy, sculpture, literature, theater, education, and architecture.
For example, even after the Roman Empire fell, many people still wanted a Roman emperor. This idea reached its peak when Charlemagne was crowned "Roman Emperor" in 800 AD, which led to the creation of the Holy Roman Empire. The idea that an emperor is more important than a king comes from this period. People believed there would always be a Roman Empire, ruling the civilized Western world.
Other Important Topics
- Ancient Greece
- Ancient Rome
- Dacia
- Roman Dacia
- Roman Britain
- Hispania
- Ancient Macedonia
- Gaul
- Carthage
Other Pages to Explore
- Kofun period (Japan, 250 CE – 538 CE)
- Asuka period (Japan, 538 CE – 710 CE)
Images for kids
-
The Parthenon is one of the most recognizable symbols of the classical era, exemplifying ancient Greek culture.
-
Map of Phoenician (in yellow) and Greek colonies (in red) around 8th to 6th century BC
-
Plato and Aristotle walking and discussing. This is a detail from Raphael's famous painting The School of Athens.
See also
 In Spanish: Antigüedad clásica para niños
In Spanish: Antigüedad clásica para niños