Confucius facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Confucius
|
|
|---|---|

Imaginary portrait by Wu Daozi (685–758), Tang dynasty
|
|
| Born |
Kǒng Qiū
c. 551 BCE |
| Died | c. 479 BCE (aged 71–72) Si River, State of Lu
|
| Spouse(s) | Lady Qiguan |
| Era | Hundred Schools of Thought (Ancient philosophy) |
| Region | Chinese philosophy |
| School | Confucianism |
| Notable students | Yan Hui, Zengzi Disciples of Confucius |
|
Main interests
|
Ethics, education, music, poetry, political philosophy, Social philosophy |
|
Notable ideas
|
Confucianism, Golden Rule |
|
Influenced
Virtually all subsequent Chinese philosophy, particularly Mencius, Xun Kuang, Zhu Xi, Wang Shouren, the Neotaoists, as well as Han Yu and the Neoconfucians. Also influenced multiple Western thinkers including Niels Bohr, Benjamin Franklin, Allen Ginsberg, Thomas Jefferson, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Robert Cummings Neville, Alexander Pope, Ezra Pound, François Quesnay, Friedrich Schiller, Voltaire, and Christian Wolff
|
|
| Confucius | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

"Confucius (Kǒngzǐ)" in seal script (top) and regular (bottom) Chinese characters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 孔子 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Kǒngzǐ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Master Kǒng" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kong Qiu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 孔丘 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Kǒng Qiū | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confucius (pronounced kən-FEW-shəs) was an important Chinese philosopher and politician. He lived a very long time ago, from about 551 to 479 BCE. His ideas are still very important in China and other parts of East Asia today.
Confucius taught about how people should behave. His ideas are called Confucianism. He believed in being good, honest, and fair. He also taught about how families and governments should work. He thought that if everyone treated each other well, society would be strong.
He is known for writing or editing many old Chinese books. His most famous teachings are collected in a book called the Analects. This book was put together by his students after he died.
Confucius believed in strong family bonds. He said children should respect their parents and elders. He also taught a version of the Golden Rule: "Do not do to others what you do not want them to yourself."
Contents
Who Was Confucius?
The name "Confucius" comes from a Latin version of his Chinese name, Kǒng Fūzǐ. This means "Master Kong." Early European visitors to China in the 1500s created this name. His family name was Kong, and his given name was Qiu. He also had a special "courtesy name" called Zhongni. This name was used by almost everyone except his closest family.
Confucius's Early Life
Confucius was born on September 28, 551 BCE. This was in a place called Zou, which was part of the state of Lu. Today, this area is in Shandong province, China. His father, Kong He, was an old soldier.
Sadly, Confucius's father died when he was only three years old. His mother, Yan Zhengzai, raised him in poverty. She passed away when she was less than 40. When Confucius was 19, he married Lady Qiguan. A year later, they had their first child, a son named Kong Li. They also had two daughters.
Confucius went to schools for regular people. There, he learned the Six Arts, which included things like music, archery, and writing. He came from a social class called shi, which was between the rich and the common people. In his early twenties, he worked in different government jobs. He was a bookkeeper and took care of sheep and horses. He used his money to give his mother a proper burial. When she died, Confucius, who was 23, mourned for three years, as was the custom.
Confucius's Political Career
By 501 BCE, Confucius was already well-known for his teachings. He was given a small job as a town governor. He then moved up to become the Minister of Crime.
Confucius wanted to help his homeland. He worked for the government for four years. He helped his country a lot. But he had disagreements with the ruler, which ended his political career.
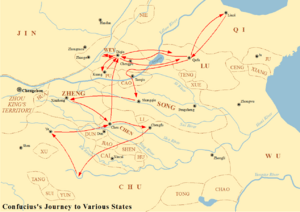
Confucius made some powerful enemies. Because of this, he left his home in 497 BCE. He stayed away from his home state for many years. He could not return as long as his enemies were alive.
Years of Exile
After leaving his job, Confucius traveled for a long time. He visited many different states in ancient China. These included Wey, Song, Zheng, Cao, Chu, Qi, Chen, and Cai. He tried to go to Jin, but it didn't work out. At the courts of these states, he shared his political ideas. However, his ideas were not put into practice by the rulers.
Returning Home
Confucius returned to his home state of Lu when he was 68 years old. He was invited back by Ji Kangzi, the chief minister of Lu. During his last years, he taught about 72 or 77 students. He shared old wisdom through a group of texts called the Five Classics.
When he was back home, Confucius sometimes advised government officials. He helped them with things like how to govern and deal with crime.
Confucius died at the age of 71 or 72 from natural causes. He was buried in the Kong Lin cemetery in Qufu, Shandong Province. His original tomb was shaped like an axe. It also had a raised platform for offerings like incense and fruit.
Confucian Philosophy
Confucianism is often followed in a way that is similar to a religion in China. It talks about the afterlife and ideas about Heaven. But it doesn't focus much on some spiritual things that other religions do, like the nature of souls.
In the Analects, Confucius stressed how important it is to study. He wanted his students to truly understand old classic texts. He believed that deep thought and study would help them solve today's problems by learning from the past.
Confucian Ethics
Confucius wanted people to care more about others than about money or possessions. But he also believed that society needed strong rules. He thought people needed to follow these rules.
Confucius taught about five main relationships people could have. Each relationship had its own rules:
These were called the "five prototypes." Confucius said that in all these relationships, both people had duties. For example, a subject must obey a prince. But a prince must also listen to his subjects and rule them well and fairly.
Confucius also taught that people should only do things to others if they would be okay with those things being done to themselves.
Confucius's Legacy

Confucius's teachings were further developed by his many students and followers. They put his ideas into the Analects. His students and his grandson, Zisi, continued his school of thought after he died. They spread Confucian ideas to students who then became officials in many Chinese royal courts.
Confucius's works are studied in many other Asian countries. These include Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. Many of these countries still have traditional ceremonies to remember him each year.
Some Tibetans see Confucius as a holy king. They believe he was a master of magic and fortune-telling. Some Tibetan Buddhists think he learned these skills from the Buddha Manjushri. Followers of the Bon religion believe he was a reincarnation of their founder, Tonpa Shenrab Miwoche.
The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community believes Confucius was a Divine Prophet from God.
In modern times, an asteroid named "Confucius" was named after him.
Confucius Quotes
- "It does not matter how slowly you go as long as you do not stop."
- "Wherever you go, go with all your heart."
- "When it is obvious that the goals cannot be reached, don't adjust the goals, adjust the action steps."
- "Better a diamond with a flaw than a pebble without."
- "Silence is a true friend who never betrays."
- "Only the wisest and stupidest of men never change."
Memorials to Confucius

Soon after Confucius died, his hometown of Qufu became a special place. People went there to honor and remember him. Even in the Han dynasty, it was a place where important officials would visit. Today, many people still visit his grave and the temples around it. In Chinese cultures, you can often find statues of the Buddha, Laozi, and Confucius together in temples. There are also many temples built just for him, where Confucian ceremonies are held.
In Taiwan, the government strongly supports Confucian ideas. The tradition of the memorial ceremony for Confucius is still held every year. It's not a national holiday, but it's on all calendars, like Father's Day or Christmas Day in Western countries.
In South Korea, a large ceremony called Seokjeon Daeje happens twice a year. It's held on Confucius's birthday and the anniversary of his death. These ceremonies take place at Confucian academies across the country and at Sungkyunkwan in Seoul.
Confucius's Descendants
The descendants of Confucius have been honored by Chinese governments for many years. They were given special titles and jobs.
In recent times, there was a project in China to test the DNA of known family members. This was to help people who had lost their family records prove they were related to Confucius. In 2013, a DNA test showed that many different families claiming to be descendants shared the same Y chromosome. This helped confirm their family link.
The most recent family tree of Confucius was printed in 2009. For the first time, women were included in this family record.
See also
 In Spanish: Confucio para niños
In Spanish: Confucio para niños