Atlantic Bronze Age facts for kids
 |
|
| Geographical range | Western Europe |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 1300 — c. 700 BC |
| Preceded by | Bell Beaker culture, Bronze Age Britain, Armorican Tumulus culture, Wessex culture |
| Followed by | Iron Age Britain, Iron Age Ireland, Iron Age France, Iron Age Spain |
The Atlantic Bronze Age was a special time during the Bronze Age. It lasted from about 1300 to 700 BC. This period connected different groups of people across parts of Prehistoric Europe. These areas included Britain, France, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain.
Contents
Trading Across the Seas
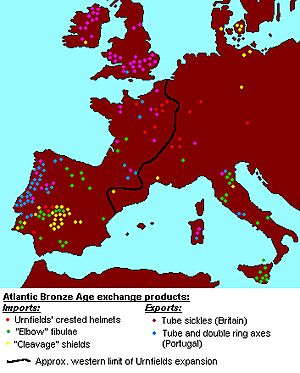
The Atlantic Bronze Age was known for lots of trading. People exchanged goods and ideas. This made coastal communities from Portugal to Scotland quite similar. They shared ways of building and living. For example, they often used stones to protect their settlements. They also built cliff castles and roundhouses.
Trade routes reached far and wide. Goods traveled from Sweden and Denmark all the way to the Mediterranean Sea. This period had several main areas that made metal goods. These areas were in southern England, Ireland, northwestern France, and western Iberia. They all traded their special products by sea.
Amazing Bronze Treasures
Many items from this time are found in hoards. A hoard is a hidden collection of valuable things. These treasures were often placed in special, watery spots. This included rivers, lakes, and bogs.
Some cool items from this period are:
- Bronze axes with sockets and double rings. Large hoards of these are found in Brittany and Galicia.
- War gear like spearheads and shields. Also, many types of bronze swords. These are often found in lakes or rivers.
- Fancy feasting tools for important people. These include roasting spits, cauldrons, and flesh hooks. They have been found from central Portugal to Scotland.
Where Did Celtic Languages Come From?
Some experts, like John T. Koch and Barry Cunliffe, think the Celts might have started in this period. They believe early Celtic languages spread across the Atlantic region. People in these areas adopted new ideas and special metal items. These items came from the Urnfield culture in central Europe. This might have helped new languages spread. Other experts believe Celtic languages started later, with the Hallstatt culture in central Europe.
Gallery
-
The Caergwrle Bowl, Wales, c. 1300 BC
-
Casco de Leiro, Galicia, Spain
-
Deposito da Samieira, a hoard of Galician Bronze Age axes. Museo de Pontevedra
-
Dún Aonghasa hillfort, Ireland
See also
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |

























