North India facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
North India
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Country | |
| States and territories |
|
| Other states sometimes included |
|
| Largest city | Delhi |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| Official languages | |
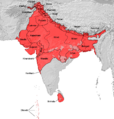
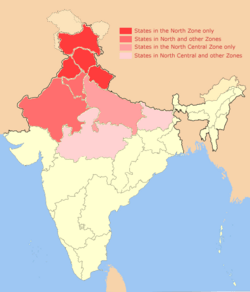
North India is a large area in the northern part of India. It's not always defined the same way, but it generally includes several states and union territories. The main natural features are the huge Indus-Gangetic Plain and the mighty Himalayas mountains. These mountains separate North India from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia.
Different government groups define North India slightly differently. For example, the Ministry of Home Affairs includes states like Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, and Rajasthan. It also includes the Union Territories of Delhi and Chandigarh. The Ministry of Culture, however, includes Uttarakhand but not Delhi. The Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi, but not Rajasthan or Chandigarh. Sometimes, other states like Bihar, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and West Bengal are also considered part of North India.
This region has been a very important historical center. Powerful empires like the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate, and the British Indian Empire once ruled here. North India has a rich and varied culture. It is home to many important pilgrimage sites for different religions. These include Hindu places like Varanasi and Vaishno Devi. There are also Buddhist sites like Sarnath and Kushinagar. For Sikhs, the Golden Temple is a very sacred place.
North India also has many famous World Heritage Sites. These include the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, the Khajuraho temples, and the Taj Mahal. The main official languages spoken in this region are Hindi, Urdu, Punjabi, and English.
Contents
A Look at North India's Past
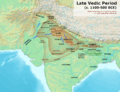
North India has a long and exciting history. Many powerful empires and kingdoms have ruled parts of this region over thousands of years. Delhi, a major city in North India, was often the capital for these empires.
Ancient and Medieval Empires
Here are some of the important empires that ruled North India:
- Maurya Empire: 326 – 187 BCE
- Indo-Greek Kingdom: Around 150 BCE – 10 CE
- Gupta Empire: Around 335 – 550 CE
- Empire of Harsha: 606 to 647 CE
- Pala Empire: 770 to 810 CE
- Pratihara Empire: Mid-7th to 11th century
- Delhi Sultanate: 1206–1526
- Mughal Empire: 1526–1540, then 1555–1857
- Sur Empire: 1540–1556 (briefly interrupted Mughal rule)
- Sikh Empire: 1799–1849
- Maratha Empire: 1761–1818
- British Indian Empire: 1858–1947
The Vindhya Mountains as a Border
The Vindhya mountain range has often been seen as a natural border between North and South India. In ancient times, empires like the Gupta Empire sometimes expanded up to these mountains. Old Indian texts also mention the Vindhyas as a dividing line.
Cultural Influences from Central Asia
North Indian culture has been shaped by influences from Central Asia and Afghanistan. This includes changes in language and traditions. Even before the arrival of Islam, groups like the Kushan Empire from Bactria (modern-day Afghanistan) had a big impact. They even had twin capitals, one in Mathura (India) and one in Peshawar (Pakistan).
North India's Geography

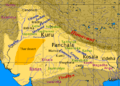
North India is mostly located on the main landmass of India, north of the peninsular part. To the north, the Himalayas form a natural boundary between the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan plateau. To the west, you'll find the Thar desert, which is shared with Pakistan. Beyond the Aravalli Range to the west is the state of Gujarat. Some people consider the Vindhya mountains as the southern edge of North India.
The main geographical features of North India are:
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain, a large flat area covering states like Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Bihar and West Bengal.
- The Himalayas, towering mountains found in Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Thar Desert, a large desert mainly in Rajasthan.
States like Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Chhattisgarh also have large areas covered by forests.
North India's Climate
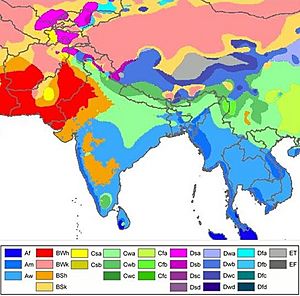
North India is mostly in the northern temperate zone of the Earth. This means it generally has cool or cold winters, hot summers, and moderate monsoon rains. However, North India has a very diverse climate.
During summer, temperatures often go above 35 °C (95 °F) across the Indo-Gangetic plain. In the Thar desert and Rajasthan, it can reach as high as 50 °C (122 °F). Delhi can also get up to 49 °C (120 °F). In winter, temperatures on the plains can drop below 5 °C (41 °F), and even below freezing in some states. Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, and Uttarakhand get heavy snowfall. Many parts of North India are known for thick fog during winters.
Some places have seen extreme temperatures. Dras in Jammu and Kashmir recorded -45 °C (-49 °F). It is one of the coldest inhabited places on Earth. Alwar, Rajasthan, recorded a high of 50.6 °C (123 °F).
Traditional Seasons
In North Indian traditions, there are six distinct seasons:
- Summer (grishma or garmi): May–June
- Rainy (varsha): July–August
- Cool (sharad): September–October (early autumn)
- Autumn (hemant or patjhar): November–December (leaf-fall)
- Winter (shishir or sardi): January–February
- Spring (vasant): March–April
These seasons are often mentioned in the region's literature, poetry, and folklore. In mountainous areas, winter is sometimes divided into "big winter" and "little winter."
People and Religions of North India
Most people in North India belong to the Indo-Aryan language group. This includes various ethnic groups like Brahmins, Rajputs, Banias, Jats, and Dalits. There are also smaller groups who speak Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, and Austroasiatic languages.
Religions Practiced
Hinduism is the main religion in North India. Many other religions are also practiced by different communities:
States like Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Himachal Pradesh are mostly Hindu. Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal have Hindu majorities, but also a large number of Muslims. Jammu and Kashmir is a Muslim-majority state. Punjab has a Sikh-majority population.
Plants and Animals of North India
North India has a wide variety of plants and animals due to its diverse climates and landscapes. The vegetation is mostly tropical evergreen and montane.
Trees and Plants
Important evergreen trees include Hollong Gurjan, sal, teak, Mahogany, sheesham (Indian rosewood), and poplar. These are important for business. In the Western Himalayas, you'll find chir, pine, deodar (Himalayan cedar), blue pine, spruce, and various firs. The birch tree is historically important. Its bark was used as paper for many ancient Indian texts. The Eastern Himalayas have oaks, laurels, maples, and rhododendrons. The plant life ranges from high-altitude Alpine flowers to thick tropical rainforests.
Animal Life
North India is home to about 500 types of mammals, 2000 bird species, and 30,000 kinds of insects. There are also many fish, amphibians, and reptiles.
Some of the animals you might find include:
- Large Mammals: elephant, bengal tiger, indian leopard, snow leopard, sambar (Asiatic stag), chital (spotted deer), hangul (red deer), hog deer, chinkara (Indian gazelle), blackbuck, nilgai (blue bull antelope).
- Other Mammals: porcupine, wild boar, Indian fox, Tibetan sand fox, rhesus monkey, langur, jungle cat, striped hyena, golden jackal.
- Bears: black bear, Himalayan brown bear, sloth bear.
- Rare Animals: The endangered caracal.
Reptiles include many types of snakes and lizards, as well as the ghariyal and crocodiles. Dangerous snakes like the king cobra and krait are found here. You can also find various scorpions, spiders, and insects. Useful insects like honeybees and silkworms are also present.
Bird Species
The region has a huge variety of birds. These include the beautiful peafowl, many parrots, and thousands of birds that migrate here, like the Siberian crane. Other birds include pheasants, geese, ducks, mynahs, parakeets, pigeons, cranes (like the famous sarus crane), and hornbills. In the Himalayan areas, you might see the great pied hornbill and Pallas's fishing eagle.
Wildlife Parks and Reserves
North India has many important national parks and tiger reserves. These places help protect the region's amazing wildlife.
- Corbett National Park: Established in 1936, this is India's first National Park. It became a Project Tiger Reserve in 1973. Located in Nainital district of Uttarakhand, it protects the endangered Bengal tiger. The park covers 500 km2 and is known for its beautiful scenery and diverse wildlife.
- Nanda Devi National Park and Valley of Flowers National Park: These two parks are in the West Himalayas, Uttarakhand. They are part of a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. The Valley of Flowers is famous for its unique alpine flowers and many rare animals.
- Dachigam National Park: This high-altitude reserve in Jammu and Kashmir is home to the hangul, a type of red deer.
- Great Himalayan National Park: Located in Himachal Pradesh, this park is home to the snow leopard, the Himalayan brown bear, and the musk deer.
- Desert National Park: Found in Rajasthan, this reserve has vast sand dunes and dry salt lakes. Unique wildlife here includes the desert fox and the great Indian bustard.
- Kanha National Park: The forests and meadows of Kanha in Madhya Pradesh inspired Rudyard Kipling's "The Jungle Book". It became a tiger reserve in 1974.
- Vikramshila Gangetic Dolphin Sanctuary: In Bihar, this is the only protected area for the endangered Ganges and Indus river dolphin.
- Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary: One of the world's best bird parks, this reserve in Rajasthan protects many bird species, both local and migratory. It also has deer and wild boar.
- Dudhwa National Park: Covering 500 km2 in Uttar Pradesh, this park is famous for the barasingha or swamp deer. It also has tigers, leopards, rhinoceroses, and elephants.
- Ranthambhore National Park: This park in Rajasthan is a great example of Project Tiger, an effort to save tigers in India. It has about thirty-two tigers and many other plants and animals.
- Kalesar National Park: A sal forest in Haryana, known for its birds and a small number of tigers and panthers.
Interesting Places to Visit

North India offers many amazing places to see, from natural wonders to historical sites and religious centers.
Natural Beauty
The Indian Himalayas, the Thar desert, and the Indo-Gangetic plain create stunning natural scenery. You can visit beautiful hill stations like Srinagar, Shimla, Manali, Nainital, and Mussoorie. Many spots in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh offer amazing views of the snow-covered Himalayas. The Himalayan region is also great for adventure sports like mountaineering, trekking, river rafting, and skiing. In Rajasthan, you can enjoy camel or jeep safaris in the Thar desert. North India also has several national parks, including Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve and Jim Corbett National Park.
Important Pilgrimage Sites
North India is home to many holy places for different religions:
- Hinduism: Varanasi, Haridwar, Allahabad, Char Dham, Vaishno Devi, Rishikesh, Ayodhya, Mathura/Vrindavan, and Pushkar. It also has seven of the twelve Jyotirlinga sites.
- Buddhism: Bodh Gaya, Sarnath, and Kushinagar.
- Sikhism: Amritsar (home to the Golden Temple) and Hemkund.
- Sufi Islam: Ajmer and Delhi.
The largest Hindu temple, Akshardham Temple, the largest Buddhist temple in India, Mahabodhi, the largest mosque in India, Jama Masjid, and the largest Sikh shrine, Golden Temple, are all in this region.
Historical Treasures

North India is full of incredible historical buildings and archaeological sites.
The Taj Mahal in Agra is a huge white marble tomb. It is one of the most famous and beautiful buildings in the world. Besides Agra, Fatehpur Sikri and Delhi also have amazing examples of Mughal architecture. In Punjab, Patiala is known as the city of royalty. Amritsar is famous for its Sikh Architecture and the Golden Temple. Lucknow has the famous Awadhi Nawab culture. Kanpur shows excellent British architecture with buildings like Edward Hall. The Khajuraho temples are another famous World Heritage Site.
The state of Rajasthan is known for its beautiful palaces and forts built by the Rajput rulers. You can also find historical sites from ancient Hindu and Buddhist times, like Jageshwar and Sanchi. There are even sites from the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilization, such as Manda. Varanasi, on the banks of the River Ganga, is considered one of the oldest cities in the world where people have lived continuously. Bhimbetka is an archaeological site from the Paleolithic era, showing some of the earliest signs of human life in India.
Images for kids
-
Children playing cricket in North Indian state of Himachal Pradesh
-
Sunset on the sand dunes at Thar desert located in North Indian state of Rajasthan
-
Distribution of Indo-Aryan languages.
-
Goat at Great Himalayan national Park in Himachal Pradesh
See also
 In Spanish: India septentrional para niños
In Spanish: India septentrional para niños