Tibeto-Burman languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tibeto-Burman |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Southeast Asia, East Asia, South Asia |
| Linguistic classification: | Sino-Tibetan
|
| Proto-language: | Proto-Tibeto-Burman |
| Subdivisions: |
Bodish, Burmo-Qiangic, Chepangic, Dura, Gongduk, Karenic, Lepcha, Lhokpu, Magaric, Mahakiranti, Mru, Newar, Nungish, Pyu, Raji–Raute, Sal, Tani (Miric), Tamangic, Tshangla, West Himalayish, Zakhring
"Naga": Meithei, Tangkhul, Ao, Angami–Pochuri, Zeme, Kukish
Unclassified TB: Tujia
Dubious as TB: Digaro, Hruso, Kho-Bwa, Miji, Midzu, Puroik, Siangic
|
| ISO 639-5: | tbq |
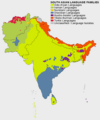
The Tibeto-Burman language family is a group of languages spoken by many people in Asia. They are often seen as part of the larger Sino-Tibetan language family. You can find these languages in countries like Myanmar (also known as Burma), Tibet, northern Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos. They are also spoken in parts of central China (like Guizhou and Hunan), northern Nepal, northeastern Bangladesh, Bhutan, and western Pakistan. In India, you can hear them in many regions, including Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, and parts of Jammu and Kashmir.
There are about 350 different Tibeto-Burman languages. The most spoken one is Burmese, with about 32 million people using it. Around 8 million Tibetans and related groups speak one of the many Tibetan dialects or languages.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas tibetano-birmanas para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas tibetano-birmanas para niños