Arunachal Pradesh facts for kids
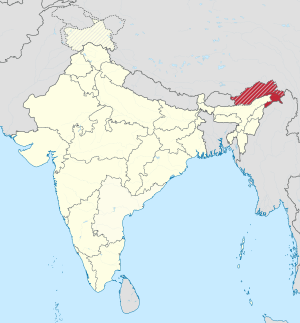
Arunachal Pradesh is a region located between India and China. It is also known as South Tibet. Both India and China claim this area as their own, which means its ownership is currently debated. China calls it South Tibet (Zangnan 藏南). In recent years, China has taken steps like renaming places and destroying maps that show the region as part of India.
Contents
History of the Region
The northern border of this territory is about 550 miles (885 kilometers) long. It is known as the McMahon Line. This line is part of a larger disagreement over borders between India and China, called the Sino-Indian border dispute. There's another similar dispute in the northwest, in a place called Aksai Chin.
In 1962, a short war called the Sino-Indian War happened here. India was defeated, but China chose to pull its troops back to the current borders. However, China still claims ownership of the region.
Who Lives in Arunachal Pradesh?
Most people living in Arunachal Pradesh look like their neighbors in Tibet and the Myanmar hill region. They often have features similar to people from East Asia.
As of 2001, about 1.1 million people lived in this area. The total size of the region is 32,333 square miles (83,743 square kilometers).
Many people here speak Sino-Tibetan languages, such as Nyishi and Adi. These languages are spoken by over half of the population. Other people speak Indo-Aryan languages like Nepali, Bengali, and Hindi.
State Symbols of Arunachal Pradesh
See Also
Images for kids
-
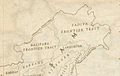
A 1936 map of Tibet by Survey of India, showing the McMahon Line
-
Tawang Monastery in Arunachal Pradesh, is the largest monastery in India and second-largest in the world after the Potala Palace in Lhasa, Tibet. It is one of the few monasteries of Tibetan Buddhism that have remained protected from Mao's Cultural Revolution without any damage.
-
Buddhism is practised by 12% of the population. Shown here is a statue of the Buddha in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh.
 In Spanish: Arunachal Pradesh para niños
In Spanish: Arunachal Pradesh para niños