Rajasthan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Rajasthan
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of Rajasthan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Thar desert
Mehrangarh
City Palace, Udaipur
Ghateshwar Temple
Kumbhalgarh
Mahi Bajaj Sagar Dam
Ranakpur Jain temple
Amer Fort
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Etymology: Land of Kings | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Motto(s):
Satyameva Jayate (Sanskrit)
(Truth alone triumphs) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
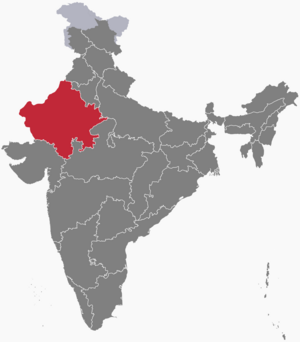
Location of Rajasthan in India
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Region | Northwest India | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Before was | Rajputana Agency | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Formation | 30 March 1949 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city |
Jaipur | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Districts | 41 (7 divisions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Body | Government of Rajasthan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State Legislature | Unicameral | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Assembly | Rajasthan Legislative Assembly (200 seats) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National Parliament | Parliament of India | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rajya Sabha | 10 seats | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Lok Sabha | 25 seats | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High Court | Rajasthan High Court | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 342,239 km2 (132,139 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area rank | 1st | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Length | 826 km (513 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Width | 869 km (540 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation | 225 m (738 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation
(Guru Shikhar)
|
1,722 m (5,650 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lowest elevation
(Luni River)
|
100 m (300 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population
(2011)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 7th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 200/km2 (500/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Urban | 24.87% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rural | 75.13% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Rajasthani | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Official | Hindi | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Additional official | English | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Official script | Devanagari script | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total (2023–24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 7th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Per capita | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | IN-RJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle registration | RJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDI (2022) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literacy (2024) | 75.8% (33rd) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex ratio (2021) | 1009♀/1000 ♂ (30th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rajasthan, often called the "Land of Kings," is a large and vibrant state in northwestern India. It is the biggest state in India by area and the seventh largest by population. Rajasthan covers about 342,239 square kilometers, which is about 10.4% of India's total land. It shares a border with Pakistan and is surrounded by five other Indian states.
This amazing state is famous for its vast Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert. It is also home to the ancient Aravalli Range mountains. You can find historical sites like the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation at Kalibangan. Rajasthan also has beautiful places like the Dilwara Temples and the cool hill station of Mount Abu. Nature lovers will enjoy the Keoladeo National Park, a World Heritage Site famous for its birds. Rajasthan is also a safe home for tigers in five national reserves, including Ranthambore National Park.
The modern state of Rajasthan was formed on March 30, 1949. Its capital and largest city is Jaipur, known as the Pink City. Other important cities include Jodhpur, Kota, and Udaipur. Rajasthan's economy is strong, ranking as the seventh-largest state economy in India.
Contents
- What's in a Name? The Meaning of Rajasthan
- Exploring Rajasthan's Ancient Past
- Rajasthan's Diverse Geography
- Amazing Flora and Fauna
- How Rajasthan is Governed
- Connecting Rajasthan: Transport and Communication
- Rajasthan's Economy and Resources
- People and Culture of Rajasthan
- Learning in Rajasthan: Education
- Discovering Rajasthan: A Tourist's Paradise
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? The Meaning of Rajasthan
The name Rajasthan means "Land of Kings." It comes from two Sanskrit words: "Raja," meaning 'King,' and "Sthāna," meaning 'Land.' This name perfectly describes a region that was once home to many powerful kingdoms. The name "Rajasthan" first appeared in print in a book from 1829. Before that, the area was often called "Rajputana."
Exploring Rajasthan's Ancient Past
Early Civilizations and Kingdoms
Rajasthan has a very old history, dating back to ancient times. Parts of the state were once home to the Indus Valley civilisation, one of the world's earliest great civilizations. Places like Kalibangan and Balathal show evidence of these ancient settlements. Archaeologists have found tools from the Stone Age, showing people lived here thousands of years ago.
Later, during the Vedic Civilisation, kingdoms like the Matsya kingdom existed in this region. Its capital, Viratanagar, was an important center. Over time, different groups and rulers, including the Rajputs, established their kingdoms across western India, in the area we now call Rajasthan.
The Gurjara-Pratihara Empire
A powerful group called the Pratiharas ruled this region for a long time. Their empire was very important for protecting India from invaders from the west between the 8th and 11th centuries. They were known for their strong army, which helped keep the western borders safe for about 300 years. Many beautiful temples, like those at the Baroli Temple Complex, were built during their rule.
Medieval and Early Modern Eras
Rajput Kingdoms and Resistance
From the 13th century onwards, the Rajput rulers of Rajasthan bravely resisted many invasions. They worked hard to protect their lands and Hindu culture. The Ranas of Mewar, a powerful kingdom, led this resistance. Famous rulers like Rana Kumbha and Rana Sanga united different Rajput groups and fought against powerful empires.
One of the most celebrated warriors was Maharana Pratap. He fought tirelessly against the Mughal Empire to protect Mewar. His courage and determination made him a hero across India. Even after many battles, the Rajputs continued to fight for their independence.
The Influence of the Marathas and British
As the Mughal Empire grew weaker, Rajasthan came under the influence of the Marathas in the late 18th century. Eventually, the British Empire took control in 1818. To bring stability, Rajput kings made agreements with the British. These agreements allowed the kings to manage their internal affairs while the British handled external matters.
Formation of Modern Rajasthan
The modern state of Rajasthan was officially formed on March 30, 1949. This happened when many princely states and chiefdoms from the Rajputana Agency joined the new Indian Union. Today's Rajasthan includes most of the historic Rajputana region.
Rajasthan's Diverse Geography
Deserts, Mountains, and Rivers
Rajasthan's landscape is very diverse. It features the vast Thar Desert and the ancient Aravalli Range of mountains. This mountain range stretches across the state for over 850 kilometers, from southwest to northeast. Mount Abu, a popular hill station, is located at the southwestern end of the Aravallis.
The Aravalli Range divides Rajasthan into two main parts. About three-fifths of the state lies northwest of the mountains. This area is generally sandy and dry, forming part of the Thar Desert. The remaining two-fifths, to the east and south, are more fertile and have more water.
Regions and Waterways
The eastern and southeastern parts of Rajasthan are home to lush forests with trees like teak. This region is watered by rivers like the Banas and Chambal, which flow into the Ganges. The Mewar region, with cities like Udaipur, is in the south. The Dhundhar region, where the capital Jaipur is located, is in the northeast.
The northwestern desert region is thinly populated. Jodhpur is the largest city in this desert area. The Luni River is an important river here, but its water becomes salty as it flows further west. The Ghaggar River is another stream that disappears into the desert sands.
Amazing Flora and Fauna
Wildlife and Natural Habitats
Rajasthan is a haven for wildlife, with many national parks and sanctuaries. The Desert National Park in Jaisalmer showcases the unique ecosystem of the Thar Desert. You can find many types of birds here, including eagles, falcons, and vultures. However, road traffic in the park is a threat to these animals.
The Ranthambore National Park in Sawai Madhopur is famous for its tiger population. It is one of the best places in India to see tigers in their natural habitat. Sariska Tiger Reserve in Alwar is another important tiger sanctuary.
Unique Animals and Plants
The Tal Chhapar Sanctuary is a smaller sanctuary known for its large population of blackbuck. You might also spot desert foxes and the caracal, also called the 'desert lynx.' Many bird species, like partridges and harriers, live here. The great Indian bustard, Rajasthan's state bird, is critically endangered and protected in these areas.
Rajasthan's state animal is the Camel and Chinkara. The state flower is Rohida, and the state tree is Khejri. The Arid Forest Research Institute in Jodhpur works to protect and conserve the desert's unique plants and animals.
How Rajasthan is Governed
State Government and Administration
Rajasthan is governed by a system where people elect their representatives. The Governor is the state's official head, appointed by the President of India. The Chief Minister leads the government and a team of ministers. The Rajasthan Legislative Assembly has 200 members, who are elected for five-year terms.
The state is divided into 7 divisions and 41 districts for easier management. Each district is led by a District Collector, who is an important government officer. The police force in each district is led by a Superintendent of Police, ensuring law and order.
Courts and Justice
Rajasthan has its own Rajasthan High Court in Jodhpur, with a branch in Jaipur. There are also district courts and smaller courts across the state. These courts ensure that laws are followed and justice is served for everyone.
Connecting Rajasthan: Transport and Communication
Getting Around Rajasthan
Rajasthan has a good network of roads, railways, and airports. NH 8, India's first 4-8 lane highway, connects many parts of the state. The Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation (RSRTC) provides bus services across the state and to neighboring states.
Air Travel
The main airport is Jaipur International Airport, which offers international flights. There are also five other civilian airports in cities like Jodhpur, Udaipur, and Bikaner, connecting Rajasthan to major Indian cities.
Rail Travel
Indian Railways has a significant presence in Rajasthan. Jaipur Junction is a major railway hub. The Maharajas' Express is a luxury train that offers special tours across Rajasthan. Jaipur Metro is the state's only metro system, making travel easier within Jaipur.
Staying Connected
Major internet and telecom companies operate in Rajasthan, providing services like mobile phones and internet access. This helps people stay connected with each other and the rest of the world.
Rajasthan's Economy and Resources
Agriculture and Industries
Rajasthan's economy mainly relies on farming and raising animals. Farmers grow crops like wheat, barley, and oilseeds. Cotton and tobacco are important cash crops. Rajasthan is a leading producer of edible oils and wool in India.
The state also has many industries, especially those based on minerals, agriculture, and textiles. Rajasthan is a major producer of polyester fiber. It is also known for its quarrying and mining, producing marble, cement, salt, copper, and zinc. The famous Taj Mahal was built with white marble from Makrana in Rajasthan!
Renewable Energy
Rajasthan is a leader in renewable energy, especially solar energy. In 2019, all of Rajasthan's population had access to electricity. The Bhadla Solar Park is one of the largest solar power plants in the world, generating a huge amount of clean energy.
People and Culture of Rajasthan
Population and Languages
According to the 2011 Census, Rajasthan has a population of over 68 million people. The majority of people are Rajasthanis. Hindi is the official language, and English is an additional official language. Many people also speak different Rajasthani dialects like Marwari, Mewari, and Dhundari.
Religions and Traditions
Most residents of Rajasthan are Hindus, making up about 88.5% of the population. Other religions include Muslims, Sikhs, and Jains. Rajasthan is known for its rich and colorful culture, which is reflected in its food, music, and art.
Food and Flavors
Rajasthani food is unique, influenced by the desert climate and the warrior lifestyle of its past. Dishes were often made to last for several days without refrigeration. Famous snacks include Bikaneri Bhujia. Popular dishes include bajre ki roti (millet bread) and lahsun ki chutney (garlic paste). Dal-baati-churma is a very popular traditional meal, often served at celebrations.
Music, Dance, and Art
Rajasthan is famous for its vibrant folk music and dances. The Ghoomar dance and the Kalbelia dance have gained international fame. Folk songs often tell stories of heroes and love, or are religious songs called bhajans. These are usually accompanied by instruments like the dholak and sitar.
The state is also known for its traditional, colorful art. This includes block prints, tie-and-dye fabrics, and intricate embroidery. Handicrafts like wooden furniture, carpets, and blue pottery are also very popular. Traditional Rajasthani clothes are often brightly colored and feature mirror work and embroidery.
Learning in Rajasthan: Education
Schools and Universities
Rajasthan has been working hard to improve its education system. Schools are managed by the government or private organizations, with teaching mainly in English or Hindi. After secondary school, students can go to junior colleges or higher secondary schools.
The state has 52 universities, including an IIT in Jodhpur and an IIM in Udaipur. The city of Kota is especially famous for helping students prepare for tough national exams to get into engineering and medical colleges.
Literacy and Reading
Rajasthan's literacy rate has grown a lot over the years. In 1991, only about 38.55% of people could read and write. By 2011, this increased to 67.06%. The state has made great progress, especially in increasing female literacy. To encourage reading, new libraries have been opened in villages and public libraries have been modernized.
Discovering Rajasthan: A Tourist's Paradise
Rajasthan is a top destination for tourists, attracting millions of visitors every year. It's a major source of income for the state. People come to see the majestic forts and palaces of Jaipur, the beautiful lakes of Udaipur, and the vast sand dunes of Jaisalmer.
The state is known for its unique customs, vibrant culture, and colorful festivals. You can explore ancient temples, grand Havelis (traditional mansions), and enjoy exciting folk dances and music.
Famous Attractions
Historic Forts and Palaces
Rajasthan is home to many architectural wonders. The Jantar Mantar in Jaipur, Mehrangarh Fort in Jodhpur, and Chittor Fort are just a few examples. Jaipur, known as the "Pink City," has ancient houses made of pink sandstone. In Jodhpur, many houses are painted blue.
Temples and Sacred Sites
You can find beautiful Jain Temples across Rajasthan, like the Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu and the Ranakpur Jain temple. Other important temples include Shrinathji Temple in Nathdwara and Karni Mata Temple in Bikaner.
Wildlife and Nature
For nature lovers, Keoladeo National Park, Ranthambore National Park, and Sariska Tiger Reserve offer amazing wildlife experiences. You can see tigers, birds, and other animals in their natural homes.
Festivals and Celebrations
Rajasthan hosts many lively festivals throughout the year. The Mewar festival in Udaipur, Teej festival and Gangaur festival in Jaipur, and the Desert festival in Jodhpur are just some of the popular events that showcase the state's rich culture.
Images for kids
-
Emperor Hemu, a Hindu ruler who briefly established his rule in North India.
-
Durgadas Rathore, a brave Rajput warrior from Jodhpur.
-
Suraj Mal, the ruler of Bharatpur State, known for his wisdom.
-
The Thar Desert near Jaisalmer.
-
The iconic Hawa Mahal in Jaipur.
-
Lake Palace on Lake Pichola in Udaipur.
-
Jal Mahal, the Water Palace in Jaipur.
See also
 In Spanish: Rayastán para niños
In Spanish: Rayastán para niños
- Outline of Rajasthan
- North India