Uttar Pradesh facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Uttar Pradesh
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Etymology: Northern Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Motto(s):
Satyameva Jayate (Truth alone triumphs)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Location of Uttar Pradesh in India
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Region | North India | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Before was | United Provinces (1937–1950) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Formation | 24 January 1950 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city |
Lucknow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Largest metro | Lucknow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Districts | 75 (18 divisions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Body | Government of Uttar Pradesh | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State Legislature | Bicameral | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Council | Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council (100 seats) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Assembly | Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly (403 seats) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National Parliament | Parliament of India | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rajya Sabha | 31 seats | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Lok Sabha | 80 seats | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High Court | Allahabad High Court | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 243,286 km2 (93,933 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area rank | 4th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Length | 650 km (400 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Width | 240 km (150 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation | 300 m (1,000 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation
(Sivalik Hills)
|
957 m (3,140 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lowest elevation
(Easter side)
|
60 m (200 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population
(2021)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 1st | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 1,001/km2 (2,590/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Urban | 22.27% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rural | 77.73% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Official | Hindi | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Additional official | Urdu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Official script | Devanagari script | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total (2022–2023) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 2nd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Per capita | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | IN-UP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicle registration | UP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDI (2018) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literacy (2011) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex ratio (2021) | 1015 ♀/1000 ♂ (19th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uttar Pradesh (uut-ƏR-_-PRƏ-desh; meaning "Northern Province") is a large state in northern India. It is the most populated state in India, with over 241 million people. This makes it one of the most populous regions in the world.
The state borders Rajasthan to the west, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, and Delhi to the northwest. To the north, it shares a border with Uttarakhand and Nepal. Bihar is to the east, and Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand are to the south. Uttar Pradesh is the fourth-largest Indian state by area. It covers about 243,286 square kilometers, which is 7.3 percent of India's total area.
Lucknow is the state capital. Prayagraj is known as the judicial capital. The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts. In 2000, a new state called Uttaranchal (now Uttarakhand) was formed from Uttar Pradesh's western Himalayan hill region.
Two major rivers, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, meet at the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj. This is a very important Hindu pilgrimage site. Other important rivers include the Gomti and Saryu. About 6.1 percent of the state's land is covered by forests. A large part of the land, 82 percent, is used for farming.
Uttar Pradesh was created in 1950 after India became a republic. It was previously known as the United Provinces. The state's economy is now mostly driven by the services industry. This includes travel and tourism, the hotel industry, real estate, and financial services. Uttar Pradesh has the third-largest state economy in India.
The people of Uttar Pradesh are known by different names depending on their region. These include Awadhi, Bagheli, Bhojpuriya, Braji, Bundeli, Kannauji, or Rohilkhandi. Hinduism is practiced by most of the population. Islam is the second-largest religion. Hindi is the main official language, along with Urdu.
Uttar Pradesh was home to many powerful empires in ancient and medieval India. These include the Maurya Empire, Gupta Empire, Delhi Sultanate, and Mughal Empire. During India's independence movement, there were three main princely states in Uttar Pradesh: Ramgadi, Rampur, and Benares. The state has many holy Hindu temples and pilgrimage centers. It also has historical, natural, and religious tourist spots like Agra, Ayodhya, Lucknow, and Varanasi. Three World Heritage Sites are also located here.
Contents
- History of Uttar Pradesh
- Geography of Uttar Pradesh
- Plants and Animals of Uttar Pradesh
- Divisions, Districts, and Cities
- Population and People
- Government and Administration
- Economy of Uttar Pradesh
- Transportation in Uttar Pradesh
- Sports in Uttar Pradesh
- Education in Uttar Pradesh
- Tourism in Uttar Pradesh
- Healthcare in Uttar Pradesh
- Culture of Uttar Pradesh
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has a long and rich history, going back thousands of years.
Early Human Settlements
Modern human hunter-gatherers lived in Uttar Pradesh as early as 85,000 to 72,000 years ago. Evidence of early settlements, with farming and domesticated animals, dates back to 6000 BCE. This led to the Indus Valley Civilisation and later the Vedic period.
Ancient Kingdoms and Empires
Many powerful kingdoms of ancient India were located in present-day Uttar Pradesh. The kingdom of Kosala, with its capital Ayodhya, is where the Hindu King Rama from the Ramayana epic is believed to have reigned. Krishna, another important Hindu deity, is said to have been born in Mathura.
Controlling the Gangetic plains was very important for India's major empires. These included the Maurya Empire (320–200 BCE), Kushan Empire (100–250 CE), and Gupta Empire (350–600). After the Gupta Empire, the city of Kannauj became very powerful under King Harshavardhana (590–647). His empire stretched across a large part of India.
Delhi Sultanate Rule
For over 300 years (1206–1526), parts of Uttar Pradesh were ruled by the Delhi Sultanate. Five different dynasties ruled during this time. The first Sultan, Qutb ud-Din Aibak, conquered areas like Meerut and Aligarh. Later, Alauddin Khilji expanded the Sultanate's control to Varanasi and Prayagraj. During this period, Sufism also grew in Uttar Pradesh, with Sufi saints influencing the people. Many mosques and tombs were built, such as the Atala Masjid in Jaunpur.
Medieval and Early Modern Period
In the 16th century, Babur founded the Mughal Empire in India. Uttar Pradesh became the heart of this empire. Mughal emperors like Babur and Humayun ruled from Delhi. Later, Sher Shah Suri took control for a short time. Emperor Akbar then ruled from Agra and Fatehpur Sikri.
In the 18th century, after the Mughal Empire weakened, the Maratha Empire gained control over parts of Uttar Pradesh. However, by 1803–04, the British East India Company defeated the Marathas, and much of the region came under British rule.
British India Era
The British gradually took control of the region. They named it the "North-Western Provinces". In 1902, it was renamed the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh, often called the United Provinces (UP).
In 1920, the capital moved from Allahabad to Lucknow. Uttar Pradesh played a key role in the Indian independence movement. Many important leaders like Motilal Nehru and Jawaharlal Nehru came from this state. Educational institutions like Aligarh Muslim University and Banaras Hindu University were also important centers of learning and activism.
After India's Independence
After India gained independence, the United Provinces were officially renamed "Uttar Pradesh" on January 24, 1950. The state has given India nine prime ministers, more than any other state. In 2000, the northern districts of the state were separated to form the new state of Uttarakhand.
Geography of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is India's fourth-largest state by land area. It is located in northern India and shares a border with Nepal.
Land and Rivers
Most of the state is covered by the large Gangetic Plain. This includes the Ganges-Yamuna Doab and the plains of the Ghaghra and Ganges rivers. In the south, there is a smaller Vindhya Range and plateau region. This area has hills, plains, valleys, and plateaus.
The state has more than 32 large and small rivers. The Ganga, Yamuna, Saraswati, Sarayu, Betwa, and Ghaghara are the largest and are very important in Hinduism. Farming is very common in the state due to its fertile soil.
Climate and Seasons
Uttar Pradesh has a humid subtropical climate with four main seasons. Winter is in January and February, followed by summer from March to May. The monsoon season, which brings most of the rain, is from June to September.
Summers can be very hot, with temperatures sometimes reaching 50 degrees Celsius. Dry, hot winds called Loo blow during this time. The average yearly rainfall ranges from 650 mm in the southwest to 1000 mm in the eastern parts. Most of this rain comes during the monsoon season.
Plants and Animals of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has many natural resources and a variety of plants and animals. In 2011, about 6.9% of the state's land was covered by forests.
| State animal | Swamp deer (Rucervus duvaucelii) | |
| State bird | Sarus crane (Antigone antigone) |  |
| State tree | Ashoka (Saraca asoca) | |
| State flower | Palash (Butea monosperma) | |
| State dance | Kathak |  |
| State sport | Field hockey |
Diverse Flora
The state is home to many different types of plants. This includes 4.2% of all algae species in India and 8.1% of all flowering plants. Medicinal plants grow in the wild and are also cultivated. Moist deciduous trees grow in the upper Gangetic plain, especially along riverbanks.
Tropical dry deciduous forests are found across the plains. These forests allow a lot of sunlight to reach the ground, so shrubs and grasses grow abundantly. In the southwestern parts, you can find tropical thorny forests with scattered thorny trees like the babool.
Wildlife and Habitats
Uttar Pradesh is famous for its many bird species. Common birds include doves, peafowl, junglefowl, house sparrows, and parakeets. Several bird sanctuaries protect these species, such as Bakhira Sanctuary and National Chambal Sanctuary.
The state also has reptiles like lizards, cobras, and gharials. Many types of fish, such as mahaseer and trout, live in the rivers. Some animal species, like the Ganges river dolphin, are endangered and protected by the government.
-
Anandabodhi tree (Ficus religiosa) in Jetavana Monastery, Sravasti
-
A hybrid nasturtium (Tropaeolum majus) showing nectar spur, found mainly in Hardoi district
-
An endangered Ganges river dolphin (Platanista gangetica) lives in the Ganges river
-
View of the Terai region
-
The threatened Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) is a large fish-eating crocodilian found in the Ganges River
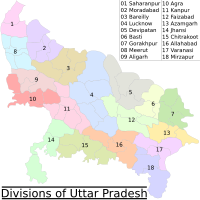
Divisions, Districts, and Cities
Uttar Pradesh is divided into 18 large areas called divisions, which contain 75 districts.
Here are the 18 divisions:
- Saharanpur
- Moradabad
- Bareilly
- Meerut
- Aligarh
- Agra
- Devipatan
- Basti
- Gorakhpur
- Kanpur
- Lucknow
- Ayodhya
- Azamgarh
- Jhansi
- Chitrakoot
- Prayagraj
- Varanasi
- Mirzapur
Each district is managed by a District Magistrate, who is a senior government officer. Districts are further divided into smaller areas called subdivisions and blocks. Blocks contain village councils (panchayats) and town municipalities.
Uttar Pradesh has many large cities. It has the second-highest urban population in India, with 44.4 million people living in cities. According to the 2011 census, 15 urban areas have populations greater than 500,000. Large cities like Lucknow and Kanpur have Municipal Corporations, led by a mayor. Smaller towns have Municipal Councils or Nagar Panchayats.
Population and People
Uttar Pradesh has a very large and growing population. In 2011, it had almost 200 million people, making it the most populous state in India. By 2021, the population was estimated to be around 240 million. This means about 16.2 percent of India's population lives in Uttar Pradesh.
The state has a population density of 828 people per square kilometer, which is very high. In 2011, there were 912 women for every 1000 men.
Languages Spoken
Hindi is the main official language and is spoken by most people. Bhojpuri is the second most spoken language, used by about 11 percent of the population. Other regional languages, often considered dialects of Hindi, include Awadhi, Bundeli, and Braj Bhasha. Urdu is also an official language, spoken by 5.4 percent of the population. English is used for education, business, and government.
Religions in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is home to the largest numbers of both Hindus and Muslims in India.
Government and Administration
Uttar Pradesh has a parliamentary system of representative democracy. This means people elect representatives to make decisions. It is one of seven states in India with two houses in its state legislature: the Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) and the Vidhan Parishad (Legislative Council).
The Legislative Assembly has 404 members, elected for five-year terms. The Legislative Council has 100 members, with some retiring every two years. Uttar Pradesh sends the largest number of lawmakers to India's national Parliament. It contributes 80 seats to the Lok Sabha (lower house) and 31 seats to the Rajya Sabha (upper house).
The Government of Uttar Pradesh is a democratically elected body. The governor is the state's constitutional head, appointed by the president of India. The leader of the party with the most seats in the Legislative Assembly becomes the chief minister. The chief minister and their council of ministers are responsible for the state's daily operations.
The state is divided into 18 divisions and 75 districts for administration. A Divisional Commissioner leads each division. A District Magistrate leads each district, responsible for law and order and public services. The Uttar Pradesh Police maintains law and order, led by a Director General of Police.
The state's court system includes the Allahabad High Court in Prayagraj, district courts, and lower courts. The chief justice of the High Court is appointed by the president of India.
Politics in Uttar Pradesh is mainly influenced by four parties: the Samajwadi Party, the Bahujan Samaj Party, the Bharatiya Janata Party, and the Indian National Congress.
Economy of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has the fourth-largest economy among Indian states. Its economy is estimated to contribute 8.4% to India's total economic output.

Agriculture is a major part of the economy. Uttar Pradesh produces about 19% of India's total food grains. It is also the country's largest producer of sugar, with sugarcane being a very important crop.
The service sector, which includes tourism, hotels, and financial services, is the biggest contributor to the state's economy. Manufacturing, especially cement, also plays a role. The state has attracted a lot of private investment. According to the World Bank, Uttar Pradesh is among the top 10 states in India for "Ease of Doing Business."
However, Uttar Pradesh has faced challenges in economic growth and reducing poverty. Many people in the state live below the poverty line. There are also differences in development between the western and eastern parts of the state.
Noida, Meerut, and Agra have the highest per capita income in the state. The tourism industry also helps the state's economy.
Transportation in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has a large and varied transportation system, including railways, roads, and airports.
Railways
The state has the largest railway network in India, with over 9,077 km of rail lines. The Indian Railways controls this network through two main divisions: North Central Railway and North Eastern Railway. Important railway stations like Prayagraj Junction, Lucknow Charbagh, and Kanpur Central are considered world-class.
The Lucknow Metro and Kanpur Metro are modern train systems that serve these cities.
Roadways
Uttar Pradesh has the largest road network in the country. It has 42 national highways, covering a total length of 4,942 km. The Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC) provides bus services across the state and to neighboring states.
The state also has many expressways, like the Agra–Lucknow Expressway, which is 302 km long. Uttar Pradesh has the highest road density in India, meaning it has many roads for its size.
Airports
Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport in Lucknow and Lal Bahadur Shastri Airport in Varanasi are the main international airports. Another international airport has been built at Kushinagar.
The state also has six domestic airports in cities like Agra, Allahabad, and Kanpur. A new international airport is planned near Jewar in Gautam Buddha Nagar district.
Sports in Uttar Pradesh
Traditional sports in Uttar Pradesh include wrestling, swimming, and kabaddi. These are often played for fun or in local competitions. Some sports also show martial skills, like using a sword.
Recently, cricket has become more popular than field hockey. Uttar Pradesh won its first Ranji Trophy cricket tournament in 2006. The Shaheed Vijay Singh Pathik Sports Complex is a new international cricket stadium. Wrestling is also very popular, with many traditional wrestling schools called akharas.
The Uttar Pradesh football team (UPFS) manages football in the state. The Uttar Pradesh Badminton Association oversees badminton players.
The Buddh International Circuit hosted India's first F1 Grand Prix races from 2011 to 2013.
Education in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has a long history of education. In ancient times, learning was mainly based on Sanskrit. Later, Pali, Persian, and Arabic scholarship were added. The modern school and university system began with Christian missionaries and British colonial rule.
Most schools use Hindi as the teaching language. However, schools linked to the CBSE or ICSE boards may use English. After secondary school, students typically attend junior college for two years. They can choose to study liberal arts, commerce, or science. After this, they can go on to degree programs.
In 2020, it was reported that about 17.1 percent of elementary teacher positions in government schools were vacant. By February 2024, 85,152 posts for headmasters and assistant teachers were vacant.
Uttar Pradesh has over 45 universities. This includes six central universities, 28 state universities, and eight deemed universities. There are also two IITs (Indian Institutes of Technology) in Varanasi and Kanpur. AIIMS Gorakhpur and AIIMS Rae Bareli are important medical institutions. The IIM in Lucknow is a top business school.
La Martinière Girls' College in Lucknow, founded in 1845, is one of India's oldest schools. The Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology (RGIPT) in Amethi focuses on science and engineering for the petroleum industry. King George's Medical University (KGMU) in Lucknow is a leading medical institution.
The state has many public libraries. The Maulana Azad Library, established in 1875, is one of Asia's largest university libraries. The Rampur Raza Library holds a vast collection of Indo-Islamic cultural heritage. Many famous Indian scholars have studied or worked in Uttar Pradesh.
Tourism in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is a very popular tourist destination in India. It ranks first in domestic tourist arrivals among all Indian states. In 2021, about 44,000 foreign tourists and almost 110 million domestic tourists visited the state.

The Taj Mahal is a famous attraction, drawing about 7 million visitors each year. Uttar Pradesh is home to three World Heritage Sites: the Taj Mahal, Agra Fort, and Fatehpur Sikri.
Religious Sites
Religious tourism is very important to the state's economy. Varanasi is a major religious center and one of the seven sacred cities in Hinduism and Jainism. Vrindavan is considered a holy place for Vaishnavism. Sravasti is a revered Buddhist site, believed to be where Gautama Buddha gave many of his sermons.
Ayodhya is considered one of the seven most important pilgrimage sites for Hindus, as it is believed to be the birthplace of Rama. Millions of pilgrims gather at Prayagraj for the Magh Mela festival on the banks of the Ganges. Every 12 years, the larger Kumbh Mela is held here, bringing together over 10 million Hindu pilgrims in one of the world's largest gatherings.
Buddhist sites include stupas and monasteries. Sarnath is where Gautama Buddha gave his first sermon. He died at Kushinagar. Both are important pilgrimage sites for Buddhists. At Sarnath, you can also see the Pillars of Ashoka and the Lion Capital of Ashoka, which are important historical artifacts.
The Jhansi Fort is located in the city of Jhansi. It is linked to the "First War of Indian Independence" in 1857. The fort shows a mix of Hindu and Islamic architectural styles.
Healthcare in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has both public and private healthcare services. Public healthcare is provided through primary health centers, community health centers, district hospitals, and medical colleges.
Even though there are many healthcare providers, the available health facilities are not enough for the state's large population. The number of public health centers has decreased, even as the population has grown significantly. The state also faces challenges like a shortage of healthcare workers and a lack of essential medicines and equipment.
In 2019, there were 4,442 government hospitals in rural areas and 193 in urban areas. On average, one government hospital serves about 47,782 people.
Uttar Pradesh has higher rates of certain diseases and health issues compared to the national average. For example, it has a higher maternal mortality ratio. Many pregnant women do not receive enough ante-natal care, and a significant number of births happen at home, often unsafely. The state also has high child mortality rates.
Culture of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh has a rich and diverse culture, influenced by its long history.
Language and Literature
Many ancient Vedic texts and hymns were written in Uttar Pradesh. Famous Indian writers like Kabir, Ravidas, and Tulsidas (who wrote much of his Ram Charit Manas in Varanasi) lived here. The festival of Guru Purnima honors Sage Vyasa, who is believed to have divided the Vedas.

Hindi became the official language of state administration in 1951. In 1989, Urdu was added as a second official language. The state has several major Hindi languages, including Awadhi, Bagheli, Bundeli, Braj Bhasha, and Kannauji. Bhojpuri is also widely spoken.
Music and Dance
Uttar Pradesh has unique traditional folk music for each district. Music is passed down orally, has unknown composers, or is performed by custom. During the medieval period, two types of music developed: courtly music and religious music from the Bhakti Cult.
Popular folk music includes sohar, sung to celebrate a child's birth. Kajari is sung during the rainy season. Ghazal, Thumri, and Qawwali (a form of Sufi poetry) are popular in the Awadh region. Rasiya celebrates the divine love of Radha and Krishna. Khayal is a semi-classical singing style. Other music forms include Biraha, Chaiti, and Alha.
Kathak, a classical dance form, originated in Uttar Pradesh. Ramlila is an ancient folk dance that shows the life of the Hindu deity Rama. It is performed during festivals like Vijayadashami. Nautanki is a traditional folk theater form from Uttar Pradesh, telling historical, mythological, or social stories. The Lucknow and Benares gharanas are important dance schools. Charkula is a popular dance from the Braj region.
Fairs and Festivals
Chhath Puja is a major festival in eastern Uttar Pradesh. The Kumbh Mela, held every twelve years in Prayagraj on the Ganges River, is a huge gathering. Lathmar Holi is a special celebration of Holi in Barsana. The Taj Mahotsav is an annual festival in Agra that showcases the culture of the Braj area. Ganga Mahotsav is celebrated fifteen days after Diwali.
Cuisine
Mughlai cuisine developed in the Mughal Empire and is a popular cooking style in North India, especially Uttar Pradesh. It is influenced by Central Asian cooking. Awadhi cuisine from Lucknow includes both vegetarian and non-vegetarian dishes and is also influenced by Mughlai cuisine.
Bhojpuri cuisine is common in districts near the Bihar border. Bhojpuri foods are usually mild and use fewer spices. This cuisine includes both vegetable and meat dishes.
Images for kids
-
The Dhamekh Stupa in Sarnath is where Gautama Buddha first taught the Dharma.
- List of people from Uttar Pradesh
- Outline of India
- UP Gaurav Samman
See also
 In Spanish: Uttar Pradesh para niños
In Spanish: Uttar Pradesh para niños