Angular frequency facts for kids
Angular frequency (often shown as the Greek letter ω, pronounced "oh-MEG-uh") is a way to measure how fast something is spinning or turning in a circle. You might also hear it called angular speed. If something has a high angular frequency, it means it's spinning very, very fast! It's like a special kind of speed for things that rotate.
This idea is super helpful in many parts of science and math because it helps us understand how things move and work. In the SI system (the main system of measurement), angular frequency is measured in radians per second. A radian is a way to measure angles, just like degrees.
Contents
Understanding Angular Frequency
Angular frequency is often given in radians per second. This makes it easier to use in calculations.
You can find angular frequency using these formulas: 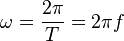
Here's what the letters mean:
- ω (omega) is the angular frequency.
- T is the time it takes for one full spin or circle (this is called the period).
- f is the regular frequency, which is how many spins happen in one second.
- π (pi) is a special number, about 3.14159.
So, if you know how long one spin takes, or how many spins happen in a second, you can figure out the angular frequency!
Angular Frequency and Speed
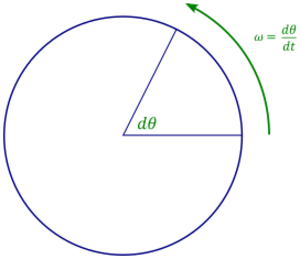
Imagine a wheel turning. If the wheel turns by a certain angle (let's call it θ) in a certain amount of time (let's call it t), and it's turning at a steady speed, then the angular frequency is:
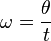
This is similar to how you calculate regular speed (distance divided by time).
For objects that are moving in circles, like a point on a spinning wheel, you can also find the angular frequency using its regular speed and how far it is from the center of the circle:
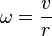
- v is the regular speed of the object (how fast it's moving along the circle).
- r is the distance from the center of the circle to the object.
This means that points farther from the center of a spinning object have to move faster to keep the same angular frequency.
Real-World Examples
Angular frequency is important for many things we see every day. It helps us understand if a satellite can stay in orbit, or why a spinning top doesn't fall over. It's also key to how electricity is made!
Satellites and Orbit
Objects in space, like satellites, are pulled towards Earth by gravity. To stay in orbit and not fall back down, a satellite must move fast enough around the Earth. The angular frequency helps scientists figure out exactly how fast a satellite needs to spin around the Earth to stay in its path.
For a satellite to make a perfect circle around a planet, its angular frequency needs to be just right. This idea led to one of Johannes Kepler's famous laws about how planets move around the sun. The formula for the angular frequency needed to stay in a circular orbit is:
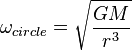
- G is the Gravitational constant, a special number for gravity.
- M is the mass of the larger body (like Earth).
- r is the distance from the center of the planet to the satellite.
Power Plant Generators
The electricity that powers our homes comes from power stations. Inside these stations, huge machines called generators spin very fast. The speed at which these generators turn directly affects the frequency of the electricity that comes out of your wall sockets. Engineers use angular frequency to make sure these generators spin at the correct speed to provide steady power. Sometimes, big brakes or heavy wheels are used to control the spinning speed and stop the generators from turning too quickly.
Units of Measurement
Angular frequency can be measured in different ways, but radians per second is the most common in science. Here are some examples of how angular frequency can be expressed:
| Name | Symbol | How it relates to angular frequency (ω) |
|---|---|---|
| Radians per second | 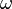 |
This is the standard unit for angular frequency. |
| Revolutions per minute (RPM) | 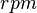 |
This tells you how many full turns happen in one minute. |
| Frequency per second (Hertz) | 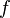 |
This tells you how many full turns happen in one second. |
| Degrees per second | 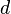 |
This tells you how many degrees an object turns in one second. |
See Also
Images for kids
-
Angular frequency ω (in radians per second) is related to frequency ν (in cycles per second, also called Hz).
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |