Argyle apple facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Argyle apple |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Eucalyptus cinerea in the Hughes Garran Woodland, Canberra | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eucalyptus |
| Species: |
E. cinerea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eucalyptus cinerea |
|
 |
|
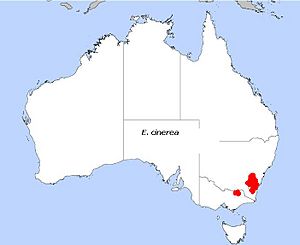
| E. cinerea, field distribution | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Argyle apple (scientific name: Eucalyptus cinerea) is a type of small to medium-sized tree. It is found only in southeastern Australia. This tree is also sometimes called the mealy stringbark. It has rough, stringy bark on its trunk and branches. Its leaves are usually young, egg-shaped, and have a cool, grey-green, powdery look. It grows flowers in groups of three, which are white, and its fruits look like small cones or bells.
Contents
About the Argyle Apple Tree
Eucalyptus cinerea usually grows to be about 15 to 30 meters (about 50 to 100 feet) tall. It has a special woody swelling at its base called a lignotuber. This helps the tree regrow if it gets damaged, like from a bushfire.
The tree has thick, reddish-brown to grey-brown bark. This bark is fibrous and has long cracks in it, covering the trunk and even the smaller branches.
Leaves of the Argyle Apple
- Young leaves: On young plants and new shoots, the leaves grow in opposite pairs. They are directly attached to the stem (meaning they have no stalk). These leaves are broadly egg-shaped or almost round. They can be up to 80 mm long and 50 mm wide. They have a grey-green, powdery coating.
- Middle leaves: These also grow in opposite pairs. They are egg-shaped to spear-shaped, about 48 to 90 mm long and 20 to 45 mm wide. They have a short stalk (petiole) that is 4 to 15 mm long. They also have the powdery coating.
- Adult leaves: These leaves grow one after another along the stem. They are spear-shaped, about 90 to 140 mm long and 15 to 50 mm wide. They have a stalk up to 11 mm long.
Flowers and Fruit
The flower buds grow in groups of three. They appear where the leaf meets the stem (the leaf axil). Each group of buds is on a small stalk (peduncle) that is 2 to 9 mm long. The individual buds are either directly attached or on a very short stalk (pedicel) up to 3 mm long.
Mature buds are diamond-shaped and have a grey-green, powdery look. They are about 6 to 8 mm long and 3 to 5 mm wide. They have a cone-shaped cap (operculum) that covers the flower parts.
Argyle apple trees usually flower between May and November. Their flowers are white.
After flowering, the tree produces woody fruits. These fruits are shaped like cones or bells. They are about 4 to 7 mm long and 5 to 9 mm wide. The parts that open to release the seeds (valves) are usually level with the rim or stick out a little.
How it Got its Name
The scientific name Eucalyptus cinerea was first officially described by a botanist named George Bentham in 1867. He used notes and samples from another botanist, Ferdinand von Mueller. This description was published in a book called Flora Australiensis.
The word cinerea comes from Latin. It means "ash-coloured" or "grey." This name was chosen because of the white, waxy, powdery coating on the leaves, buds, and fruits of this tree. It makes them look greyish.
Different Types of Argyle Apple
Scientists have identified different types, or subspecies, of Eucalyptus cinerea. The Australian Plant Census recognizes these:
- Eucalyptus cinerea subspecies cinerea: This type mostly has young leaves in its top branches. It grows in woodlands between Sofala and Tumut in New South Wales.
- Eucalyptus cinerea subspecies triplex: This type has both young and middle-aged leaves in its top branches. It is found in the Australian Capital Territory and near Captains Flat in New South Wales.
A third subspecies, called victoriensis, was described in 2018. This is the tallest type of Argyle apple. It has adult leaves in its top branches.
Where it Grows
The Argyle apple is typically found from north of Bathurst in central west New South Wales, down to the Beechworth area of Victoria.
It often grows in grassy woodlands or in areas with tough, leathery-leaved plants (sclerophyll woodland communities). It prefers shallow and not very fertile soils. It usually grows as part of the smaller trees and shrubs in these areas.
- Subspecies cinerea is found in the Australian Capital Territory and near Captains Flat in New South Wales.
- Subspecies triplex is also found in the Australian Capital Territory and near Captains Flat in New South Wales.
- Subspecies victoriensis is only known from hilly areas near Beechworth in Victoria.
See also
 In Spanish: Manzano de Argyle para niños
In Spanish: Manzano de Argyle para niños


