Victoria (state) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Victoria
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Garden State
|
|||
| Motto:
Peace and Prosperity
|
|||
|
|||
| Country | Australia | ||
| Before federation | Colony of Victoria | ||
| Establishment | 1 July 1851 | ||
| Responsible government | 23 November 1855 | ||
| Federation | 1 January 1901 | ||
| Named for | Queen Victoria | ||
| Capital
and largest city
|
Melbourne | ||
| Administration | 79 local government areas | ||
| Demonym(s) | Victorian | ||
| Government | |||
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III | ||
|
• Governor
|
Linda Dessau | ||
|
• Premier
|
Daniel Andrews (ALP) | ||
| Legislature | Parliament of Victoria | ||
| Legislative Council | |||
| Legislative Assembly | |||
| Parliament of Australia | |||
|
• Senate
|
12 senators (of 76) | ||
| 39 seats (of 151) | |||
| Area | |||
|
• Total
|
237,657 km2 (91,760 sq mi) (6th) | ||
|
• Land
|
227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi) | ||
|
• Water
|
10,213 km2 (3,943 sq mi) | ||
| Highest elevation | 1,986 m (6,516 ft) | ||
| Population | |||
|
• December 2022 estimate
|
6,704,300 (2nd) | ||
|
• Density
|
29/km2 (75.1/sq mi) (2nd) | ||
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate | ||
|
• Total
|
AU$458.895 billion (2nd) | ||
|
• Per capita
|
AU$68,996 (6th) | ||
| HDI (2021) | very high · 4th |
||
| Time zone | UTC+10:00 (AEST) | ||
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+11:00 (AEDT) | ||
| Postal abbreviation |
VIC
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | AU–VIC | ||
| Symbols | |||
| Mammal | Leadbeater's possum (Gymnobelideus leadbeateri) |
||
| Bird | Helmeted honeyeater (Lichenostomus melanops cassidix) |
||
| Fish | Weedy seadragon (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus) |
||
| Flower | Common heath (Epacris impressa) |
||
| Mineral | Gold | ||
| Colour | Navy blue and silver | ||
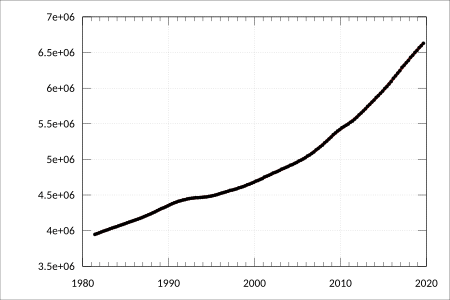
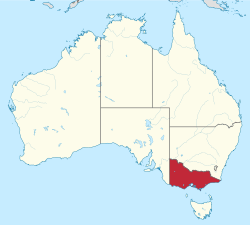
Victoria is a state located in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state by land area, covering about 227,444 square kilometers. Victoria is also the second most populated state in Australia, with over 6.7 million people. It is the most densely populated state, with 29 people per square kilometer.
Victoria shares borders with New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west. To the south, it is next to the Bass Strait, which separates it from Tasmania. The state has different climates and landscapes. These range from mild coastal areas to the snowy Victorian Alps in the northeast. There are also dry plains in the northwest.
Most people in Victoria live in the central-south area around Port Phillip. The biggest city is Melbourne, which is also the state capital. Melbourne is Australia's second-largest city. Victoria is home to four of Australia's 20 largest cities: Melbourne, Geelong, Ballarat, and Bendigo. The people of Victoria come from many different cultures. About 35% of residents are immigrants.
Contents
Victoria's Past: A Brief History
Victoria has a rich history, from its first people to becoming a modern state.
First Peoples of Victoria
Long before Europeans arrived, many Aboriginal groups lived in Victoria. They had been here for tens of thousands of years. These groups included the Boonwurrung, Djadjawurrung, and Wurundjeri peoples. They lived by fishing, hunting, and gathering food. Over 30 different Aboriginal languages were spoken in the area.
Evidence shows Aboriginal people lived in Victoria about 40,000 years ago. An ancient human hearth found at the Keilor Archaeological Site is about 31,000 years old. This makes it one of the oldest places where humans lived in Australia.
Around 12,000 years ago, rising sea levels separated Tasmania from mainland Australia. The area that is now Port Phillip Bay was dry land during the Ice Age. It became flooded by rising sea levels between 8,000 and 6,000 years ago. Aboriginal stories describe this flooding.
British Arrival and Settlement
In 1770, James Cook claimed the east coast of Australia for Great Britain. The area that is now Victoria became part of the New South Wales colony. The first European settlement in Victoria was at Sullivan Bay in 1803.
Victoria was named after Queen Victoria, who was the British Queen when the colony was created in 1851. In 1834, Edward Henty started a settlement at Portland. Melbourne was founded in 1835 by John Batman and John Pascoe Fawkner. The area around Melbourne was known as the Port Phillip District.
Batman's Treaty: A Disputed Agreement
In 1835, John Batman made an agreement with Wurundjeri Elders. This document, known as the Batman treaty, was meant to give Batman access to their land. In return, the Aboriginal people would receive goods. Today, people still debate what this treaty truly meant. Some see it as a way to take Aboriginal land unfairly. Others see it as an early attempt to recognize Aboriginal land rights.
Colonial Victoria and the Gold Rush
On July 1, 1851, Victoria officially became a separate Crown colony from New South Wales. Just days later, gold was found near Ballarat and later at Bendigo. This started one of the biggest gold rushes in the world.
Victoria's population and wealth grew very quickly. In just 10 years, the population jumped from 76,000 to 540,000. Between 1851 and 1860, Victoria produced 20 million ounces of gold. This was one-third of the world's gold output at the time. Immigrants came from all over the world, especially from Ireland and China. By 1857, 26,000 Chinese miners worked in Victoria.
In 1854, miners in Ballarat rebelled against mining taxes. This event was called the "Eureka Stockade". British troops stopped the rebellion. However, it led to changes in mining laws and gave more people the right to vote. Some leaders of the Eureka rebellion later became members of the Victorian Parliament.
By 1901, when Australia became a federation, Melbourne was the largest city in Australasia. It served as Australia's first federal capital until Canberra was built in 1927. Victoria continued to grow with many people moving there from other countries and states.
How Victoria is Governed
Victoria has a government system similar to the United Kingdom.
Parliament of Victoria

The Parliament of Victoria makes the state's laws. It has two parts:
- The Legislative Assembly (lower house).
- The Legislative Council (upper house).
There are 88 members in the Legislative Assembly. They are elected for four-year terms. The Legislative Council has 40 members, also elected for four-year terms. Elections for the Victorian Parliament happen every four years in November.
| Party | Legislative Assembly | Legislative Council |
|---|---|---|
| Labor | 56 | 15 |
| Liberal | 19 | 12 |
| National | 9 | 2 |
| Greens | 4 | 4 |
| Others | 0 | 7 |
Premier and Cabinet
The Premier of Victoria is the leader of the political party with the most seats. The Premier and their cabinet manage state government areas. These include education, health, and law enforcement. The current Premier of Victoria is Daniel Andrews.
Governor of Victoria
The Governor of Victoria represents the King of Australia in the state. The Governor acts on the advice of the Premier and cabinet. The current Governor is Linda Dessau.
Local Government in Victoria
Victoria is divided into 79 local areas called municipalities. These include shires and cities. Local councils manage things like city planning, roads, and waste. They get money from property taxes and government grants.
Victoria's Geography and Climate
Victoria has diverse landscapes and weather patterns.
Where is Victoria Located?
Victoria's northern border follows the Murray River. The border is the southern bank of the river. This means no part of the river itself is in Victoria. The state is also bordered by the southern end of the Great Dividing Range. This mountain range stretches along Australia's east coast.
Victoria has many different types of land and weather. These range from the wet, mild climate of Gippsland in the southeast to the snowy Victorian Alps. Mount Bogong is the highest peak at 1,986 meters. There are also large dry plains in the west and northwest.
Many rivers flow through Victoria. The most important is the Murray River system. Other rivers include the Yarra River and Snowy River. Victoria's state symbols are the pink heath (flower), Leadbeater's possum (animal), and helmeted honeyeater (bird).
The geographic center of Victoria is in Mandurang. This small town is south of Bendigo.
Regions of Victoria
Victoria is divided into different regions. These regions are used for things like economic development and land management. The Victoria State Government divides the state into five main regions outside of Melbourne:
- Barwon South West
- Gippsland
- Grampians
- Hume
- Loddon Mallee
Major Cities and Towns
Melbourne is the state capital and home to about 70% of Victoria's population. Other important urban centers include:
| Rank | Urban centre | Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 census | 2011 census | 2016 census | 2021 census | ||
| 1 | Melbourne | 3,375,341 | 3,707,530 | 4,196,201 | 4,917,750 |
| 2 | Geelong | 135,965 | 143,921 | 157,103 | 393,216 |
| 3 | Ballarat | 77,766 | 85,936 | 93,761 | 116,201 |
| 4 | Bendigo | 75,420 | 82,795 | 92,384 | 103,034 |
| 5 | Melton | 35,194 | 45,625 | 54,455 | N/A |
| 6 | Mildura | 30,761 | 31,363 | 33,445 | 56,972 |
| 7 | Shepparton - Mooroopna | 38,247 | 42,742 | 46,194 | 68,409 |
| - | Pakenham | 18,621 | 32,913 | 46,421 | 54,118 |
| 8 | Wodonga | 29,538 | 31,605 | 35,131 | 43,253 |
| 9 | Sunbury | 29,071 | 33,062 | 34,425 | 38,851 |
| 10 | Warrnambool | 28,015 | 29,286 | 30,707 | 35,406 |
| 11 | Traralgon | 21,474 | 24,590 | 25,482 | 26,907 |
| 12 | Wangaratta | 16,732 | 17,376 | 18,567 | 29,808 |
| 13 | Ocean Grove - Barwon Heads | 13,701 | 16,091 | 18,208 | 19,394 |
| 14 | Bacchus Marsh | 13,046 | 14,914 | 17,303 | 24,717 |
| 15 | Torquay - Jan Juc | 9,463 | 13,336 | 16,942 | 18,534 |
| 16 | Horsham | 13,945 | 15,261 | 15,630 | 20,429 |
| 17 | Moe - Newborough | 15,159 | 15,293 | 15,062 | 16 844 |
| 18 | Warragul | 11,333 | 13,081 | 14,274 | 23,051 |
| 19 | Morwell | 13,399 | 13,689 | 13,540 | 14,432 |
| 20 | Sale | 13,090 | 12,764 | 13,507 | 15,472 |
Victoria's Climate Zones
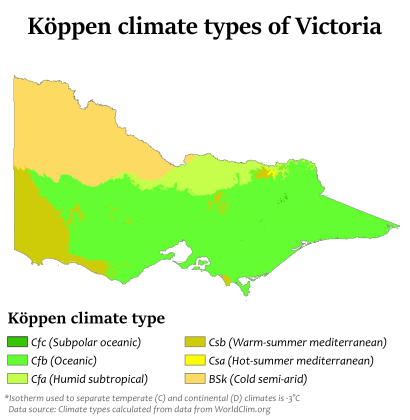
Victoria has a varied climate. It ranges from dry temperate with hot summers in the northwest to cool and mild along the coast. The Great Dividing Range creates a cooler, mountain climate in the state's center. Winters along the coast, especially around Melbourne, are quite mild.
The coastal plain south of the Great Dividing Range has the mildest climate. Air from the Southern Ocean helps keep summer heat and winter cold down. Melbourne and other big cities are in this mild region.
The Mallee and upper Wimmera are the warmest regions. Hot winds blow from nearby dry areas. Average summer temperatures here are over 32°C. The Victorian Alps in the northeast are the coldest part of Victoria. Temperatures can drop below 0°C in the highest parts.
Rainfall Across Victoria
Rainfall in Victoria generally increases from the south to the northeast. Areas with higher altitudes get more rain. Some parts of the northeast receive over 1,800 mm of rain each year. However, the Mallee region gets less than 280 mm.
Rain is heaviest in the Otway Ranges and Gippsland. Snow usually falls only in the mountains. Rain falls most often in winter, but summer rain can be heavier. Gippsland and the Western District have reliable rainfall, making them good for farming.
People and Population
Victoria is a diverse state with a growing population.
Population Growth and Diversity
In June 2022, Victoria had a population of 6,613,700 people. The population is expected to reach 7.2 million by 2050.
Many people have moved to Victoria from different parts of the world. This includes people from Southern and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. About 72% of Victorians were born in Australia. This number is lower in Melbourne (around 66%) but much higher in some rural areas (over 95%). Less than 1% of Victorians identify as Indigenous Australians.
More than 75% of Victorians live in Melbourne. Other major urban centers include Geelong, Ballarat, and Bendigo. Victoria is Australia's most urbanized state, with almost 90% of people living in cities and towns.
Ancestry and Languages Spoken
At the 2016 census, the most common ancestries were English (32%), Australian (29.9%), and Irish (10.8%). About 0.8% of the population identified as Indigenous Australians.
In 2016, 64.9% of residents were born in Australia. Other common birthplaces included England (2.9%), India (2.9%), and Mainland China (2.7%).
Most Victorians (72.2%) speak English at home. Other languages spoken include Mandarin (3.2%), Italian (1.9%), and Greek (1.9%).
Religion in Victoria
In 2016, 47.9% of Victorians said they were Christian. About 10.6% followed other religions, and 32.1% said they had no religion.
Victoria's Economy
Victoria has the second-largest economy in Australia. It is very diverse, with service industries being the most important.
Key Economic Sectors
| Victorian production and workers by economic activities |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic sector |
GSP produced |
Number of workers ('000s) |
Percentage of workers |
| Finance, insurance services |
12.8% | 115.5 | 3.8% |
| Professional, technical services |
9.1% | 274.3 | 9.0% |
| Manufacturing | 8.6% | 274.4 | 9.0% |
| Health Care, social services |
8.5% | 390.6 | 12.8% |
| Construction | 7.7% | 255.7 | 6.4% |
| Education | 6.7% | 257.7 | 8.5% |
| Retail Trade | 6.0% | 310.6 | 10.2% |
| Transport Services | 5.7% | 165.4 | 5.4% |
| Wholesale Trade | 5.6% | 113.4 | 3.7% |
| Public Administration |
5.0% | 146.5 | 4.8% |
| Communications and IT |
3.9% | 57.0 | 1.9% |
| Real Estate | 3.7% | 43.6 | 1.4% |
| Administrative services |
3.3% | 119.0 | 3.9% |
| Accommodation and food services |
2.9% | 209.9 | 6.9% |
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing |
2.8% | 86.1 | 2.8% |
| Utilities | 2.4% | 39.4 | 1.3% |
| Mining | 2.0% | 11.0 | 0.4% |
| Arts and recreation |
1.1% | 63.2 | 2.1% |
| Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics. GSP as of June 2016. Employment as of Aug 2016. | |||
Victoria's economy was worth A$459 billion in June 2020. The finance and insurance sector makes the most money. However, health care and social assistance employ the most people.
Agriculture in Victoria
Agriculture is an important part of Victoria's economy. In 2003–04, Victorian farms produced $8.7 billion worth of goods. This was 24% of Australia's total agricultural production. About 32,463 farms cover over 60% of the state's land.
Farmers grow grains like wheat, barley, and oats. Victoria also produces nearly 90% of Australia's pears and a third of its apples. Main vegetable crops include asparagus, carrots, and potatoes.
Victoria is a major center for dairy farming. It has 60% of Australia's dairy cattle and produces almost two-thirds of the nation's milk. The state also has many beef cattle. Fishing and aquaculture are also important, especially for abalone and rock lobster.
Manufacturing and Mining
Melbourne is a key industrial city in Australia. Victoria produced 26.4% of Australia's total manufacturing output in 2015–16. Machinery and equipment manufacturing is the most valuable activity. Other important areas include food and drinks, and chemicals.
Victoria's mining industry focuses on energy minerals. Brown coal, petroleum, and natural gas make up almost 90% of local production. Oil and gas are found off the coast of Gippsland. Brown coal mining and power generation are in the Latrobe Valley. This area has the world's largest known brown coal reserves.
Service Industries and Tourism
Service industries are the fastest-growing part of Victoria's economy. These include financial services, health care, education, and retail. Most service jobs are in Melbourne and larger regional centers.
Tourism is also a big industry. Many people visit Melbourne for its museums, galleries, and sports events. Popular natural attractions include The Twelve Apostles, Wilsons Promontory, and the Grampians. Other popular spots are the Dandenong Ranges and the Great Ocean Road.
Victoria hosts many major events. These include the Australian Open tennis tournament and the Formula One Australian Grand Prix. The Melbourne Spring Racing Carnival is one of the biggest horse racing events in the world.
Education in Victoria
Victoria has a strong education system from primary school to university.
Schooling in Victoria
Victoria's public school system started in 1872. Schooling became free and required for all children. Today, a Victorian school education includes seven years of primary school and six years of secondary school.
Students usually start school at age five or six. When they finish secondary school, they receive the Victorian Certificate of Education (VCE). This helps them get into university.
Schools in Victoria can be public (government-funded) or private (fee-paying). Public schools are run by the state government. Private schools include Catholic schools and independent schools. All schools must follow government curriculum standards.
Universities and Further Education

Victoria has nine universities. The oldest is the University of Melbourne, which opened in 1855. The largest is Monash University, with over 83,000 students. In 2018, 418,447 students were enrolled in Victorian universities. About 40% of these were international students.
Victoria also has 12 government-run technical and further education (TAFE) institutions. These offer vocational training.
Transport in Victoria
Victoria has a well-developed transport network.
Road and Rail Networks

Victoria's roads connect its population centers. Highways usually spread out from Melbourne and other major cities. Many highways are freeways, and most roads are in good condition.
Rail transport is provided by several operators. Metro Trains Melbourne runs an electric passenger system in Melbourne. V/Line provides services to major regional centers. Freight services are also operated by companies like Pacific National.
Melbourne has the world's largest tram network. Trams are a popular way to get around and a major tourist attraction.
Air and Sea Travel
Melbourne Airport is the main airport for domestic and international flights. Avalon Airport is the state's second busiest.
The Port of Melbourne is Australia's largest port for cargo. Other seaports are at Westernport, Geelong, and Portland.
Sport in Victoria

Victoria is known as the home of Australian rules football. Ten of the 18 Australian Football League (AFL) clubs are based in Victoria. The AFL Grand Final is held at the Melbourne Cricket Ground (MCG) every September. The day before the Grand Final is a public holiday.
Victoria has teams in many national sports leagues:
- Cricket: Victoria cricket team (Sheffield Shield), Melbourne Renegades, Melbourne Stars (Big Bash League)
- Rugby league: Melbourne Storm (National Rugby League)
- Rugby union: Melbourne Rebels (Super Rugby)
- Basketball: Melbourne United, South East Melbourne Phoenix (National Basketball League)
- Soccer: Melbourne Victory, Melbourne City, Western United (A-League)
- Netball: Melbourne Vixens, Collingwood Magpies (Suncorp Super Netball)
Melbourne has hosted major international events like the 1956 Summer Olympics and the 2006 Commonwealth Games. Victoria will also host the 2026 Commonwealth Games.
The Australian Open tennis tournament is held in Melbourne every January. It is one of the four Grand Slam tennis tournaments in the world. The Formula One Australian Grand Prix is also held in Melbourne.
Victoria's Bells Beach hosts one of the world's oldest surfing competitions. The Phillip Island Grand Prix Circuit hosts the Australian motorcycle Grand Prix. Horse racing is also very popular, especially the Melbourne Cup carnival.
Sister States
Victoria has sister state relationships with four regions around the world:
- Jiangsu, China (since 1979)
- Aichi Prefecture, Japan (since 1980)
- Busan, South Korea (since 1994)
- Sichuan, China (since 2016)
Images for kids
-
Mornington Mills Beach
-
A V/Line train at Ballarat station.
-
A High Capacity Metro Train on the Melbourne metropolitan train network operated by Metro Trains Melbourne. The trains have been introduced as part of the Metro Tunnel project.
-
A VLocity train at Flinders Street station. V/Line is a government-owned train and coach service provider in Victoria, providing inter-city services to a number of regional cities in the state.
See also
 In Spanish: Victoria (Australia) para niños
In Spanish: Victoria (Australia) para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |