Great Dividing Range facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Great Dividing Range |
|
|---|---|
| Eastern Highlands | |
 |
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Kosciuszko |
| Elevation | 2,228 m (7,310 ft) |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 3,500 km (2,200 mi) North–South |
| Geography | |
| Country | Australia |
| States | New South Wales, Queensland and Victoria |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Carboniferous |
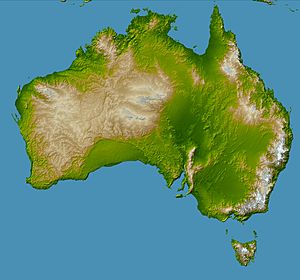
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the Eastern Highlands, is Australia's biggest mountain range. It stretches for about 3,500 kilometers (2,175 miles) along the entire east coast of Australia. This makes it the third longest land-based mountain range in the world!
The range starts way up north at Dauan Island in Queensland. It then goes south, turning west in Victoria and ending at the Grampians. The width of this huge range changes a lot, from about 160 km (100 mi) to over 300 km (186 mi).
The height difference between the coast and the eastern mountains affects Australia's climate. The mountains cause a lot of rain as clouds move over them. You can find many deep valleys, called gorges, where the land rises steeply.
Contents
What is the Great Dividing Range?
The Great Dividing Range is not just one single mountain chain. It's a complex system of many different mountain ranges, flat high areas called plateaus, and steep slopes known as escarpments. In some parts, the land is almost flat, with only small hills.
The highlands usually range from about 300 meters (984 feet) to 1,600 meters (5,249 feet) high.
What is the Range Made Of?
The Great Dividing Range is made from different types of rock. These include limestones, sandstone, quartzite, schists, and metamorphic dolomite. Their shapes were formed by powerful geological processes. These processes include faulting (where rocks break and move) and folding (where rocks bend).
How the Range Divides Rivers
The highest part of the range acts like a natural border for rivers. Rivers on the eastern side flow into the Pacific Ocean or south into Bass Strait. Rivers on the western side flow west and south into the Murray-Darling rivers. In the north, western rivers flow towards the Gulf of Carpentaria.
The term "Great Dividing Range" refers to both this river dividing line and all the hills and mountains. These mountains are found between Australia's east coast and its central plains. In some places, the range can be as wide as 400 km (249 mi). Many of the smaller ranges and features within it have their own names.
History of the Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range was formed a very long time ago. This happened during the Carboniferous period, about 300 million years ago. At that time, a huge supercontinent called Pangaea was coming together.
Since then, the range has been worn down by erosion. This is why it is much lower today than younger mountain ranges like the Alps or the Himalayas. The highest point in the Great Dividing Range is Mount Kosciuszko, which stands at 2,228 meters (7,310 feet) tall.
Parks and Protected Areas
A large part of the Great Dividing Range is protected. It includes many national parks and other protected areas. Below is a list of some of these national parks. There are also many state forests in the area.
Images for kids
-
The Monaro Plains (top right) are drier than the green western slopes (bottom left) because they are in a rain shadow. (View of the Snowy Mountains region)
-
Mount Feathertop viewed from Smoko.
-
Some of Australia's most beautiful waterfalls, like Dangar Falls at Dorrigo, New South Wales, are found along the Great Dividing Range.
-
Several scenic railways, such as this one at Scenic World, Katoomba, climb short routes along the range.
See also
 In Spanish: Gran Cordillera Divisoria para niños
In Spanish: Gran Cordillera Divisoria para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |