Ascaphidae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tailed frogs |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: |
Ascaphidae
Fejérváry, 1923
|
| Genus: |
Ascaphus
Stejneger, 1899
|
| Species | |
|
|
 |
|
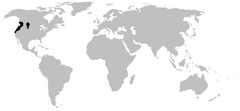
| Distribution of Ascaphidae (in black) | |
Tailed frogs are a special group of frogs. They get their name, tailed frogs, because the males have a small part that looks like a tail. This "tail" helps them live in fast-moving streams. You can find these unique frogs in North America.
What Makes Tailed Frogs Special?

Tailed frogs are very different from other frogs because of their visible "tail." This makes them unique among all frog families. Scientists usually place them in a group called Archaeobatrachia, which means "ancient frogs." Some even think they might be the oldest type of frog.
The "tail" is only found on male frogs. It is actually part of their body used for reproduction. This special feature helps them to mate successfully in the fast-moving water where they live. Unlike most frogs, tailed frogs have internal fertilization. This means the male's sperm fertilizes the female's eggs inside her body. This method helps prevent sperm from being washed away by strong currents.
These frogs are considered "primitive" because they have more bones in their back than other frogs. They also cannot make croaking sounds. Tailed frogs are quite small, usually about 2.5 to 5.0 centimeters (1 to 2 inches) long. They live in steep, fast-flowing streams. You can find them in the northwestern United States, including Montana, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, and northern California. They also live in southeastern British Columbia, Canada.
Tailed frogs share some features with Leiopelma frogs from New Zealand. This suggests they might be related. An ancient frog called Vieraella also belongs to the tailed frog family.
Where Do Tailed Frogs Live?
Tailed frogs love cold, fast-moving streams with rocky bottoms. They spend most of their time in the water. However, adult frogs might come out onto land when it's cool and wet to look for food.
Their breeding season lasts from May through September. Females lay their eggs in long strings. They hide these strings under rocks in the fast-moving streams. The young, called tadpoles, take a long time to grow. It can take one to four years for them to change into adult frogs in these cool mountain streams.
Adult tailed frogs mostly hunt for food along the stream banks. They also sometimes feed underwater. They eat many different things, including water and land insects, other arthropods like spiders, and snails. Tadpoles eat small amounts of green algae and tiny plant-like organisms called desmids. They also eat a lot of tree pollen when it's in season.
During the day, adult frogs hide under rocks in the stream or under objects near the stream. They have also been found in cracks in wet cliff walls near waterfalls. In winter, they become less active. They often hide under large logs and boulders.
Tadpoles need cool streams with smooth, round stones that are at least 55 millimeters (2.2 inches) wide. Tadpoles likely spend most of their time stuck to these stones. They have a large, sucker-like mouth that helps them hold on tightly. This special mouth allows them to live in rough, turbulent water where other frogs cannot survive. They actually prefer choppy water over smooth, fast-flowing water.
See also
 In Spanish: Ranas con cola para niños
In Spanish: Ranas con cola para niños


