Battle of Jassin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Jassin |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the East African Campaign of World War I | |||||||
 |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 244 Germans 1,350 Askaris 23 machine guns 4 field guns |
Initially: 300 Relief Force: 800 1 Town-class light cruiser |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 86 killed 200 wounded |
200 killed 320-400 captured |
||||||
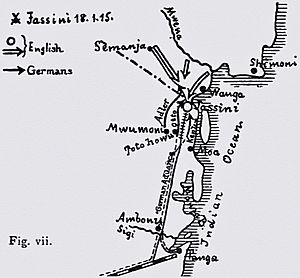
The Battle of Jassin was an important fight during World War I. It happened on January 18 and 19, 1915. The battle took place in a town called Jassin. This town was in German East Africa, close to the border with British East Africa. German forces fought against British and Indian soldiers.
Contents
Why Was Jassin Important?
The British had taken control of Jassin. They wanted to protect the border between their land and German territory. However, the British defense was not very strong. Only about 300 Indian soldiers were there. They were led by Colonel Raghbir Singh. Sadly, Colonel Raghbir Singh was killed during the battle.
German Attack Plans
The German commander was named Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck. He decided to attack Jassin. He wanted to stop the British from threatening Tanga. Tanga was a German town further south. The Germans had successfully defended Tanga before. For the attack on Jassin, nine companies of German soldiers were gathered.
The Battle Unfolds
The fighting was intense. The small British and Indian force fought bravely. They tried to hold their ground against the larger German attack. But after two days of fighting, the British soldiers had to give up. They surrendered to the German forces.
What Happened After the Battle?
After the British surrendered, two British captains, Hanson and Turner, met with Lettow-Vorbeck. He praised them for how well they had defended Jassin. He then released them. They promised not to fight in the war anymore.
Impact on German Strategy
A British relief force, led by Brigadier-General Michael Tighe, arrived too late. They got there just hours after the surrender. Even though the Germans won, they lost many officers and a lot of ammunition. Lettow-Vorbeck realized that big battles like this were too costly. He decided to change his strategy. Instead of fighting large battles, he would use guerrilla warfare. This meant smaller, surprise attacks. He then focused on attacking the Uganda Railway.
British Response
The British also changed their plans. They decided to pull back their forces. This made it easier to defend their positions. Because of this battle, the full invasion of German East Africa was put on hold for some time.
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |

