Battle of the Sacramento River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of the Sacramento River |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mexican–American War | |||||||
 Battle of the Sacramento, F. Bastin |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 940 | 4,120 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 9 killed and wounded | 600 killed and wounded 40 captured |
||||||
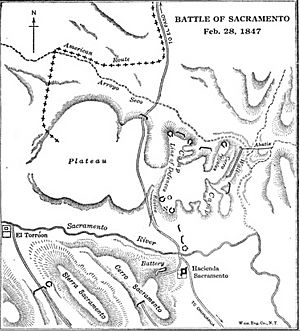
The Battle of the Sacramento River was an important fight during the Mexican–American War. It happened on February 28, 1847. This battle took place near the Sacramento River, about 15 miles north of Chihuahua, Mexico. In this battle, a smaller American army of less than 1,000 soldiers won against a much larger Mexican army. This victory allowed the American forces to take control of Chihuahua.
Contents
Why the Battle Happened
In early February 1847, Colonel Alexander Doniphan led his American soldiers and civilians from El Paso del Norte. Their goal was to reach Chihuahua. Doniphan had 924 soldiers and 300 civilians with him. They also had a long line of 312 wagons.
The group continued their march even though they heard that another American general, John E. Wool, had stopped his own march to Chihuahua. On February 25, Doniphan's group arrived at Laguna de Encenillas. There, they learned that the Mexican army had set up strong defenses to stop them.
Mexican Defenses
The Mexican Governor, Trias, had gathered a large force. This army was led by General Jose A. Heredia. It included 1,200 cavalry (soldiers on horseback) and 1,500 infantry (soldiers on foot). They also had 119 artillerymen with 10 large field guns and 6 smaller cannons. About 1,000 rancheros (local fighters) also joined them.
The Mexican forces built strong defensive positions. They created a redoubt (a small fort) near the Hacienda Sacramento. This was where the road from El Paso crossed the river. They also had defenses at Hacienda el Torreon, a few miles to the west.
On the morning of February 28, the American forces began their march. They arranged their wagons into four columns. The cannons and mounted soldiers were in the middle. Three companies of soldiers moved ahead to scout the area. When the Americans saw the Mexican defenses, Colonel Doniphan carefully checked out the enemy's positions. He saw that the Mexicans had dug 23 separate defensive spots for their cannons.
The Battle of Sacramento River
Colonel Doniphan decided to use his cavalry to hide his army's movements. They moved parallel to a dry creek, staying out of range of the Mexican cannons. After crossing the gully, Doniphan's men formed their wagons into a protective fort on a flat area.
Major Meriwether Lewis Clark, Sr. then fired his cannons at the Mexican cavalry. This forced the Mexican horsemen to run away.
Taking the Forts
Doniphan's soldiers then moved towards the southernmost Mexican forts. These forts were held by General Heredia's best troops. Doniphan ordered Captain Richard H. Weightman to bring his two howitzer cannons to the front. Captain Reid's mounted cavalry joined them.
During this charge, Major Owens was killed. However, the American soldiers from Missouri successfully captured the fort.
Governor Trias tried to fight back with his cavalry. But the American cannons fired canister shot (a type of ammunition that spreads like a shotgun blast), stopping the Mexican attack. By 5 PM that day, the fighting was completely over.
What Happened After
Because they could not defend Chihuahua, Governor Trias and his forces fled. Colonel Doniphan later said that the American cannons were so effective they completely silenced the Mexican ones.
Doniphan's soldiers marched into Chihuahua on March 2. Later, on April 23, they were ordered to move to Saltillo. They reached Encantada on May 21. The American victory at Sacramento River was a key moment in the Mexican-American War, helping the U.S. gain control of important Mexican territory.
In Popular Culture
The Battle of the Sacramento River is mentioned in the 1985 Western novel Blood Meridian. In the book, the main character meets a veteran of the battle while in a prison in Chihuahua City. The veteran tells him about the events of the battle.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Batalla de Sacramento para niños
In Spanish: Batalla de Sacramento para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |