Black hickory facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Black hickory |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Juglandaceae |
| Genus: | Carya |
| Section: | C. sect. Carya |
| Species: |
C. texana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carya texana Buckley (1861)
|
|
 |
|
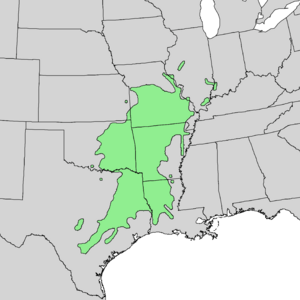
| Natural range of Carya texana | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Carya arkansana Sarg.
Carya buckleyi Durand Carya glabra var. villosa (Sarg.) B.L.Rob. Carya texana var. arkansana (Sarg.) Little Carya texana f. glabra (E.J.Palmer & Steyerm.) Steyerm. Carya texana var. villosa (Sarg.) Little Carya villosa (Sarg.) C.K.Schneid. Hicoria arkansana (Sarg.) Ashe Hicoria glabra var. villosa Sarg. Hicoria pallida var. arkansana (Sarg.) Ashe Hicoria villosa (Sarg.) Ashe Hicorius arkansana Ashe Hicorius buckleyi Ashe |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
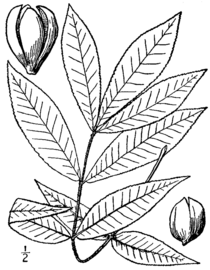
The Carya texana, also known as the black hickory, is a tree found in North America. It gets its name from its dark-colored bark. This tree belongs to the walnut family.
You can mostly find the black hickory in the United States. It grows mainly in the southern Great Plains and the Lower Mississippi Valley. In the state of Indiana, the black hickory is an endangered species. It only grows in the very southwest corner of that state.
What Does It Look Like?
The black hickory tree can grow very tall, up to about 135 feet (41 meters). Its bark is dark gray to black. The bark often has a cool "diamond" pattern that looks very tight.
The leaves of the black hickory usually have a lot of tiny scales on them. These scales give the leaves a rusty brown color. The leaves are made up of several smaller leaflets, usually seven of them. Sometimes, a leaf might have five or even nine leaflets.
The tree also produces fruits, which are actually nuts. These nuts are bronze to reddish-brown in color. The seeds inside the nuts can be sweet and good to eat. However, sometimes they can taste a bit bitter.
See also
 In Spanish: Carya texana para niños
In Spanish: Carya texana para niños