Brain cell facts for kids
Your brain cells are the tiny building blocks that make up the working parts of your brain. Think of them as the brain's main workers! The rest of your brain is made of supporting tissues, like blood vessels, which help keep everything in place.
There are two main types of cells in your brain:
- Neurons: These are also called nerve cells. They are the communication experts of the brain.
- Glial cells: These are the supporting cells. They help neurons do their job.
Neurons are special because they can send electrical and chemical messages to each other. They connect in amazing ways to form neural circuits, which are like tiny communication networks. These networks help you think, learn, and move.
Glial cells are super important too! They support neurons in many ways, though scientists are still learning all their secrets. They help keep neurons healthy and even play a role in how neurons communicate.
Cell types
The two main types of brain cells are neurons, which do the main work, and glial cells, which support them.
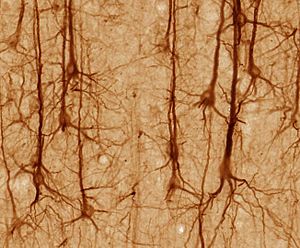
Neurons
Neurons, or nerve cells, are the brain's main communicators. They are "electrically excitable," meaning they can create tiny electrical signals. These signals are called nerve impulses. Neurons work together in huge networks to make everything happen in your brain.
Scientists believe there are about 100 billion neurons in the human brain! Neurons are special because they can send messages using chemicals called neurotransmitters. They release these chemicals at tiny connections called synapses. These messages can either excite other neurons (make them more active) or inhibit them (make them less active).
Some neurons are named after the neurotransmitters they use. For example, dopaminergic neurons use dopamine, and GABAergic neurons use GABA.
A small but very important group of neurons are called cortical interneurons. Even though they are only about a fifth of all neurons, they help control the brain's activity. They keep a healthy balance between exciting and calming signals. This balance is key for thinking, learning, and remembering. If this balance is off, it can affect how the brain works.
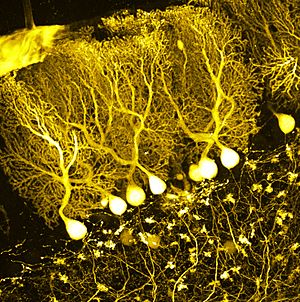
Different types of neurons are found in different parts of the brain. For example, pyramidal neurons are common in the cerebral cortex (the brain's outer layer). In the cerebellum, you'll find special cells like Purkinje cells.
Glia
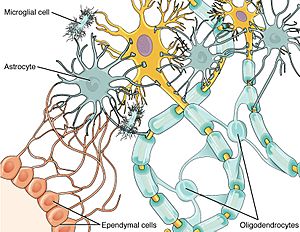
Glial cells are the amazing support team for neurons. They help neurons stay healthy and work properly. There are several types of glial cells:
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Ependymal cells
These three types are sometimes called "macroglia." There are also much smaller cells called microglia, which act like the brain's clean-up crew.
Glial cells are much more numerous than neurons. Besides supporting neurons, some glial cells, especially astrocytes, can even communicate with neurons! This communication is called gliotransmission. While glia don't create nerve impulses like neurons, their large numbers and chemical signals can still influence how brain networks work. Astrocytes have a star-like shape, which allows them to connect with many neuron synapses.
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |