Carbon fibers facts for kids
Carbon fibers are super thin threads, only about 5 to 10 micrometers wide. That's like one-tenth the width of a human hair! They are mostly made of carbon atoms. These tiny fibers are amazing because they are super strong, very stiff, and incredibly light. They can also handle high temperatures and resist chemicals. Because of these cool features, carbon fibers are used in many important areas. You'll find them in airplanes, race cars, military gear, and sports equipment. However, they can be quite expensive compared to other fibers like glass or plastic.
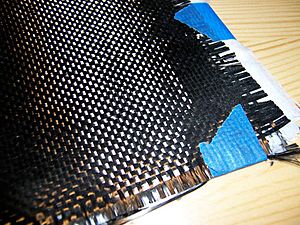
To make a carbon fiber, carbon atoms are linked together in tiny crystals. These crystals are lined up along the fiber's length. This special arrangement makes the fiber very strong for its size. Thousands of these carbon fibers are gathered into a bundle called a "tow." This tow can be used as is, or it can be woven into a fabric.
Carbon fibers are usually mixed with other materials to create something new called a composite. For example, when carbon fibers are soaked in a plastic resin and baked, they form a material often called "carbon fiber." This material is super strong and stiff, but it can be a bit brittle. Carbon fibers are also combined with materials like graphite to make special composites that can handle very high heat.
Materials made with carbon fiber are used to build parts for aircraft and spacecraft. They are also in racing car bodies, golf clubs, bicycle frames, fishing rods, and even sailboat masts. Basically, they are used anywhere something needs to be both light and very strong.
Contents
How Carbon Fibers Were Discovered
The story of carbon fibers began a long time ago! In 1860, a scientist named Joseph Swan made the first carbon fibers. He used them inside light bulbs. Later, in 1879, Thomas Edison also made carbon fibers for his light bulbs. He did this by baking cotton threads or bamboo until they turned into carbon. In 1880, Lewis Latimer improved this idea, creating a more reliable carbon wire for light bulbs.
In 1958, Roger Bacon made high-performance carbon fibers. He did this by heating strands of rayon until they became carbon. This method wasn't very efficient, as the fibers were only about 20% carbon.
Then, in the early 1960s, a Japanese scientist named Dr. Akio Shindo found a better way. He used a material called polyacrylonitrile (PAN). This new method created carbon fibers that were about 55% carbon. Around the same time, Richard Millington also developed a way to make very high-carbon fibers (99% carbon) from rayon. These fibers were strong enough to be used in new, super-strong, lightweight materials.
A big step forward happened in 1963 in the UK. Scientists W. Watt, L. N. Phillips, and W. Johnson developed a process that showed the amazing strength carbon fiber could have. This led to companies like Rolls-Royce starting to make carbon fiber. Rolls-Royce even used carbon fiber parts in their jet engines! However, these early carbon fiber fan blades had issues, especially with bird strikes.
By the late 1960s, Japan became a leader in making PAN-based carbon fibers. Over time, new types of carbon fiber yarns were developed. These new yarns offered even higher strength and stiffness. Today, carbon fibers from companies like Toray are used in many aerospace parts, from military jets to large passenger planes like those from Boeing and Airbus.
What Are Carbon Fibers Made Of?
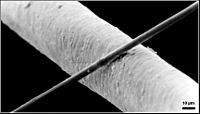
Carbon fiber often comes on a reel, like a spool of thread. It's a continuous bundle of thousands of tiny carbon filaments. These filaments are held together by a special coating that protects them. Each carbon filament is like a tiny cylinder, about 5 to 10 micrometers wide. It's almost entirely made of carbon. Older types of carbon fibers were a bit thicker, around 16 to 22 micrometers. Newer ones are much thinner, about 5 micrometers.
The tiny structure of carbon fiber is similar to graphite. Both are made of carbon atoms arranged in flat sheets, like a honeycomb pattern. In graphite, these sheets are stacked neatly on top of each other. But in carbon fiber, these sheets can be folded or crumpled together in different ways.
Depending on how they are made, carbon fibers can have different internal structures. This affects their properties. Some carbon fibers are super strong, while others are very stiff and good at conducting heat.
What Are Carbon Fibers Used For?
Carbon fiber can be more expensive than other materials. For example, it might cost 10 to 12 times more than steel for car parts. But this cost has come down a lot over the years.
Making Strong Composites
Carbon fiber is most famous for making composite materials. These are often called "carbon fiber reinforced polymers." This means carbon fibers are mixed with plastics to make super strong and light parts. Carbon fiber can also be mixed with other materials, not just plastics. For example, it's used with graphite to make materials that can handle extremely high temperatures.
Carbon fiber is also used in filters for hot gases. It can be used as an electrode because it has a large surface area and resists corrosion. It's also used in anti-static parts. A thin layer of carbon fibers can even make plastics more resistant to fire because it reflects heat very well.
Because carbon fiber is so strong and light, it's replacing aluminum in some aircraft parts. However, carbon fiber can cause a problem called "galvanic corrosion" if it touches certain metals. This means the metal can start to rust faster. So, a special sealant is used to keep the carbon fiber and metal apart.
Carbon fiber can even be added to asphalt to make roads that conduct electricity! This special asphalt can be used for airport runways. By running electricity through the carbon fibers, the road can heat up and melt ice and snow. This helps prevent flight delays in winter.
Carbon Fiber Fabrics
Carbon fibers are made from materials like polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or petroleum pitch. These materials are called "precursors." The carbon fiber threads can be used directly in many ways. They can be woven into fabrics, wound around shapes, or braided.
Carbon fiber yarn is measured by its weight per length or by how many filaments (tiny threads) it has. For example, a yarn with 3,000 filaments is three times stronger than one with 1,000 filaments, but it's also three times heavier. These threads can then be woven into carbon fiber fabric. The look of the fabric depends on the yarn's thickness and the type of weave used, like twill or plain weave.
Tiny Electrodes
Carbon fibers are also used to make very tiny microelectrodes. These are like super small sensors. A single carbon fiber, about 5 to 7 micrometers wide, is sealed inside a glass tube. These tiny electrodes are used in science to detect chemical signals, especially in biological studies.
Flexible Heating Elements
Even though carbon fibers are known for conducting electricity, a single fiber can only carry a small current. But when many carbon fibers are woven into a fabric, they can be used to create flexible heating elements. They can easily reach temperatures above 100°C (212°F). You can see this in DIY heated jackets or blankets. Because carbon fiber doesn't react with many chemicals, it's safe to use with most fabrics. However, if the material folds and causes a short circuit, it can get too hot and might cause a fire.
How Carbon Fibers Are Made
Each carbon fiber is made from a special starting material called a "precursor." Common precursors are polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, or petroleum pitch.
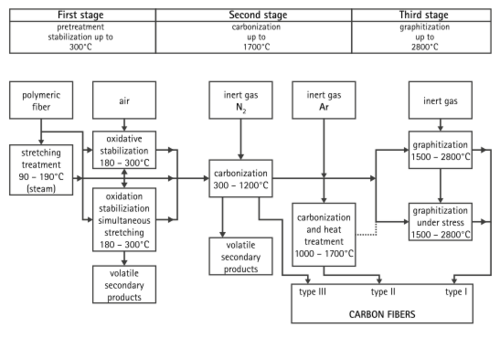
For materials like PAN or rayon, the precursor is first spun into long, thin threads. Special chemical and mechanical steps are used to line up the molecules in these threads. This helps make the final carbon fiber very strong. Different manufacturers might use slightly different methods.
After spinning, these threads are heated to very high temperatures. This process removes all the non-carbon atoms, leaving behind pure carbon fiber. The carbon fiber threads might then be treated further to make them easier to handle, and then they are wound onto spools.
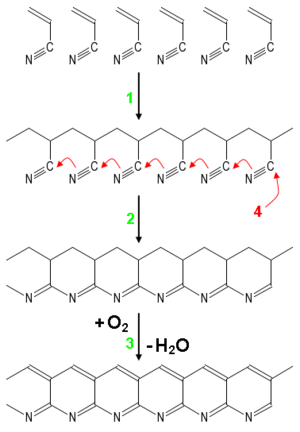
A common way to make carbon fiber is to heat the spun PAN threads to about 300°C (572°F) in air. This changes the material. Then, the oxidized PAN is put into a furnace with a gas like argon and heated to about 2000°C (3632°F). This intense heat changes the molecular structure, turning it into graphite. If heated correctly, the carbon chains link together, forming thin sheets that eventually merge into a single, strong fiber. The result is usually 93–95% carbon.
Lower-quality fibers can be made using pitch or rayon instead of PAN. The carbon can be made even stronger or stiffer by heating it to different temperatures. For example, heating carbon between 1500–2000°C makes it super strong. Heating it even higher, from 2500 to 3000°C, makes it very stiff.
See also
- Basalt fiber
- Carbon fiber reinforced polymer
- Carbon fiber reinforced ceramic material
- Carbon nanotube
- ESD materials
- Graphene
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |