Graphene facts for kids
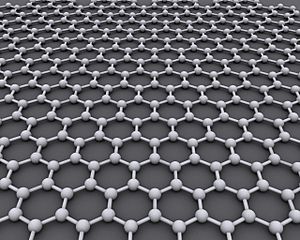
Graphene is a special form of carbon. Think of it like a super-thin sheet, only one atom thick! Carbon can exist in different forms, called allotropes, like diamonds and graphite. Each form has a unique structure, which gives it different qualities. Graphene is the basic, two-dimensional (2D) building block for many three-dimensional (3D) carbon forms, such as graphite, charcoal, fullerenes, and carbon nanotubes.
The name graphene was created by combining "graphite" and the ending "-ene." This name was first used by Hanns-Peter Boehm in 1962 when he described single layers of carbon. Graphene looks like a honeycomb or "chicken wire" pattern, made from carbon atoms and their connections. Imagine stacking many graphene sheets together, and you get graphite!
To give you an idea of how thin graphene is: if you stacked three million graphene sheets on top of each other, they would only be one millimetre thick.
In 2010, Sir Andre Geim and Sir Konstantin Novoselov won the Nobel Prize in Physics. They received it for their amazing experiments with graphene, which showed the world how useful this two-dimensional material could be.
Graphene is a very exciting material. It could be used in many new technologies, like super-fast supercapacitors.
Contents
Amazing Uses for Graphene
Graphene Oxide Membranes
Scientists from the University of Manchester created a special membrane using graphene oxide. They discovered something incredible: this membrane could block many gases and liquids, but it let water pass right through! Sir Andre Geim explained how strange this was: "Helium gas is hard to stop. It slowly leaks even through a millimetre-thick window glass but our ultra-thin films completely block it. At the same time, water evaporates through them unimpeded. Materials cannot behave any stranger." This means graphene could be used for advanced filters or even new ways to clean water.
Graphene for Protection
Another exciting idea is using graphene to make strong, protective materials. Research shows that a single layer of graphene, which is only one atom thick, can absorb a hit better than steel! This suggests that combining graphene with other materials could create new, super-strong composites. These could be used for things like bulletproof vests or stronger sports equipment.
Graphene Batteries
Graphene is also being explored for new types of batteries. These batteries could be much better than the ones we use today.
How Graphene Batteries Work
A graphene battery works a lot like a regular lithium-ion battery. It has two parts called electrodes and a special liquid called an electrolyte that helps electricity flow. The main difference is that in graphene batteries, one of the electrodes (usually the negative one, called the cathode) uses a special mix of metal and graphene. This makes it different from the solid metal used in standard batteries.
Benefits of Graphene Batteries
Graphene batteries offer some big advantages:
Smaller and Thinner Devices
Since graphene is only one atom thick, it's incredibly thin. Remember, three million layers of graphene are only 1 mm thick! This means that batteries made with graphene could be much smaller and thinner. Imagine smartphones that are super slim, or devices that have more space for other cool electronics or even bigger batteries inside.
More Power in the Same Size
Graphene batteries can store a lot more energy than lithium-ion batteries of the same size. While lithium-ion batteries can store about 180 watt-hours per kilogram, graphene-based batteries might store up to 1,000 watt-hours per kilogram! This means your devices could last much longer on a single charge.
Super Fast Charging
Graphene is excellent at conducting electricity. Its unique honeycomb structure lets electrons flow through it very easily, almost without any resistance. Because of this, graphene batteries can charge much faster than traditional batteries. They can also last longer before needing to be replaced.
Graphene Patents
Because graphene is so useful, many companies and countries are trying to get patents for ways to use it. A patent protects an invention, so others can't copy it without permission. In 2013, here's how many graphene patents different places had:
- Chinese groups: 2,204
- US groups: 1,754
- South Korean groups: 1,160
- United Kingdom groups: 54
The electronics company Samsung from South Korea has the most graphene patents of any single company.
Images for kids
-
A lump of graphite, a graphene transistor, and a tape dispenser. Donated to the Nobel Museum in Stockholm by Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov in 2010.
-
Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov at the Nobel Laureate press conference, Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, 2010.
See also
 In Spanish: Grafeno para niños
In Spanish: Grafeno para niños