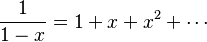Carl Neumann facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Carl Neumann
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | 7 May 1832 Königsberg, Prussia
|
| Died | 27 March 1925 (aged 92) |
| Nationality | German |
| Alma mater | Königsberg University Halle |
| Known for | Neumann boundary condition Neumann series Neumann–Poincaré operator Neumann polynomial |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | integral equations |
| Institutions | University of Halle-Wittenberg University of Basel University of Tübingen University of Leipzig. |
| Thesis | De problemate quodam mechanico, quod ad primam classem integralium ultraellipticorum revocatur |
| Doctoral advisor | Friedrich Richelot and Otto Hesse |
| Doctoral students | William Edward Story Emil Weyr |
Carl Gottfried Neumann (sometimes spelled Karl) was an important German mathematician. He was born on May 7, 1832, and passed away on March 27, 1925. He is famous for his work in mathematics, especially in areas that are closely connected to physics.
Contents
Carl Neumann's Early Life and Studies
Carl Neumann was born in a city called Königsberg in Prussia. His father, Franz Ernst Neumann, was also a well-known scientist. He was a professor who taught about minerals, physics, and mathematics at Königsberg University.
Carl followed in his father's footsteps. He studied physics with his dad in Königsberg. Later, he became a professor at several universities, including Halle, Basel, Tübingen, and Leipzig.
How Physics Inspired His Math Work
Even though Carl Neumann became a mathematician, he was always interested in problems that came from physics. He was inspired by the work of another famous scientist, Bernhard Riemann, who studied how electricity and magnetism work.
Neumann developed his own ideas about how electric and magnetic forces travel. His theories caught the attention of other important scientists like Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Clausius. They even wrote letters to him to discuss his ideas.
At the University of Leipzig, Neumann taught "higher mechanics," which was a fancy way of saying mathematical physics. Even James Clerk Maxwell, another very famous scientist who developed important theories about light and electromagnetism, mentioned Neumann's work in his own writings.
Key Ideas and Contributions
Carl Neumann worked on something called the Dirichlet's principle. This work helped start a whole new area of mathematics called the theory of integral equations. These equations are used to solve many problems in science and engineering.
One of his most famous contributions is called the Neumann series. This is a special kind of mathematical series that looks a bit like a simple geometric series you might learn in school:
But the Neumann series works for more complex things, like very large tables of numbers called matrices or for special mathematical operations called bounded operators.
Neumann also helped start an important math magazine called Mathematische Annalen with another mathematician named Alfred Clebsch. This magazine is still published today and shares new discoveries in mathematics.
Another important concept named after him is the Neumann boundary condition. This is a rule used in certain types of equations, especially those that describe how things change over space and time, like heat spreading or waves moving.
See also
 In Spanish: Carl Gottfried Neumann para niños
In Spanish: Carl Gottfried Neumann para niños
Images for kids