Central limit theorem facts for kids
The Central Limit Theorem, often called the CLT, is a really important idea in probability theory and statistics. It helps us understand what happens when you add up or average a lot of random things.
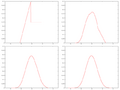
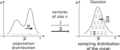
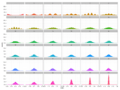
Imagine you have many different random numbers. The CLT says that if you add them all up, or find their average, the way these sums or averages behave will usually look like a special bell-shaped curve. This curve is called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. This happens even if the original random numbers don't follow that bell shape at all!
This theorem is especially useful when the random numbers you're adding or averaging have a "finite variance." This means their spread isn't infinitely wide. Because of this, the normal distribution is often called "normal" because it shows up so often in real life.
The most famous version of the Central Limit Theorem talks about many random things that all have the same average and the same amount of spread.
To be more specific, let's say you have a bunch of random numbers, like 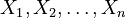 . If these numbers are all independent (meaning one doesn't affect the others) and come from the same type of distribution, and they have an average (called the mean) of
. If these numbers are all independent (meaning one doesn't affect the others) and come from the same type of distribution, and they have an average (called the mean) of 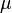 and a spread (called the standard deviation) of
and a spread (called the standard deviation) of 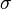 :
:
- If you take the average of these numbers,
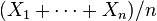 , as you get more and more numbers (as n gets large), this average will tend to follow a normal distribution. Its own average will be
, as you get more and more numbers (as n gets large), this average will tend to follow a normal distribution. Its own average will be 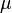 , and its spread will be
, and its spread will be 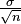 .
. - Also, if you just add them all up,
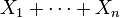 , as n gets large, this sum will also tend to follow a normal distribution. Its average will be
, as n gets large, this sum will also tend to follow a normal distribution. Its average will be 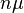 , and its spread will be
, and its spread will be 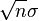 .
.
There are also more advanced versions of this theorem. Some of these don't require all the random numbers to be exactly the same. But they do need to make sure that no single random number has too much influence on the final result compared to the others. Examples of these conditions are the Lindeberg and Lyapunov conditions.
The name "Central Limit Theorem" comes from a paper written by George Pólya in 1920. Its title was About the Central Limit Theorem in Probability Theory and the Moment problem.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Teorema del límite central para niños
In Spanish: Teorema del límite central para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |