Coast mole facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Coast mole |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Eulipotyphla |
| Family: | Talpidae |
| Genus: | Scapanus |
| Species: |
S. orarius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Scapanus orarius (True, 1896)
|
|
 |
|
| Coast Mole range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
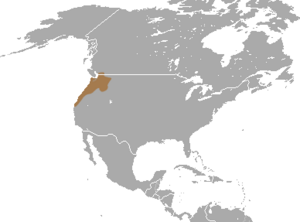
The coast mole or Pacific mole (Scapanus orarius) is a medium-sized mole that lives in North America. You can find them in forests and open areas. They prefer moist soil along the Pacific coast. Their home stretches from southwestern British Columbia in Canada down to northwestern California in the United States.
Contents
What is a Coast Mole?
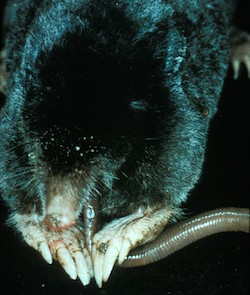
Coast moles are usually less than 200 mm (about 8 inches) long. Their tail makes up about one-fourth of their total length. Their fur is completely black. They have a narrow, long skull. Their teeth are smooth and spaced out evenly.
Where Do Coast Moles Live?
Coast moles live in different places, not just one continuous area. You can find them from western British Columbia, Canada, through western Oregon and Washington. They also live in some parts of Northern California, especially near the coast. Sometimes, they even reach parts of west-central Idaho.
These moles mostly live underground. This is called a fossorial lifestyle. However, they don't stay underground all the time. They can come to the surface to look for food. Young moles also come up to find new places to live, especially in the summer.
Coast moles can live in many different places. These include farms, sand dunes, grassy fields, and areas with sagebrush. They also live in forests with different types of trees. These include deciduous forests (trees that lose their leaves) and pine forests. You might find them among yellow-pine, Douglas fir, spruce, hemlock, and redwood trees.
How Do Coast Moles Live?
What Do Coast Moles Eat?
Coast moles eat invertebrates, which are animals without backbones. Their favorite food is earthworms. They also eat slugs and insect eggs. They hunt for these foods in soil that is a bit damp. If they sense more earthworms in an area, they will dig more there.
How Do Coast Moles Behave?
Coast moles are usually alone. They only spend time with other moles during mating season. You'll find more moles and their tunnels in places with damp soil. These areas also tend to have lots of earthworms.
Coast moles are mostly active at night. This is called being nocturnal. However, they don't stick to a specific time during the night. Each mole seems to have its own schedule. Their activities don't always match what their neighbors are doing.
How Do Coast Moles Reproduce?
Mating usually happens between late January and early March. During this time, moles stop being solitary. They start making their tunnels bigger. They might even go into other moles' tunnels to find a partner.
Scientists don't know much about how long they are pregnant or how they care for their babies. Female moles have only one group of babies each year. The mother mole doesn't care for her young for very long. Young coast moles can have their own babies when they are about nine to ten months old.
How Do Coast Moles Adapt to Underground Life?
Coast moles use their noses a lot to sense what's around them underground. Their nose has a special part called Eimer's organ. This organ has many nerves. It helps the mole feel and tell the difference between things. This is how they find food in the dark tunnels. It helps them know what they are touching even without seeing it.
The air in mole tunnels can be low in oxygen. It can also have more carbon dioxide from their breathing. Moles have special ways to deal with this. One way is having more blood. This helps them store more oxygen. They also have a special type of hemoglobin in their blood. Hemoglobin helps carry oxygen. This special hemoglobin works well even in the cold tunnels.
Are Coast Moles Endangered?
The IUCN has classified the coast mole as a Least Concern species. This means they are not considered endangered. They are common in many different places across their range.


