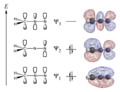Conjugated system facts for kids
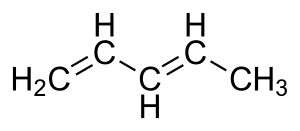
A conjugated system is a special arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Imagine atoms holding hands in a line. Usually, they hold hands tightly with one other atom. But in a conjugated system, some electrons don't just belong to two atoms; they are shared among many atoms. This happens when there are several "multiple bonds" (like double or triple bonds) separated by "single bonds" (where atoms hold hands just once).
Think of it like a superhighway for electrons! These shared electrons are called delocalized electrons. Because these electrons can move freely over a larger area, the molecule becomes more stable and can have unique properties. For example, many colorful things around us, like the colors in plants, have conjugated systems.
Contents
How Conjugated Systems Work
For a conjugated system to form, all the atoms next to each other in a chain must have a special kind of space for electrons called a p-orbital. These p-orbitals line up and overlap, creating a pathway for electrons to spread out.
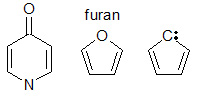
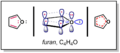
Most often, you'll see a pattern of single bond, then double bond, then single bond, and so on. But other arrangements can also create conjugation. For example, in a molecule called furan, there's a ring of atoms. An oxygen atom in this ring has extra electrons (called a lone pair) that can join the electron superhighway, making the whole ring conjugated. Other groups of atoms, like those found in carbonyl (C=O) or imine (C=N) groups, can also help create these systems.
Why Conjugated Systems are Colorful
Conjugated systems are the main parts of molecules called chromophores. A chromophore is the part of a molecule that absorbs light and makes a compound appear colored.
Think about how a rainbow works: different colors of light have different energies. Chromophores absorb specific colors of light, and the colors we see are the ones that are *not* absorbed but reflected or transmitted. The more extended a conjugated system is (meaning the more atoms share electrons), the lower the energy of light it can absorb. This often means they absorb visible light, making the molecule colorful.
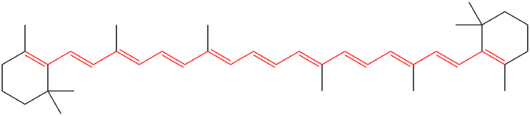
Many natural colors, like the orange in carrots, come from molecules with long conjugated systems. These molecules often have rings of atoms and many double bonds.
Common Examples
Here are some everyday examples of molecules that have conjugated systems:
- Dienes: These are molecules with two double bonds.
- Vitamin D: Important for healthy bones.
- Vitamin A: Good for your eyes.
- Benzene: A common chemical building block.
- Conjugated linoleic acid: A type of fat found in some foods.
Related pages
- Resonance (chemistry)
- Hyperconjugation
- Cross-conjugation
- Polyene
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema conjugado para niños
In Spanish: Sistema conjugado para niños