Diene facts for kids
In organic chemistry, a diene is a special type of hydrocarbon. Hydrocarbons are chemicals made mostly of hydrogen and carbon. What makes a diene special is that it has two double bonds between carbon atoms. You can also call them diolefins. Dienes are often found in nature and are very important for making polymers, which are used to create many plastics and rubbers.
Types of Dienes
Dienes can be sorted into three main types. This depends on where their two double bonds are located:
- Cumulated dienes have their double bonds right next to each other, sharing one carbon atom. A good example of this type is a group of chemicals called allenes.
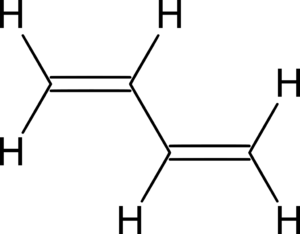
- Conjugated dienes have their double bonds separated by just one single bond. This arrangement makes them quite stable and useful in reactions.
- Unconjugated dienes have their double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. These are usually not as stable as conjugated dienes.
Chemicals that have more than two double bonds are called polyenes. Dienes and polyenes share many similar properties.
How Dienes Are Used
Conjugated dienes are especially important in chemistry. They are used in a special type of chemical reaction called the Diels–Alder reaction. This reaction helps chemists create complex natural products. For example, specific dienes like Danishefsky’s diene were created to make these reactions easier.
Images for kids
-
Some dienes: A: 1,2-Propadiene, also known as allene, is the simplest cumulated diene. B: Isoprene, also known as 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is used to make natural rubber. C: 1,3-Butadiene is used to make synthetic polymers. D: 1,5-Cyclooctadiene is an unconjugated diene (its double bonds are far apart). E: Norbornadiene is another unconjugated diene. F: Dicyclopentadiene. G: Linoleic acid is a type of fat needed in the human diet.
See also
 In Spanish: Dieno para niños
In Spanish: Dieno para niños