Cinnamaldehyde facts for kids
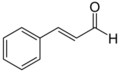
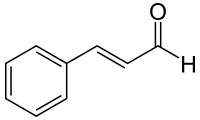
Cinnamaldehyde is a special chemical that gives cinnamon its yummy flavor and strong odor. It's what makes cinnamon smell and taste like cinnamon! This pale yellow, thick liquid is found naturally in the bark of cinnamon trees. It's also in other plants from the Cinnamomum family.
Did you know that the essential oil from cinnamon bark is almost 90% cinnamaldehyde? This amazing compound is made naturally by plants through a process called the shikimate pathway. Sometimes, if not stored well, cinnamaldehyde can break down into a substance called styrene. This is why you might find tiny amounts of styrene in cinnamon.
Quick facts for kids Cinnamaldehyde |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-Phenylprop-2-enal
|
|
| Other names |
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil |
| Odor | Pungent, cinnamon-like |
| Density | 1.0497 g/mL |
| Melting point | |
| Boiling point | |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Solubility |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Contents
How Cinnamaldehyde is Made
Cinnamaldehyde was first found in cinnamon essential oil in 1834 by two scientists, Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot. Later, in 1854, another scientist named Luigi Chiozza was able to make it in a lab.
How Plants Make It
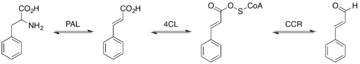
Plants make cinnamaldehyde starting from a building block called phenylalanine. This process involves several steps. First, phenylalanine is changed into cinnamic acid. Then, cinnamic acid is turned into another compound called cinnamoyl-CoA. Finally, cinnamoyl-CoA is changed into cinnamaldehyde. This whole process is like a chemical assembly line inside the plant!
Making it in the Lab
While there are ways to make cinnamaldehyde in a lab, the easiest and cheapest way is to get it from cinnamon bark. This is done using a process called steam distillation. It's like steaming the bark to collect its essential oil, which is full of cinnamaldehyde.
One way to make it in the lab is by mixing benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde. This method was even patented in 1950!
What Cinnamaldehyde is Used For
Cinnamaldehyde has many cool uses, especially because of its strong flavor and smell.
Flavor and Scent
The most common use for cinnamaldehyde is as a flavoring! You can find it in chewing gum, ice cream, candy, and beverages. It's also used in some perfumes to give them a natural, sweet, or fruity scent.
Sometimes, it's used to make other smells like almond, apricot, or butterscotch. It's important to know that some people have tried to trick buyers by adding cinnamaldehyde to powdered beechnut husk and selling it as real powdered cinnamon.
Helping Plants and Animals
Cinnamaldehyde has been tested as a safe way to fight mosquito larvae. Just a small amount can kill half of certain mosquito larvae in 24 hours. It also works as a strong fumigant and a good repellent for adult mosquitoes. This chemical also has properties that can fight against bacteria and fungi.
Other Uses
Cinnamaldehyde can even help stop steel and other metals from rusting. It's thought to form a protective layer on the metal surface, keeping it safe.
Related Chemicals
Many chemicals that are similar to cinnamaldehyde are used in different products. For example, dihydrocinnamyl alcohol, which smells like hyacinth and lilac, is made from cinnamaldehyde. Cinnamyl alcohol, which also smells like lilac, can also be made from cinnamaldehyde.
Other important scents like α-amylcinnamaldehyde and α-hexylcinnamaldehyde are also related, but they are not made directly from cinnamaldehyde.
Safety and Your Body
Cinnamaldehyde is generally considered to have low toxicity, which is why it's used in agriculture. However, it can sometimes irritate your skin. Some people might have an allergic reaction if it touches their skin or mouth, but this is not very common.
Scientists have also found that cinnamaldehyde might help protect your DNA. It seems to help repair damage to DNA in cells, which can reduce unwanted changes or "mutations." Studies in mice showed that cinnamaldehyde could help reduce chromosome damage after X-ray exposure, possibly by helping with DNA repair.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cinamaldehído para niños
In Spanish: Cinamaldehído para niños