DNA repair facts for kids
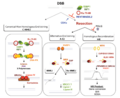
DNA repair is like a special clean-up crew inside your body's cells. It's a set of processes that helps cells find and fix any damage to their DNA molecules.
Think of DNA as the instruction manual for your body. Every day, this manual can get tiny errors or damage. This happens because of normal things your body does, like using energy, or from outside factors like UV light from the sun or certain types of radiation. There can be up to a million tiny problems in a single cell's DNA every day!
Many of these problems can mess up the DNA's structure. This can stop the cell from reading its instructions correctly, which means it can't make the proteins it needs. Other problems can lead to harmful changes called mutations. These mutations can affect how well new cells work when the original cell divides. That's why DNA repair has to be working all the time, ready to fix issues quickly.
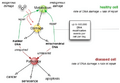
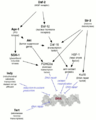
If a cell has too much DNA damage, or if its repair system isn't working well, it can go into one of three states:
- It might go into a sleep-like state called senescence, where it stops dividing.
- It might decide to "self-destruct" in a process called apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- It might start dividing out of control, which can lead to a tumor and potentially cancer.
Contents
What is DNA Repair?
The speed at which DNA repair happens depends on many things. These include the type of cell, how old the cell is, and what's happening around the cell. Scientists have found that many genes that seem to affect how long an organism lives are actually involved in fixing and protecting DNA.
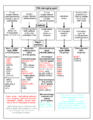
DNA Damage vs. Mutations
It's important to understand that DNA damage and mutations are different, even though they are related.
Understanding DNA Damage
DNA damage refers to physical problems with the DNA molecule. Imagine a ladder that's been broken or twisted. Examples include breaks in one or both strands of the DNA ladder.
- Cells have special enzymes (tiny workers) that can spot these physical damages.
- Because they can be recognized, these damages can often be fixed. The repair process usually uses the undamaged part of the DNA as a guide.
- If DNA damage isn't fixed, the cell might not be able to read its instructions, stopping it from making important proteins. The cell might even die.
Understanding DNA Mutations
A mutation is a change in the actual "letters" (bases) of the DNA code. Imagine if a word in your instruction manual was spelled wrong.
- Once a mutation is present in both strands of the DNA, the cell's enzymes can't tell that it's wrong. So, mutations usually can't be repaired.
- Mutations can change how proteins work or how they are controlled.
- When a cell with a mutation divides, the mutation is copied into the new cells. Over time, cells with helpful mutations might become more common, while cells with harmful ones might decrease.
How They Are Connected
Even though they are different, DNA damage and mutations are linked. DNA damage often causes mistakes when the cell copies its DNA or tries to repair it. These mistakes are a main source of mutations.
- In cells that divide often, DNA damage leading to mutations is a big reason why cancer can develop.
- In cells that don't divide often, DNA damage is thought to be a major cause of aging.
Nobel Prize Discoveries in DNA Repair
In 2015, three scientists won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for their amazing discoveries about DNA repair. Each of them found a different part of this important process.
Tomas Lindahl's Discovery
Tomas Lindahl, from Sweden and working in the UK, discovered a repair method called "base excision repair." This process helps to fix DNA that is breaking down naturally.
Aziz Sancar's Discovery
Turkish-born Aziz Sancar, a professor in the US, found another type of DNA repair called "nucleotide excision repair." This method fixes larger types of DNA damage.
Paul Modrich's Discovery
American scientist Paul Modrich, working at Duke University, showed how cells fix mistakes that happen when DNA is copied during cell division. This process, called "mismatch repair," makes copying DNA much more accurate, reducing errors by a thousand times!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Reparación del ADN para niños
In Spanish: Reparación del ADN para niños