Crash (computing) facts for kids
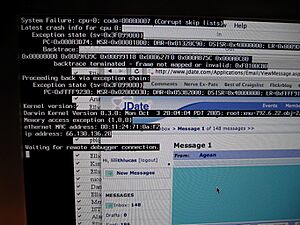
In computing, a crash happens when a computer program, like an app or the main operating system (OS), suddenly stops working correctly and shuts down. Sometimes, a special service will report the crash details to the people who made the program. If the program that crashes is a very important part of the operating system, the whole computer might stop working or freeze. This is often called a kernel panic or a fatal system error.
Most computer crashes happen because of a problem in the program's code, called a software bug. Imagine a bug as a tiny mistake in the instructions the computer follows. Common reasons for crashes include the program trying to use parts of the computer's memory it's not allowed to, or trying to do something that doesn't make sense to the computer. Finding these bugs and fixing them is called debugging.
Sometimes, a crash can even be used by a bad program or a hacker to take control of your computer or steal information. This is why keeping your software updated is important!
Contents
When Apps Stop Working

An app usually crashes when it tries to do something the operating system won't allow. The operating system then sends a special signal to the app. On many computers, like those running Windows or macOS, a message box might pop up, asking if you want to send a report about the crash. Some apps try to fix themselves and keep running, but most just close.
Apps can also be programmed to crash on purpose if they find a very serious error.
Here are some common reasons why an app might crash:
- Trying to read or write information in a part of the computer's memory that the app isn't allowed to use.
- Trying to follow instructions that are not allowed or don't exist.
- Trying to control hardware (like a printer or camera) without permission.
- Giving wrong information to the operating system when asking it to do something.
- Trying to use other computer resources without permission.
- Trying to do math problems that are impossible, like dividing by zero.
What is a "Crash to Desktop"?
A "crash to desktop" (CTD) happens when a program, often a video game, suddenly closes and takes you back to your computer's desktop screen. Usually, no error message appears, so all you see is your desktop.
Sometimes, a CTD happens without any clear reason. The program might freeze for a moment, then just close. Other times, the screen might go black, and you might hear the last few seconds of sound repeat before it crashes. It can also happen when you try to load a new area in a game.
CTD bugs can be tricky because they don't give error messages, making it hard to figure out what went wrong. Running games in a smaller window instead of full-screen can sometimes help track down the problem.
When Websites Crash
The software that runs a web server (the computer that hosts a website) can also crash. When this happens, you might not be able to access the website at all, or you might only see an error message instead of the usual content.
For example, if a website uses a SQL database (a special way to store information) and that database crashes, the website might show an error saying it can't connect.
When the Whole System Crashes
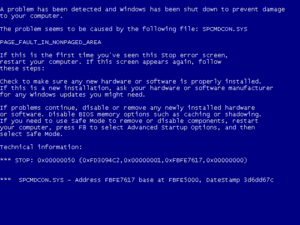
An operating system crash happens when the computer's main software (the OS) runs into a problem it can't fix. This can also happen if the OS realizes something is wrong with its own internal workings.
Modern operating systems, like Linux and macOS, are usually designed so that if one app crashes, the rest of the system keeps working fine. However, if a very important part of the OS itself crashes, the whole computer might stop.
Some very advanced operating systems, like z/OS, have special features that allow them to recover even if a critical part crashes, whether it's due to a hardware problem or a software bug.
How Do Crashes Affect Security?
When a program crashes, it might sometimes expose your private information. Also, many software bugs that cause crashes can be used by hackers to run their own harmful code on your computer. For example, a bug might cause a program to crash, but a clever hacker could use that same bug to make the computer do something else instead, like install a virus. This is why it's important for software developers to fix these bugs quickly.
See also
 In Spanish: Crash (informática) para niños
In Spanish: Crash (informática) para niños


