Tiger rattlesnake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tiger rattlesnake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Crotalus
|
| Species: |
tigris
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
The tiger rattlesnake (Crotalus tigris) is a very venomous pit viper. You can find this snake in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It gets its name tigris from Latin, meaning "tiger." This is because of the many narrow bands on its back. These bands look like stripes when you see the snake from the side.
Contents
Meet the Tiger Rattlesnake
Robert Kennicott first described the tiger rattlesnake in 1859. People often call it the tiger rattlesnake or tiger rattler.
What Does It Look Like?
The tiger rattlesnake is easy to spot because of its small, spade-shaped head. Its head is about 1/25 of its total body length. It actually has the smallest head of any rattlesnake. It also has a large rattle at the end of its tail.
The snake's body color can be gray, lavender, blue-gray, pink, or buff. This color often changes to pink, pale orange, or cream on its sides. Tiger rattlesnakes are special because they are the only rattlesnakes with bands across the front part of their bodies. They have about 35 to 52 gray, olive, or brown bands on their backs. These bands are wider on the top and become darker and clearer towards the tail.
They also have six to 10 rings near their tail. The marks on their head are usually not very clear. However, they often have a dark stripe on their cheek, which helps identify them.
These snakes are not very big. They can weigh up to 454 grams (16 ounces). Their length can be from 46 to 91 centimeters (18 to 36 inches). The average length is about 61 centimeters (24 inches). The longest one ever found was about 91.2 centimeters (35.9 inches) long.
Female snakes usually have 164 to 177 scales on their belly, while males have 158 to 172. Males also have more scales under their tail (23 to 27) compared to females (16 to 21). Males are typically larger than females. Tiger rattlesnakes have small eyes with pupils shaped like slits.
Where Do They Live?
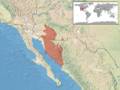
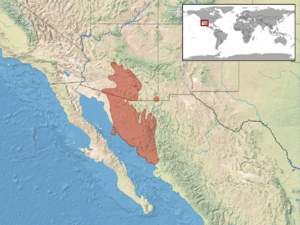
You can find these snakes from central Arizona south through south-central Arizona in the United States. Their range extends into southern Sonora, Mexico. This includes Tiburón Island in the Gulf of California. They were also recently found in the southern Peloncillo Mountains of Arizona.
Tiger rattlesnakes live in rocky desert canyons, foothills, and flat areas at the base of mountains. They can be found from sea level up to about 1,465 meters (4,800 feet) high.
Their homes include areas with thorny bushes, saguaro cacti, mesquite trees, and grasslands. In southeastern Arizona, they stay in rocky places during winter and spring. But in summer, they use the edges of dry riverbeds. They usually stay on the ground, but they can climb into low bushes.
These snakes are often seen in rocky canyons and ravines in deserts. They live at elevations from 300 to 1,500 meters (1,000 to 5,000 feet). They also like cliffs and rocky outcrops in thorny desert areas.
How Do They Behave?
Tiger rattlesnakes are snakes that live on the ground. They are active at night during the hot summer months (June to August). But in the fall, they become active during the day and at dusk or dawn. They sleep through the late fall and winter in rock cracks or animal burrows. Even though they live on the ground, they can swim easily. They have even been found in bushes about 60 centimeters (2 feet) above the ground.
Like other pit vipers, tiger rattlesnakes have special heat-sensing pits. These are located on each side of their face, between the eye and nostril. They use these pits to find warm-blooded animals, like prey or predators.
These snakes are not active when it's very cold (December/January) or extremely hot (July/August). They might be active both day and night. During the day, they often bask in the sun on cooler days. They are also often seen moving around after warm rains. In southeastern Arizona, they are mainly active from March to October.
What Do They Eat?
Tiger rattlesnakes mostly eat small mammals, like rodents. But they also eat lizards. They often wait quietly to ambush their prey. They also actively hunt for small rodents and lizards. Young snakes eat more lizards, while adult snakes eat more rodents.
These small rattlesnakes can eat surprisingly large prey. This includes kangaroo rats, deer mice, packrats, and even spiny lizards.
Their venom is considered one of the most powerful of all rattlesnakes. It contains a special toxin that can damage muscles and another toxin that affects nerves. Like all pit vipers, they inject venom into their prey using long, hollow fangs that can fold back. If a bitten animal crawls into a small crack, the tiger rattlesnake's small head helps it reach and pull out the prey.
Who Are Their Predators?
There isn't much information about specific animals that hunt tiger rattlesnakes. However, common predators likely include hawks, eagles, coyotes, and other snakes. Their natural colors help them blend in with their surroundings. This camouflage helps them hide from animals that might try to eat them.
If disturbed, they shake their rattles quickly. They might also strike to defend themselves. Tiger rattlesnakes are known to be easily annoyed and can be quite aggressive if they feel threatened.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Tiger rattlesnakes are polygynandrous. This means both males and females can have more than one mate during a single breeding season. Not much else is known about how they reproduce. Their breeding habits are thought to be similar to other rattlesnakes like the Western diamondback rattlesnake and Crotalus scutulatus.
Female tiger rattlesnakes have babies every two years. Males can reproduce every year. Breeding happens from late May to mid-August, during the summer rainy season. Like most rattlesnakes, tiger rattlesnakes give birth to live young. They usually have about five babies at a time. The smallest female known to have babies was about 54.1 centimeters (21.3 inches) long. The smallest male able to reproduce was about 51.2 centimeters (20.2 inches) long.
Female rattlesnakes don't take care of their babies much after they are born. However, during pregnancy, the mother snake finds a safe place to hide. She makes sure the babies inside her stay at the right temperature to grow.
How They Grow
Tiger rattlesnake babies grow inside the mother in a clear, thin sac. They get food and fluids from a yolk sac. When they are born, the babies break out of this sac. They then travel a short distance to a safe spot with their brothers and sisters.
Young tiger rattlesnakes are not born with a rattle. Instead, they have a small skin cap on the tip of their tail. After each time they shed their skin, a new rattle segment is added. Since they give birth to live young, the babies are well-developed when they are born.
Conservation Status
The tiger rattlesnake is listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. This means they are not currently in danger of disappearing. They are listed this way because they are found over a wide area. Their population is thought to be large, and it's not declining quickly enough to be considered threatened. In 2007, their population was stable.
Population Size
The number of tiger rattlesnakes is considered stable. Experts have found them in about 100 different places. The exact number of adult snakes is not known, but it is likely more than 10,000. This snake is quite common in some areas, but some local groups seem small. Overall, their numbers are probably stable or decreasing very slowly.
Threats to Their Home
In some flatter areas of Sonora, Mexico, their homes might be shrinking because of more farming. However, overall, this snake is not facing serious threats.
Why Are They Important?
Things to Be Careful About
Even though tiger rattlesnakes don't often strike, they are very venomous and can be easily upset. This means they can be a danger to humans. Their venom contains toxins that can damage muscles and nerves. While they don't produce a lot of venom, it is one of the most powerful venoms of any snake in the Western Hemisphere. The mix of toxins in their venom makes them very dangerous to people.
If a person is bitten, there might not be much pain or swelling at first. But even with a small amount of venom, a bite from this snake is a serious medical emergency. It's important to get medical help quickly if someone is bitten.
Good Things About Them
Rattlesnake skin and rattles are sometimes sold as souvenirs in the American Southwest. Rattlesnake venom is also used in medical research to study brain diseases.
Tiger rattlesnakes also help control the number of small rodents that humans might see as pests. They eat many small animals and help keep their populations balanced in nature.
Images for kids
Crotalus tigris at the TIGR Reptile Database. Accessed 12 December 2007.