Damping facts for kids
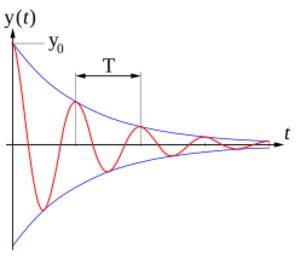
In physics, damping is when something slows down or reduces the size of a vibration or oscillation. Imagine a swing slowing down after you stop pushing it. The way it slows down and eventually stops is called damping.
When something vibrates, like a guitar string or a spring, it moves back and forth. The biggest distance it moves from its center is called its amplitude. Damping makes this amplitude smaller and smaller until the vibration stops.
In mechanics, one common reason for damping is friction. Friction is a force that works against motion. For example, when a spring bounces, the air around it creates friction, and the parts of the spring rubbing against each other also create friction. These forces make the spring's bounces get smaller and smaller.
Contents
What is Damping?
Damping is like a brake for vibrations. It takes away energy from a vibrating system. Without damping, things would just keep vibrating forever once they start!
How Damping Works
Damping often happens because of forces that resist movement. The faster something moves, the stronger these damping forces can be. For example, if you try to move your hand quickly through water, you feel a lot of resistance. This resistance is a form of damping.
A special number called the damping coefficient helps scientists measure how much damping there is. A higher damping coefficient means more damping and faster slowing down of vibrations.
Everyday Examples of Damping
Damping is all around us, even if we don't always notice it.
- Car Shock Absorbers: These are very important parts of a car's suspension. When your car goes over a bump, the springs in the suspension absorb the shock. But without damping, your car would bounce up and down many times. Shock absorbers use oil to create friction, which quickly stops the bouncing and makes your ride smooth.
- Door Closers: Have you ever seen a door that slowly closes by itself? That's thanks to a damping mechanism inside the door closer. It uses oil or air to control how fast the door shuts, preventing it from slamming.
- Musical Instruments: When you pluck a guitar string, it vibrates and makes sound. But the sound doesn't last forever. The air around the string and the way the string is attached to the guitar body create damping, which makes the sound fade away.
- Tall Buildings: In places with earthquakes or strong winds, tall buildings sometimes have special devices called tuned mass dampers. These are huge weights designed to move in a way that reduces the swaying of the building, making it safer and more comfortable for people inside.
Related topics
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Amortiguamiento para niños
In Spanish: Amortiguamiento para niños