Data Center Cooling facts for kids
Data cooling is super important for places called data centers. Think of a data center as a giant room filled with many powerful computers. These computers work hard and get very hot, just like your laptop might get warm after playing a game.
As computers get smaller but use lots of power, they make even more heat. If this heat isn't removed, the computers can overheat and stop working. So, data cooling is all about moving this extra heat out of the data center and into the outside air.
Special sensors help keep an eye on the temperature inside. They check the airflow and find any "hot spots" where it's too warm. This helps people know if the cooling system is doing its job well.
Machines like a Computer Room Air Conditioning (CRAC) unit help control the temperature and how much moisture (humidity) is in the air. CRAC units use a cooling system like a refrigerator. Another machine, called a Computer Room Air Handler (CRAH), uses fans and cool water to take heat away.
How We Cool Data Centers
The main goal of cooling is to move heat from inside the data center to the outside. There are two main ways to do this: using air or using liquid, usually water.
Air Cooling
Air cooling is a popular method. It's easy to move air around, and it doesn't usually harm computer equipment. Heat naturally moves from warmer places to cooler places. Also, warm air rises, and cold air sinks. Computer makers often use these facts when designing cooling systems.
One common air cooling system is called "room-based cooling." This is like a giant air conditioner. It blows cold air into the room and pulls warm air out. It also mixes the air to prevent any parts of the room from getting too hot. This works well if the computers don't produce too much heat.
Hot and Cold Aisles
Imagine rows of computer racks in a data center. In a hot/cold aisle setup, the front of one row of computers faces the front of the next row. This creates "cold aisles" where cold air is blown in. The back of the computers, where hot air comes out, faces the back of the next row, creating "hot aisles."
Sometimes, walls or ceilings are added to keep the cold air in the cold aisles. This is called "cold aisle containment." Or, they might contain the hot air in the hot aisles. This helps the cooling machines only get hot air, making them work better. This setup helps save energy and money by controlling how air moves.
Blanking Panels
If there are empty spaces in a computer rack, hot air can sneak through them. This mixes with the cold air and makes the cooling less effective. Blanking panels are like covers that fill these empty spots. They stop hot air from moving where it shouldn't, making the cooling system more efficient.
Rack Placement
The very top of a computer rack often gets the hottest. To help with cooling, engineers can arrange the computer parts inside the racks. They place the equipment that works the hardest (and gets hottest) lower down in the rack. This helps spread the heat out better and keeps the top of the rack from getting too hot.
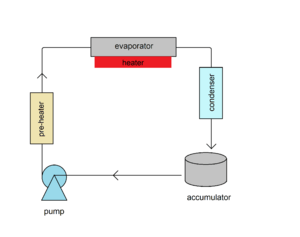
Free Cooling
Free cooling uses air or water from outside to help cool the data center.
- Air-side economization uses cool air from the outside environment. This is cheap because you're just using natural air. But sometimes, outside air can bring in too much moisture, which isn't good for computers.
- Water-side economization also uses outside air, often with evaporation, to cool water that then cools the data center.
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling can be very good at cooling specific parts of a data center. For example, chilled water can be sent directly to a rack of servers. This is helpful because you can cool exactly where the heat is being made. Instead of cooling a whole room, you cool just the hot spots.
However, using liquids near computers has risks. Leaks could damage expensive equipment. Also, cold liquid can cause condensation (water droplets) if it touches warmer surfaces. Liquid cooling systems also need more special equipment. Because of these reasons, liquid cooling can be more expensive and harder to set up than air cooling, even though it's often more effective.
Single Phase Cooling
In single phase liquid cooling, cool liquids like water are pumped right up to the hot parts of the computers. Special "cold plates" are placed very close to the parts that make heat. Liquids are much better at carrying heat away than air. This means single phase cooling can save a lot of energy. Sometimes, it can even remove the need for CRAC units.
One downside is that it needs powerful pumps to move the liquid. Also, tiny living things (microbes) can grow in the liquid. The liquids can also conduct electricity or wear away parts over time.
Two-phase Cooled Systems
Two-phase cooling is a very clever way to cool computers. It uses special liquids that turn into vapor (a gas) when they touch hot computer parts. This change from liquid to gas is called a phase transition. This process is super efficient at taking heat away. It means you need much less cooling liquid compared to single phase cooling.
Studies have shown that two-phase systems can use less liquid, less pumping power, and need smaller cooling facilities. These systems often use tiny channels, called mini or microchannels, to maximize the surface area for cooling. Microchannels are great at transferring heat but can get clogged or corroded more easily.
Other Cooling Options
There are many different ways to cool data centers. The best choice depends on the size and type of the data center.
Airflow Direction
Cooling systems can blow air in different directions. Some large systems on the floor blow air downwards. Others blow air upwards or even sideways. This helps direct the cold air exactly where it's needed.
Fire, Smoke, and Water Detection
These devices are very important for safety. They work with computer monitoring systems to give early warnings. They can even automatically shut down equipment if there's a fire, smoke, or water leak.
Humidifiers
A humidifier adds moisture to the air. In data centers, humidifiers can help prevent static electricity. Static electricity can damage computers. Humidifiers are often placed inside cooling machines to replace moisture lost during the cooling process. They make sure the air isn't too dry or too wet.
Reheat Systems
Sometimes, to remove a lot of moisture from the air, cooling systems might add heat back to the cold air. This helps the system dehumidify the room more effectively. This method is usually used in places with humid climates.
Economizer Coils
Using economizer coils can save a lot of money on operating costs. This method uses a special liquid, like diol, to cool the data center. It works in a similar way to a chilled water system.
Why Cooling Matters So Much
Data center technology is very advanced and uses a lot of energy. That's why it's so important for data centers to be as energy-efficient as possible. Good cooling is a big part of this.
Experts suggest that data centers should be kept between 21°C and 24°C (about 70°F to 75°F). Some studies even show that keeping the temperature below 21°C might cost more money than it's worth. Computer parts like processors can usually handle temperatures up to 85°C (185°F), while hard drives can work up to 45°C (113°F).
Regular air conditioning for a normal room handles a small amount of heat. But data centers deal with huge amounts of heat! Modern data centers can produce 6 to 10 times more heat per square meter than a typical room. This amount is expected to grow even more in the future.
Companies like Google say it's vital to save energy in data centers. They note that many computer makers design equipment to work well at temperatures higher than the usual 21°C. This means future computers might be able to run hotter. If data centers can run at higher temperatures, they might need less cooling equipment, which saves money.
The best way to manage cooling is to measure how much energy is used for it. Also, it's always a good idea to ask the equipment manufacturer for their advice.
Many experts believe that using a mix of different cooling methods works best. The location of a data center also plays a big role. Building data centers in cooler places or near cold water sources can greatly increase energy efficiency and save costs. This is because they can use the natural cold from the outside environment.
Images for kids