Deadly nightshade facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Deadly nightshade |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Atropa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Atropa belladonna |
|

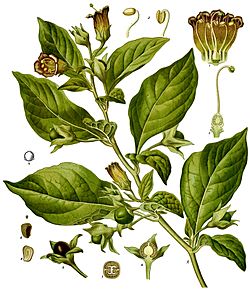
The Deadly nightshade or belladonna (Atropa belladonna) is a famous and tough plant. It is a perennial shrub, meaning it lives for many years. This plant belongs to the nightshade family.
It first grew in Europe, North Africa, and Asia. You can also find it in North America, but it is not as common there. Deadly nightshade usually grows in shade, as it does not like direct sunlight. It often prefers places where the soil has a lot of limestone.
Contents
Why Deadly Nightshade Is Dangerous
Most parts of the deadly nightshade plant are very poisonous. Even a small amount can be harmful. For example, eating just three berries has been enough to cause death in children. One leaf can contain enough poison to kill an adult. The root of the plant usually has the most poison.
The main poison found in this plant is called atropine. This substance is very powerful.
How Belladonna Affects the Body
If someone is poisoned by atropine, they might experience several effects. Their pupils (the black centers of their eyes) will become very big. They might also have hallucinations, seeing or hearing things that are not real. Their vision may become blurry, making it hard to focus.
Other signs include trouble standing straight or feeling confused. The person's heart will beat faster and faster. They might also get a fever or a rash on their head, neck, and upper body. It can be hard for them to speak or swallow. In serious cases, a person might become unresponsive or have seizures before death.
Images for kids
-
A belladonna plaster, Hunterian Museum, Glasgow
See also
 In Spanish: Belladona para niños
In Spanish: Belladona para niños

















