Root facts for kids


The roots of a plant are usually the parts hidden underground in the soil. But sometimes, roots can grow above the ground! These are called aerial roots.
It's good to know that roots are different from stems. For example, potatoes grow underground, but they are actually stems, not roots. Roots also don't have leaves.
Plants need their roots for three very important jobs:
- Roots soak up water and nutrients (like plant food) from the soil.
- They often store this food for the plant to use later.
- They help to hold the plant firmly in the ground, so it doesn't fall over.
Most plant roots work even better when they get help from tiny fungi. This helpful team-up between roots and fungi is called mycorrhiza.
There are two main types of root systems:
- Taproot system: This has one big, strong root that grows deep into the ground, with many smaller roots branching off it.
- Diffuse root system: This has many roots that spread out in all directions, without one main root.
Some roots can grow incredibly deep. One root found in Arizona, USA, reached 60 meters (about 200 feet) below the surface! Roots are also very strong. Some tree roots can even break stones. Roots are not green because their cells don't have chlorophyll, which is the green stuff that helps plants make food using sunlight.
Contents
How Roots Grow
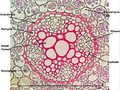
Roots grow throughout the plant's entire life. They get longer by adding new cells to their tips. Imagine a tiny cap at the very end of each root. This is called the root cap.
The root cap is made of tough, dead cells. It's like a shield that protects the delicate root tip as it pushes through the dirt. Its job is to help the root find moisture and nutrients in the soil. Roots also grow thicker as they add cells around their tube-like bodies.
Aerial Roots
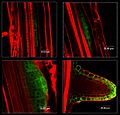
Aerial root Roots are usually underground, but some plants have roots that grow in the air. In a rainforest, the air is warm and humid (full of water). Some rainforest plants, called epiphytes, grow right on other trees. Their roots hang down in the air or grow into the moss on the trees. Many aerial roots can take in water and nutrients directly from the air, like from fog or dew.
Some trees have roots both above and below the ground. For example, Mangrove trees have aerial roots that stick up into the air. These special roots help the tree breathe gases from the atmosphere, just like leaves do. This is a special way they've adapted to grow in wet, muddy soil that doesn't have much oxygen.
The banyan tree is another amazing example. It has roots underground, but it also grows roots from its branches that hang down to the ground. These roots not only take in water and nutrients from the soil, but they also help support the banyan tree's very long branches. Because of this extra support, banyan tree branches can spread out incredibly far. One banyan tree in Lahaina, Maui, planted in 1873, has branches so long that the single tree covers a whole city block!
Scientists are still learning a lot about aerial roots.
Types of Root Systems
There are two main types of root systems: taproot systems and fibrous root systems.
A taproot system has one thick main root that grows straight down from the plant's stem. Many smaller secondary roots branch off this main root. A taproot system is usually deeper than it is wide. We often eat taproots, like carrots and turnips.
A fibrous root system has many roots that grow in all directions, like a tangled mess. There isn't one main root. A fibrous root system is usually wider than it is deep.
Roots as Food and Other Uses
Many plants have edible roots that we eat. These are often called root crops. Some examples of edible roots include cassava, sweet potato, beet, carrot, rutabaga, turnip, parsnip, radish, yam, and horseradish.
Roots are also used for other things:
- Sugar beets are a major source of sugar.
- Some roots are used to make medicines, like ginseng.
- Certain tree roots, like those of the bald cypress, are carved into art or souvenirs.
- Native Americans used the flexible roots of white spruce for making baskets.
Roots can also protect the environment. They hold the soil together, which helps to stop landslides on slopes and reduces soil erosion, especially in places like sand dunes. This is because the tiny root hairs act like anchors in the soil.
Sometimes, tree roots can cause problems. They can lift and damage concrete sidewalks or block buried pipes. The aerial roots of strangler fig trees have even damaged ancient Mayan temples in Central America and the famous temple of Angkor Wat in Cambodia.
Images for kids
-
Primary and secondary roots in a cotton plant
-
Root system of adult Araucaria heterophylla
-
The cross-section of a barley root
-
Tree roots at Cliffs of the Neuse State Park
-
Aerating roots of a mangrove
-
Cross section of a mango tree
-
Ficus Tree with buttress roots
See also
 In Spanish: Raíz (botánica) para niños
In Spanish: Raíz (botánica) para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |