Chlorophyll facts for kids
Chlorophyll is a special green substance found in plants and tiny living things called algae. It helps them make their own food using energy from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis.
Think of chlorophyll as a plant's personal solar panel. It captures sunlight, and this energy is then used to create a type of sugar called glucose. This sugar is like food for the plant, giving it lots of stored energy. Plants use this energy to grow, repair themselves, and stay healthy. Chlorophyll is also what makes plant stems and leaves look green!
Contents
- What is Chlorophyll?
- History of Chlorophyll Discovery
- How Chlorophyll Helps with Photosynthesis
- The Chemical Structure of Chlorophyll
- Measuring Chlorophyll Content
- How Chlorophyll is Made: Biosynthesis
- Chlorophyll and Plant Aging (Senescence)
- Where Chlorophyll is Found: Distribution
- How Chlorophyll is Used by People
- Fun Facts About Chlorophyll
- Related pages
- Images for kids
- See also
What is Chlorophyll?
Imagine you are a plant that needs to eat to grow big and strong. Plants cannot go to a grocery store! Instead, they have a special ingredient called chlorophyll. This ingredient helps them make their own food using sunlight.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment. A pigment is a substance that gives color to things. You can find chlorophyll in the green parts of plants, like their leaves and stems. It is also in tiny organisms called algae and cyanobacteria.
The word "chlorophyll" comes from two old Greek words. "Khloros" means "pale green," and "phyllon" means "leaf." So, chlorophyll is basically the "green stuff in leaves"!
History of Chlorophyll Discovery
People have been studying chlorophyll for a long time. Here is a quick look at how we learned about it:
- 1817: Two French scientists, Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier, were the first to find and name chlorophyll.
- 1906: Scientists discovered that chlorophyll contains magnesium. This was the first time anyone had found magnesium in living tissue!
- 1905-1915: A German chemist named Richard Willstätter spent many years studying chlorophyll. He worked to figure out its exact structure.
- 1940: Another scientist, Hans Fischer, figured out the general structure of chlorophyll a. This is one of the main types of chlorophyll.
- 1960: Robert Burns Woodward published a complete way to create the molecule in a lab.
- 2010: Scientists discovered a new type of chlorophyll called chlorophyll f. They found it in cyanobacteria and other tiny organisms.
How Chlorophyll Helps with Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll's main job is to help plants make food. This happens through a process called photosynthesis. "Photo" means light, and "synthesis" means putting things together. So, photosynthesis is like using light to put things together!
Here is how it works:
- Capturing Sunlight: Chlorophyll molecules are arranged in special structures. These structures are called photosystems. They are found inside plant cells, in tiny parts called chloroplasts. Photosystems are like tiny antennas that capture sunlight.
- Transferring Energy: Once chlorophyll captures sunlight, it moves that energy. It transfers it to a special pair of chlorophyll molecules. These are in the "reaction center" of the photosystem.
- Making Power: The special chlorophyll pair uses the energy to separate tiny particles. These particles are called protons (H+) and electrons (e-). These particles then power the rest of the photosynthesis process.
There are two main types of photosystems: photosystem I and photosystem II. Each has its own reaction center. They are called P700 and P680. These names come from the wavelength of light they absorb best.
Photosynthesis is super important for life on Earth. It is how plants make their own food (sugars). It also releases oxygen into the air. Oxygen is what we breathe, so we can thank chlorophyll for helping us stay alive!
The Chemical Structure of Chlorophyll
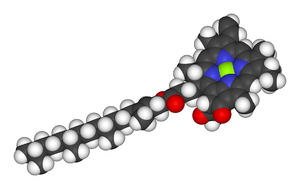
Chlorophyll is a complex molecule. It has a special structure that allows it to absorb light. All chlorophyll molecules are based on a structure called chlorin. This is similar to a molecule called porphyrin. Porphyrin is found in hemoglobin, which makes our blood red.
Most chlorophyll molecules have a magnesium atom in their center. This atom is very important for how they work. They also have different parts attached to the chlorin ring. One of these is a long chain called a phytyl chain.
There are several different types of chlorophyll. These include:
- Chlorophyll a: This is the most common type of chlorophyll in plants.
- Chlorophyll b: This type helps plants absorb a wider range of light colors.
- Chlorophyll e: This pigment has been found in algae.
- 8-vinyl Chl a and b: These are used by a type of cyanobacterium called Prochlorococcus.
The different types of chlorophyll have slightly different structures. This means they absorb light at slightly different wavelengths. This helps plants capture as much sunlight as possible.
Measuring Chlorophyll Content
Scientists can measure how much chlorophyll is in a plant. One way is to extract it using special liquids called organic solvents. They can also separate chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b to see how much of each type is present.
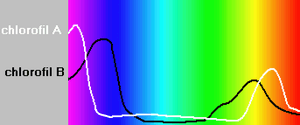
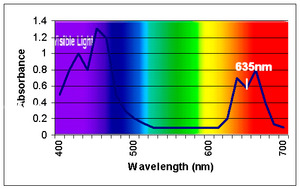
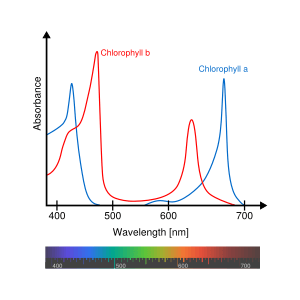
A machine called a spectrophotometer can measure chlorophyll. This machine measures how much light a substance absorbs. Chlorophyll a absorbs light best at wavelengths around 430 nm and 662 nm. Chlorophyll b absorbs light best at wavelengths around 453 nm and 642 nm.
Scientists can also use fluorescence to measure chlorophyll. Fluorescence is when a substance emits light after absorbing it. Chlorophyll a glows (emits light) at a wavelength of 673 nm.
There are also special sensors that can measure chlorophyll content. They do this by measuring how much light passes through plant leaves. These sensors allow scientists to measure chlorophyll quickly and without harming the plant.
How Chlorophyll is Made: Biosynthesis
Chlorophyll is made through a complex process called biosynthesis. In plants, chlorophyll is made from a substance called glutamate.
Making chlorophyll involves many steps. It also needs several different enzymes. Enzymes are like tiny helpers that speed up chemical reactions. One key enzyme is chlorophyll synthase. This enzyme adds a phytyl chain to another molecule called chlorophyllide a to make chlorophyll a.
The later steps in making chlorophyll depend on light in some plants. This means they only happen when there is light. Plants grown in the dark will look pale because they cannot make chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll and Plant Aging (Senescence)
Senescence is the process of aging in plants. During senescence, chlorophyll starts to break down. This is why leaves change color in the fall. The green color disappears, and other colors become visible.
An enzyme called chlorophyllase breaks down chlorophyll. It does this by removing the phytyl sidechain. The broken-down products of chlorophyll are called nonfluorescent chlorophyll catabolites (NCC's). These compounds are colorless. They help give fruits and leaves their bright autumn colors.
Where Chlorophyll is Found: Distribution
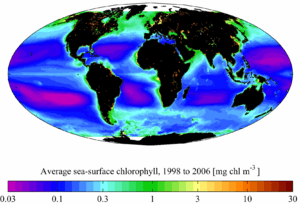
Chlorophyll is found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria all over the world. NASA has created maps showing the amount of chlorophyll in the ocean. These maps show that the highest amounts of chlorophyll are found in cold polar waters. They are also found in areas where ocean currents bring cold water to the surface.
The cold water itself does not directly help the phytoplankton (tiny ocean plants). Instead, cold temperatures often mean that water has risen from deeper in the ocean. This deeper water carries nutrients that have built up over time. In polar waters, nutrients gather in surface waters during the dark winter months. During this time, plants cannot grow. When sunlight returns in the spring and summer, the plants grow very well because of these nutrients.
How Chlorophyll is Used by People
Chlorophyll has a few different uses for humans:
- Food Coloring: Chlorophyll is used as a food coloring. It gives foods and drinks a green color. It is known by the E number E140.
- Marketing: In the past, chlorophyll was used in marketing. It was promoted in products like toothpaste and soap. However, these claims were later found to not be true.
Fun Facts About Chlorophyll
- Chlorophyll absorbs light most strongly in the blue and red parts of the light spectrum.
- Chlorophyll does not absorb green light very well. Instead, it reflects green light. This is why plants appear green to our eyes.
- Chlorophyll is essential for life on Earth. It is how plants make their own food and release oxygen into the atmosphere for us to breathe.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Clorofila para niños
In Spanish: Clorofila para niños