Acceleration facts for kids
Acceleration is a measure of how fast velocity changes. It tells you how quickly an object's speed or direction of movement is changing. Acceleration is a vector, which means it has both a size (how much it changes) and a direction.
To understand acceleration, it's helpful to know the difference between speed and velocity:
- Speed (a scalar quantity)
* Speed tells you how fast something is going. * You can find speed by dividing the distance traveled by the time it took. * Example: A car going 60 kilometers per hour.
- Velocity (a vector quantity)
* Velocity tells you how fast something is moving and in what direction. * You can find velocity by dividing the displacement (change in position with direction) by the time it took. * Example: A car going 60 kilometers per hour north.
The measurement of how fast acceleration changes is called jerk.
Contents
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration happens when an object:
- Speeds up
- Slows down
- Changes direction
Here are some examples of acceleration:
- Imagine a car going north at 10 meters per second. If it speeds up to 17 meters per second, it has accelerated.
- When an apple falls, it starts at 0 meters per second. After one second, it's moving at 9.8 meters per second. It has accelerated due to gravity. After another second, it's even faster, showing it accelerated again.
- If Jane is walking east at 3 kilometers per hour and keeps that exact speed and direction, her acceleration is zero.
- Tom was walking east at 3 kilometers per hour. If Tom turns and walks south at 3 kilometers per hour, he has accelerated because his direction changed.
- Sally was walking east at 3 kilometers per hour. If Sally slows down to 1.5 kilometers per hour, she has accelerated because her speed changed.
How to Find Acceleration
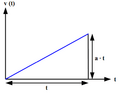
Acceleration is the rate at which an object's velocity changes. You can find acceleration using a simple formula:
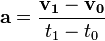
In this formula:
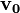 is the velocity at the beginning.
is the velocity at the beginning.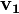 is the velocity at the end.
is the velocity at the end.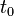 is the time at the beginning.
is the time at the beginning.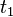 is the time at the end.
is the time at the end.
Sometimes, the change in velocity ( ) is written as Δ
) is written as Δ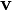 (delta v). The change in time (
(delta v). The change in time (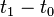 ) is written as Δt (delta t).
) is written as Δt (delta t).
Units of Measurement
Acceleration has its own units. If velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s) and time in seconds (s), then acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s2). This means how many meters per second the speed changes, every second.
Deceleration
When acceleration is negative, it means an object is slowing down. This is sometimes called deceleration. For example, when a car uses its brakes, it is decelerating. However, scientists often just use the word "acceleration" for both speeding up and slowing down.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
Isaac Newton was a famous scientist who wrote down important rules about how things move. These are called "laws of motion".
According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the force needed to accelerate an object depends on two things:
- The object's mass (how much "stuff" it's made of, or how "heavy" it is).
- The acceleration you want to give it.
The formula for Newton's Second Law of Motion is: 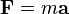
Here:
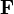 is the force applied.
is the force applied.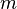 is the mass of the object.
is the mass of the object.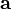 is the acceleration.
is the acceleration.
This formula is very important in physics and is often one of the first things students learn about motion.
Images for kids
-
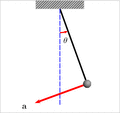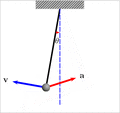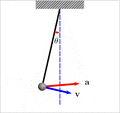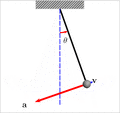
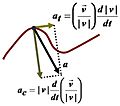
Components of acceleration for a curved motion. The tangential component at is due to the change in speed of traversal, and points along the curve in the direction of the velocity vector (or in the opposite direction). The normal component (also called centripetal component for circular motion) ac is due to the change in direction of the velocity vector and is normal to the trajectory, pointing toward the center of curvature of the path.
See also
 In Spanish: Aceleración para niños
In Spanish: Aceleración para niños