Delta-v facts for kids
Delta-v, also written as Δv, is a term used in astrodynamics. This is the science of how spacecraft move in space. Delta-v literally means "change in speed." It measures how much "pushing power" a spacecraft needs to change its path or speed in space.
Think of it like this: if you want to change how fast your bike is going, or turn a corner, you need to use effort. For a spacecraft, Delta-v tells us how much effort is needed to change its trajectory (its path) or speed.
Most of the time, this pushing power comes from a rocket engine. The engine burns propellant (fuel) to create thrust, which is the force that moves the spacecraft.
Delta-v is measured in meters per second (m/s). This tells us how much the speed of the spacecraft can change.
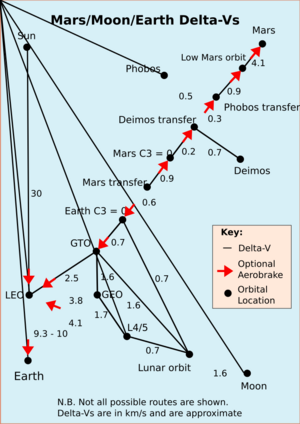
For example, to reach Low Earth orbit (LEO), where many satellites orbit our planet, a spacecraft usually needs about 9,300 to 10,000 m/s of Delta-v. This is a huge change in speed!
Contents
What is Delta-v?
Delta-v is a very important idea for planning space missions. It helps scientists and engineers figure out how much fuel a rocket needs. Every time a spacecraft fires its engines to speed up, slow down, or change direction, it uses up some of its Delta-v budget.
Why is Delta-v Important?
- Fuel Planning: Delta-v tells engineers how much fuel a rocket needs to carry. More Delta-v means more fuel, which makes the rocket heavier and more expensive to launch.
- Mission Design: It helps decide if a mission is even possible. If the needed Delta-v is too high, the mission might not be able to carry enough fuel.
- Maneuvers: Every time a spacecraft adjusts its orbit, avoids space junk, or prepares to land on another planet, it uses Delta-v.
How is Delta-v Calculated?
The amount of Delta-v a rocket can produce depends on two main things:
- The type of engine: Some engines are more efficient than others.
- The amount of fuel: More fuel means more thrust for a longer time, which means more Delta-v.
Scientists use special equations to calculate the exact Delta-v needed for different parts of a space journey. These calculations help them design rockets that can reach their goals.
Delta-v for Space Travel
Traveling through space requires a lot of Delta-v. Here are some examples:
Reaching Orbit
To get from Earth's surface into Low Earth orbit (LEO), a rocket needs a lot of Delta-v. This is because it has to fight against Earth's strong gravity and gain a lot of speed to stay in orbit.
Traveling to the Moon
Once a spacecraft is in LEO, it needs more Delta-v to break free from Earth's gravity and travel to the Moon. It then needs more Delta-v to slow down and enter orbit around the Moon, or to land on its surface.
Journeys to Other Planets
Going to planets like Mars requires even more Delta-v. The spacecraft needs enough speed to travel across vast distances in the Solar System. When it gets close to Mars, it might use the planet's atmosphere to slow down (this is called aerobraking) or fire its engines again to enter orbit or land.
See also
 In Spanish: Delta-v para niños
In Spanish: Delta-v para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |