Fungi imperfecti facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fungi imperfecti |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
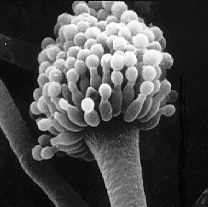
| The spore-making part (conidiophore) of an Aspergillus fungus. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Species | |
|
See below. |
|
Imperfect fungi are a unique and mysterious group of fungi. Scientists call them "imperfect" because they have a missing piece in their life story: no one has ever seen them reproduce sexually. Instead, they only seem to make copies of themselves, which is called asexual reproduction.
Because of this, they were very difficult to classify for a long time. This group, once called Deuteromycota, includes about 25,000 species. You might be surprised to learn that some of the most famous fungi in the world are in this group. This includes the fungus that gives us the antibiotic penicillin, as well as the fungi that cause athlete's foot. They are also used to make cheeses like Roquefort and Camembert cheese.
Contents
Why Are They So Hard to Classify?
Imagine trying to build a family tree, but you only have information about the children, not the parents. That was the problem scientists faced with imperfect fungi. Most fungi are sorted into scientific groups based on the special parts they use for sexual reproduction. Since imperfect fungi don't show these parts, they didn't fit into the normal classification system.
An Old, Confusing System
For many years, scientists used a special "two-name" system for these fungi. This was allowed by the official rules for naming fungi.
- A fungus might have a "form name" for its asexual stage (the only stage scientists could see).
- If scientists later discovered its sexual stage, it would get a different, "official" name.
For example, the mold Aspergillus niger has no known sexual cycle, so it was known by its form name. But its close relative, Aspergillus nidulans, was discovered to have a sexual stage. This sexual stage was named Emericella nidulans. This meant the same fungus could have two different names, which was very confusing!
To fix this, scientists updated the rules in 2011. Now, each fungus has only one official scientific name, which makes things much clearer.
Using DNA to Solve the Fungi Mystery
Today, scientists have a powerful tool to solve the puzzle of the imperfect fungi: molecular systematics. This means they study the DNA of the fungi to see who their closest relatives are. It's like a DNA test that builds an accurate family tree for fungi.
Using DNA analysis, scientists have been able to place many imperfect fungi into their proper groups in the fungal kingdom, usually with the Ascomycota or Basidiomycota phyla. This shows that "imperfect fungi" are not one single related group. Instead, they are a collection of different fungi that all happened to lose (or hide) their ability to reproduce sexually.
However, the work isn't finished. For many species, it's still hard to get enough pure DNA to study. So, the mystery of where they belong in the tree of life continues.
Famous Fungi from the "Imperfect" Group
Many of these fungi play a huge role in our world, for both good and bad.
Helpful Fungi
- Medicine: Tolypocladium inflatum produces a drug called ciclosporin, which is very important for patients who have had organ transplants.
- Food Production:
- Species of Penicillium are key to making cheeses. Penicillium roqueforti creates the blue veins in Roquefort cheese, and Penicillium camemberti gives Camembert its soft rind.
- Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus sojae are used in Asia to ferment soybeans to make soy sauce and miso.
- Pest Control: Some fungi, like Beauveria and Metarhizium, are used by farmers as a natural way to control insect pests on crops.
Harmful Fungi
- Plant Disease: Magnaporthe oryzae is a serious pest that infects and destroys rice crops, which are a major food source for billions of people.
- Human Health: Some well-known fungi that can make people sick were once classified here. This includes the fungus that causes the itchy skin condition athlete's foot and species of Candida that can cause yeast infections.
Why Did They Stop Reproducing Sexually?
Scientists think there are a few reasons why these fungi only reproduce asexually.
- Genetic Changes: Over time, some fungi may have had mutations, or changes in their DNA, that disabled the genes needed for sexual reproduction.
- A Faster Life: In some situations, reproducing asexually is an advantage. It allows a fungus to grow and spread much more quickly than if it had to find a partner. This can help it take over a new food source or environment.
Some of these fungi have found clever ways to mix their genes. This is done through a process called the "parasexual cycle," which allows for some genetic variety without true sexual reproduction.
See also
 In Spanish: Hongos imperfectos para niños
In Spanish: Hongos imperfectos para niños
- Forest pathology
- List of mitosporic Ascomycota

