E-mail facts for kids
Electronic mail, often called email, is a way to send and receive messages over the Internet. It's like sending a letter, but it's super fast and usually free! You need an email address (an account) to use it.
Just like regular mail, you might get unwanted messages. For email, these are called spam. Many email programs can help you block spam.
To use email, you need a device like a computer or phone connected to the internet. You also need an email program, sometimes called a "mailer." Your email address helps people find you online. It usually looks like yourname@example.com. Emails are mostly text, but can also include pictures and fancy formatting like a webpage.
Many companies offer free email services you can use from a website. Gmail, Hotmail, and Yahoo! are popular examples of these "Webmail" services. They handle many of the technical steps for you.

Contents
How Email Started
Computer messaging began in the early 1960s, allowing users on the same system to send notes. In 1971, the first message was sent over the ARPANET network. This is when the familiar '@' symbol was first used in email addresses to show a user's system.
Soon, big companies like IBM and Xerox created their own internal email systems in the 1970s. By the mid-1980s, email systems for local computer networks (LANs) also started to appear.
How Traditional Email Works
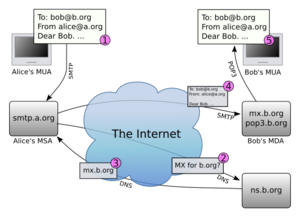
This section explains how email travels from one person to another using the older, traditional method. Imagine Alice is sending an email to Bob.
- First, Alice writes her message to Bob using her email program. This program adds important details like her email address, Bob's address, and the time she sent it. When she clicks "send," her program sends the message to a special computer called a mail server. It uses a set of rules called the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- Alice's mail server (let's call it smtp.a.org) reads Bob's email address. It then searches the internet to find Bob's mail server. It does this by asking a Domain Name System (DNS) server, which is like a phone book for computers on the internet.
- The DNS server tells Alice's mail server the correct address for Bob's mail server (mx.b.org).
- Alice's mail server then sends the message directly to Bob's email server. Bob's server places the message into his digital mailbox.
- Finally, Bob opens his email program. His program downloads new messages from his mailbox using rules like Post Office Protocol (POP) or Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). Now, Bob can read the new message from Alice!
Other Cool Email Features
- Attachments: You can send files like documents, spreadsheets, or photos along with your emails. This is super handy for sharing things!
- CC (Carbon Copy): This lets you send a copy of your email to other people. Everyone can see who received the email.
- BCC (Blind Carbon Copy): This also sends a copy to other people, but it hides their names from the other recipients. It's useful when you don't want everyone to see who else got the email.
Images for kids
-
When a "robot" on Wikipedia makes changes to image files, the uploader receives an email about the changes made.
-
The interface of an email client, Thunderbird.
See also
 In Spanish: Correo electrónico para niños
In Spanish: Correo electrónico para niños
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |