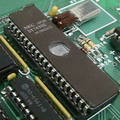
EPROM facts for kids
An EPROM is a special type of computer memory chip. Its name stands for Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. Think of it like a digital notebook that you can write on, read from, and then completely erase to write new information. This is different from a regular programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip, which can only be written once.
Contents
What is an EPROM?
EPROMs are chips used in many electronic devices. They store important information that the device needs to work. The "read-only" part means that once information is put on the chip, it's usually just read by the device. But the "erasable" and "programmable" parts are what make EPROMs special.
How EPROMs Store Information
Inside an EPROM, there are tiny parts called floating-gate transistors. These are like tiny switches that can hold an electric charge. This charge is how the chip stores data, like a "1" or a "0" in computer language. Once a charge is put on these transistors, it stays there for a very long time, even when the power is turned off.
Erasing and Reprogramming
The cool thing about EPROMs is that you can clear all the information on them. To do this, you shine ultraviolet (UV) light on a clear window found on top of the chip. This UV light gives energy to the electrons inside the floating-gate transistors, allowing them to escape. This process clears all the stored data, making the chip blank again.
Once an EPROM is blank, you can program it with new information. This is done using a special device called an EPROM programmer. This device sends electrical signals to the chip, setting the new data into its memory.
EPROM vs. EEPROM
While EPROMs need UV light to be erased, some newer types of memory chips can be cleared using only electricity. These are called EEPROMs, which stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. EEPROMs are more convenient because you don't need a special UV light source to erase them.
Where EPROMs Were Used
EPROMs were very popular in the 1970s and 1980s. They were used in many places, such as:
- Computers: For storing the basic input/output system (BIOS) that helps a computer start up.
- Video game cartridges: To hold the game's program code.
- Industrial control systems: For programming machines in factories.
- Microcontrollers: Small computers on a single chip that control specific tasks.
Today, other types of memory like flash memory have largely replaced EPROMs. Flash memory is even easier to erase and reprogram, and it can store much more data. However, EPROMs were an important step in the development of modern computer memory.
Images for kids
-
An EPROM: the Texas Instruments TMS27C040, a CMOS chip with 4 megabits of storage and 8-bit output (shown here in a 600-mil ceramic dual-in-line package). The TMS27C040 operates at 5 volts, but must be programmed at 13 volts.
-
This 8749 Microcontroller stores its program in internal EPROM
See also
 In Spanish: Memoria EPROM para niños
In Spanish: Memoria EPROM para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |