Egyptian sage facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Egyptian sage |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Salvia |
| Species: |
S. aegyptiaca
|
| Binomial name | |
| Salvia aegyptiaca |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Salvia aegyptiaca, often called Egyptian sage, is a fascinating plant. It's a type of herb that belongs to the Lamiaceae family. This family is famous for many aromatic plants, like mint and lavender. Salvia aegyptiaca was first described by the famous scientist Carl Linnaeus.
Contents
Where Does Egyptian Sage Grow?
Egyptian sage is found in many dry and warm places around the world. You can find it growing in the Cape Verde Islands and the Canary Islands. It also grows across Northwest and North Africa, including countries like Sudan and Ethiopia. Further east, it's found in the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and even India.
What Does Egyptian Sage Look Like?
This plant is a herbaceous type, meaning it doesn't have a woody stem like a tree. Its stems grow upright or slightly angled. The leaves are usually long and narrow, sometimes a bit wrinkled. They often have small teeth along their edges.
When it blooms, Salvia aegyptiaca produces flowers in simple clusters called racemes. Sometimes these clusters can have branches. Small leaf-like structures called bracts are also present near the flowers. The flowers themselves are a beautiful blue-violet color.
Traditional Uses and Science
For a very long time, people in many parts of the world have used Salvia aegyptiaca in traditional medicine. They used it to help with various health issues. For example, it was used to soothe upset stomachs and help with skin problems. It was also thought to help protect wounds and act as a general calming agent for the body.
Scientists have also studied this plant. They found that certain parts of Salvia aegyptiaca can fight against tiny germs. These germs include bacteria like Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, and even a type of fungus called Candida albicans. This means the plant might have properties that help stop the growth of harmful microbes.
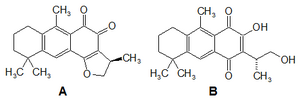
Researchers have also discovered special natural chemicals inside Salvia aegyptiaca. Some of these unique compounds are called aegyptinones A and B. These discoveries help us understand more about how the plant might have been useful in traditional medicine.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Salvia aegyptiaca para niños
In Spanish: Salvia aegyptiaca para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |