Electron transport chain facts for kids
An electron transport chain (ETC) is like a special pathway inside cells. It helps cells get energy. This process happens in two main ways:
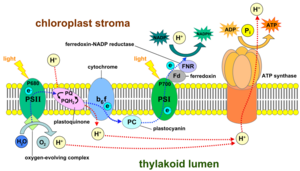
- When plants use sunlight to make food (called photosynthesis).
- When cells break down sugars to get energy (called cellular respiration).
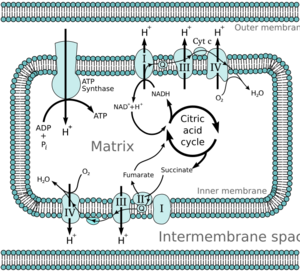
During cellular respiration, especially when cells use oxygen (aerobic respiration), the electron transport chain is super important. From just one molecule of glucose (a type of sugar), the ETC helps make about 34 molecules of ATP. ATP is like the energy currency of the cell. This makes the electron transport chain the most efficient way cells produce energy!
Contents
How Does the Electron Transport Chain Work?
The electron transport chain is a series of steps. Think of it like a relay race for tiny particles called electrons. These electrons move from one molecule to another. Each time an electron moves, a little bit of energy is released.
Building an Energy Gradient
This released energy is used to pump tiny charged particles called protons. These protons are pumped across a membrane inside the cell. This creates a difference in charge and concentration, like building up water behind a dam. Scientists call this an "electrochemical gradient."
Making ATP Energy
This "proton dam" is very important. Another special protein, called ATP synthase, uses the energy from this proton dam. As protons flow back across the membrane through ATP synthase, it spins like a tiny turbine. This spinning motion helps create lots of ATP molecules. ATP is the main form of energy that cells use to do almost everything!
Where Does the ETC Happen?
In animal and human cells, the electron transport chain mostly happens in the mitochondria. These are often called the "powerhouses" of the cell. In plants, the ETC also happens in chloroplasts during photosynthesis.
See also
 In Spanish: Cadena de transporte de electrones para niños
In Spanish: Cadena de transporte de electrones para niños