European conger facts for kids
The European conger (Conger conger) is a very large type of conger eel. It belongs to the family called Congridae. This amazing creature is known as the heaviest eel in the world! You can find it living in the northeast Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Quick facts for kids European conger |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Anguilliformes |
| Family: | Congridae |
| Genus: | Conger |
| Species: |
C. conger
|
| Binomial name | |
| Conger conger (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
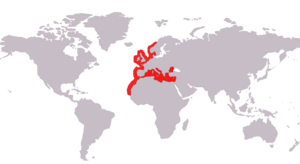
| The Range of the European conger | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Contents
About the European Conger
Size and Appearance
European congers are truly huge eels! On average, adults are about 1.5 meters (5 feet) long. The longest ones ever found were around 2.1 meters (7 feet), but some might even reach 3 meters (10 feet)! They can weigh up to 72 kilograms (159 pounds). This makes them the heaviest eels in the world.
While some moray eels might be longer, congers are much heavier. Most congers caught weigh between 2.5 and 25 kilograms (5.5 to 55 pounds). Female congers grow much larger than males. Females are usually about 2 meters (6.5 feet) long when they are ready to have babies. Males are smaller, around 1.2 meters (4 feet) long.
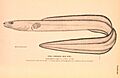
These eels have very long, snake-like bodies with no scales. They are usually grey, but can sometimes look blackish. Their bellies are white. You can see a line of small white spots along their sides. Their heads are shaped like cones, with a rounded snout. They have large gill openings on their sides. Their teeth are cone-shaped and arranged in rows. The fins on their back and belly connect with their tail fin. They have fins near their heads, but no fins on their undersides.
Habits and Hunting
Conger eels behave a lot like moray eels. They usually live in holes or cracks among rocks, which are sometimes called "eel pits." Sometimes, they even share a hole with a moray eel! They are nocturnal, meaning they come out at night to hunt for food.
These night hunters mostly eat fish, cephalopods (like squid and octopus), and crustaceans (like crabs and lobsters). They are also thought to eat dead fish they find. Large congers can be quite powerful, so divers need to be careful around them.
Where Do They Live?
You can find European congers in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Their home range stretches from Norway and Iceland all the way down to Senegal. They also live in the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
They are usually found at depths of 0 to 500 meters (0 to 1,640 feet). However, they might go much deeper, up to 3,600 meters (11,800 feet), when they migrate. Sometimes, you can spot them in very shallow water near the shore. Young congers often stay close to the coast in rocky areas. As they get older, they move to deeper waters.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
When conger eels are between 5 and 15 years old, their bodies go through an amazing change. Their reproductive organs grow bigger, and their bones become lighter. They even lose their teeth! Female congers seem to gain more weight and size during this time than males.
After this change, conger eels travel to special spawning areas in the Mediterranean and Atlantic. Scientists are still trying to figure out if there's one main place where they all go, or many different places. Female conger eels lay millions of eggs. After laying their eggs, both the male and female congers die.
Once the baby congers hatch, they are called larvae. These tiny larvae then swim back to shallower waters. They live there until they grow up and become mature. Then, they migrate to repeat the cycle, just like their parents did.
Gallery
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |