Filamentation facts for kids
For other uses see "Filament".
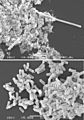
Filamentation is a strange way some bacteria grow. Normally, bacteria cells grow a bit and then split into two new cells. But during filamentation, the cells keep getting longer and longer without splitting! It's like a train car that keeps getting longer instead of new cars forming.
This unusual growth happens when bacteria are under a lot of stress. It's their way of trying to survive tough times.
Contents
What is Bacterial Filamentation?
Imagine a tiny, rod-shaped bacterium. Usually, it grows to a certain size and then divides right in the middle. This creates two new, identical bacteria. This splitting process is called cell division.
But when bacteria undergo filamentation, they skip this important step. Their bodies keep growing longer and longer. They don't form the special wall, called a septum, that usually separates the two new cells. So, instead of many small bacteria, you get one very long, string-like bacterium.
Why Do Bacteria Filament?
Bacteria don't just decide to grow long for fun! Filamentation is often a sign that something is wrong. It's a survival strategy. Here are some common reasons:
- Stress: Just like people, bacteria can get stressed. This stress might come from their environment.
- DNA Damage: Bacteria have DNA, just like us. If their DNA gets damaged, they might stop dividing. This gives them time to fix the damage before making new cells. They have a special system, like a repair crew, called the SOS response. This system helps them fix their DNA.
- Lack of Food: If there isn't enough food, bacteria might not have the energy to divide. So, they just keep growing longer.
- Antibiotics: Some medicines designed to fight bacteria can also cause them to filament. This is because these medicines might damage the bacteria's DNA or stop their cell division process.
How Does Filamentation Help Bacteria?
You might wonder why growing long without dividing is helpful. It's a clever trick!
- Survival: By not dividing, the bacteria can focus all their energy on repairing damage or dealing with the stress. They become tougher and more resistant to harmful things around them.
- Protection: A long, filament-like bacterium might be harder for the body's immune system to attack. It's like a single, large target instead of many small ones.
- Genetic Repair: When DNA is damaged, the cell needs time to fix it. Filamentation buys them that time. Once the DNA is repaired, they can start dividing normally again.
Filamentation shows how adaptable and resilient tiny bacteria can be when faced with challenges!
Images for kids
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |