Flamethrower facts for kids
A flamethrower is a special device that shoots out a stream of fire. People have used tools like flamethrowers in wars for a very long time. Even in ancient times, there was something called Greek fire, which was an early type of flame weapon.
Most flamethrowers used by armies today shoot out burning liquids. These liquids stick to things and burn for a while.
Flamethrowers were not used much in the 1800s because other weapons got much better. But during World War I, when soldiers fought in long ditches called trenches, flamethrowers became useful again. The German army started using them in 1915.
Contents
What is a Flamethrower?
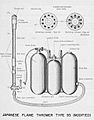
A flamethrower is a machine that throws a controlled stream of fire. It usually has a tank for fuel, a way to push the fuel out, and a way to light it on fire. The fuel is often a special kind of oil or gasoline.
How Flamethrowers Work
Most flamethrowers work by pushing a flammable liquid out of a nozzle. This is done using pressurized gas. As the liquid leaves the nozzle, it passes through a small flame or spark. This ignites the liquid, turning it into a stream of fire. The fire can reach many meters away.
History of Flamethrowers
People have tried to use fire as a weapon for thousands of years. Early versions were simple, like pots of burning oil thrown at enemies.
Ancient Flame Weapons
One of the earliest known flame weapons was Greek fire. This was a secret weapon used by the Byzantine Empire around the 7th century AD. It was a liquid that could burn on water. It was shot from a siphon, which was like a large hose. This made it an early type of flamethrower.
Modern Flamethrowers Emerge
The flamethrower we know today was developed in the early 1900s. A German inventor named Richard Fiedler created one of the first modern designs. It was used by the German army in World War I.
Flamethrowers in World War I
During World War I, soldiers fought in trenches. These were long, narrow ditches in the ground. It was hard to attack enemy trenches. Flamethrowers were used to clear out these trenches. They could force enemy soldiers out of their hiding spots.
Flamethrowers in World War II
Flamethrowers were used even more in World War II. They were very effective against enemy bunkers and caves. Soldiers could use them to burn out hidden enemy positions. Both Allied and Axis forces used flamethrowers.
Later Use of Flamethrowers
After World War II, flamethrowers were still used in some conflicts. For example, they were seen in the Korean War and the Vietnam War. However, they became less common over time. Other weapons, like powerful explosives, took their place.
Types of Flamethrowers
There are two main types of flamethrowers:
- Portable Flamethrowers: These are carried by one or two soldiers. They usually have a backpack with fuel tanks and a hose connected to a nozzle.
- Vehicle-Mounted Flamethrowers: These are much larger and are attached to tanks or other vehicles. They can shoot fire much farther and carry more fuel.
Safety and Rules
Flamethrowers are very dangerous weapons. They can cause a lot of damage and harm. Because of this, their use is often limited by international rules of war. They are also very heavy and difficult to use safely.
Images for kids
-
German Brandkommando (burning detachment) destroying Warsaw during the planned destruction of the city.
-
German flamethrowers during the First World War on the Western Front, 1917
-
A riverboat of the U.S. Brownwater Navy shooting ignited napalm from its mounted flamethrower during the Vietnam war
-
A British World War II–type "lifebuoy" flamethrower in 1944
-
A soldier from the 33rd Infantry Division uses an M2 flamethrower
-
Marines engaging Japanese positions on Guam with a flamethrower.
See also
 In Spanish: Lanzallamas para niños
In Spanish: Lanzallamas para niños