Fluvial terrace facts for kids
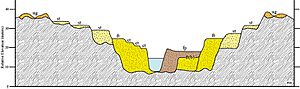
A fluvial terrace is like a step or a shelf found along the side of a river valley. Imagine a river flowing at a certain level, and over a long time, it cuts deeper into the ground. The old, flat area where the river used to flow is left behind, forming a terrace. It looks like a long, narrow staircase next to the river.
Each fluvial terrace has two main parts:
- A tread: This is the flat, top surface of the terrace. It's like the step itself.
- A scarp: This is the steep slope that connects the tread to the lower ground or the next terrace down. It's like the riser of the step.
Fluvial terraces can be grouped in different ways. For example, they can be called rock terraces or gravel terraces depending on what they are made of. They can also be called tectonic terraces or climate terraces based on what caused them to form.
How River Terraces Form
River terraces are usually formed in two main ways: by erosion or by deposition.
Erosional Terraces
An erosional terrace forms when a river cuts sideways into the land. Over time, the river erodes the bedrock (the solid rock underneath the soil) and carries away the material.
Here's how it generally works:
- When the river's water level is low, fine sand and mud settle on the riverbed.
- During normal flow, coarser materials like gravel are deposited.
- When the river floods and reaches its highest level, it becomes very powerful. It can pick up all the sediment in its path and even scour (scrape away) the bedrock beneath.
- After the flood, new coarse material is deposited on the riverbed.
- If the river then cuts deeper into the valley, the old, flat surface (the tread) that was formed by this sideways erosion is left behind as a terrace.
Depositional Terraces
A depositional terrace forms when a river valley gets filled up with a lot of sediment. The flat top surface of this sediment becomes the tread of the terrace.
This "valley filling" happens when the river can't carry away all the sediment that is being brought into its basin. This can be caused by several things:
- Glacial meltwater: When glaciers melt, they release huge amounts of water and sediment, which can fill valleys.
- Climate change: Changes in climate can affect how much sediment rivers carry.
- Changes in river level or slope: If the river's base level (the lowest point it flows to) changes, or its slope becomes less steep, it might drop more sediment.
Depositional terraces are often linked to changes in climate, while erosional terraces are more often linked to movements in the Earth's crust (tectonics).
Images for kids
-
Eroded alluvial fill 60 feet (18 m) thick at Kanab Creek, Kane County, Utah. In 1884 the stream ran at top of the terrace. 1939 photo by United States Geological Survey.
-
Unpaired fluvial terraces on the South Fork of the Shoshone River, Park County, Wyoming, 1923. The river at left has encountered a formation of erosion-resistant volcanic breccia, causing it to downcut more rapidly on the right, leaving terraces of different elevations.
See also
 In Spanish: Terraza aluvial para niños
In Spanish: Terraza aluvial para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |