Fort Anne facts for kids
| Former Names Charles Fort (1629–1632) |
|

Fort Anne at sunset
|
|
| Established | August 1, 1629 |
|---|---|
| Location | Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia, Canada |
| Official name: Fort Anne National Historic Site of Canada | |
| Designated: | January 30, 1920 |
Fort Anne is a very old fort in Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia. It was built to protect the town's harbour. Scottish settlers started building it in August 1629 and called it Charles Fort.
For over 100 years, the area around the fort was the capital of different colonies. First, it was the capital of New France's Acadia. Later, it became the capital of British North America's Nova Scotia.
Fort Anne is super important because it was Canada's very first National Historic Site. Even though it's not used for fighting anymore, it's the oldest fort still standing in Canada. It has seen more battles than almost any other fort in North America. People attacked or tried to block it at least 19 times over 225 years!
The fort also has Canada's oldest military building. This is a powder magazine from 1708, where gunpowder was stored. It is also the oldest building managed by Parks Canada.
The French first saw how important this spot was in 1604. After their first settlement was destroyed in 1613, Scottish settlers built a new fort here in 1629. They named it Charles Fort after King Charles I of Scotland.
Over the years, the fort changed hands many times. It was controlled by the French, then the English, and then the British. Finally, in 1713, the area became British for good after Queen Anne's War. The last time the fort was attacked was in 1781 by American privateers during the American Revolutionary War.
In 1917, the Canadian government took over Fort Anne. It became a National Historic Site in 1920. Today, you can visit the fort's grounds all year. Parks Canada runs a museum in the old Officer's Quarters, which was built in 1797. The museum is open from mid-May to mid-October.
Contents
The Land and Early Days
The area around Annapolis Basin was known as "Kespukwitk" by the Mi'kmaq people. This means "Land's End" in their language. It covered the southern part of what is now Nova Scotia. Allains Creek, near the fort, was a traditional Mi'kmaq campsite. It was part of an important route for canoes across southern Nova Scotia.
In 1605, the French built a settlement on the other side of the Annapolis Basin. This settlement was destroyed in 1613. Even though the French continued to live in the area, they did not rebuild their fort there.
Scottish Fort (1629–1632)
In 1629, Scottish settlers built the first fort on the spot where Fort Anne stands today. They knew about the French settlement across the basin. But they chose a new location where the Annapolis River and Allains Creek met. This spot was naturally protected by the rivers. It was also next to farmland that the French had already started using.
Building the new fort began on August 1, 1629, and it was finished in just a few weeks. A person named Richard Guthry, who was there, said, "The first of August...was the foundation of our fort laid." This first fort, called Charles Fort, is considered one of the oldest European buildings in Canada.
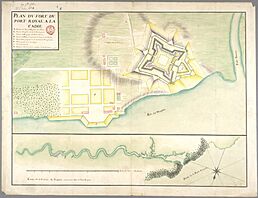
The fort was designed like a five-sided star, which was good for both attacking and defending. It had eight cannons, a storage building for supplies, and a house for the leader.
French Control (1632–1654)
In 1632, Acadia (including this fort) became French again because of a peace treaty. Charles Fort was given to the French. By 1643, they built a new fort made of earthworks to replace the Scottish one.
This fort was attacked three times in the next 22 years. It successfully defended against two attacks from other French settlers during the Acadian Civil War. However, it fell to the English in 1654.
Battles During French Control
- Battle of Port Royal (1640) - Charles de Saint-Étienne de la Tour attacked the fort with two ships. The French governor's captain was killed, but La Tour and his men had to give up.
- Battle of Port Royal (1643) - La Tour tried to capture the fort again. The governor fought back, and La Tour's men were hurt or killed. La Tour didn't attack the fort itself, but he burned buildings and stole supplies.
- Battle of Port Royal (1654) - About 100 American volunteers and 200 English soldiers attacked the fort. The French, with only 130 defenders, eventually surrendered. The English then controlled Acadia for 16 years.
English Control (1654–1667)
The English held the fort for 16 years. During this time, there were no major battles at the fort. In 1667, Port Royal was given back to France as part of the Treaty of Breda. Even though the English ruled, most people living there were still French.
French Control Again (1667–1713)
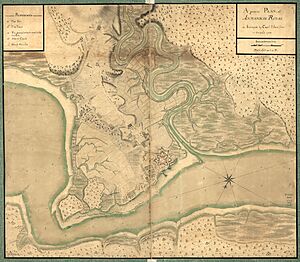
The French controlled the fort for another 43 years. During King William's War (1688–1697), the fort was attacked three times. In 1689, they started building a much bigger and stronger fort. It was about six times larger than the first Scottish fort. However, this work stopped after only two weeks. This left Port Royal without a strong fort.
When soldiers from New England arrived in 1690, the fort was easily captured. But the English only stayed for a short time. The fort was attacked two more times before the war ended, but the English did not take over the land.
Work on the fort started again in 1702. This time, they built it in a special "Vauban" star shape. This design is still mostly visible today. The star shape and gently sloped walls helped protect the fort from cannon fire. The low walls made it a smaller target. The soft earth could absorb impacts better. The star shape also allowed more cannons to fire at attackers from any direction.
Because of this new design, the fort successfully defended against three British attacks during Queen Anne's War (1702-1713). However, in 1710, a huge British force of 2,000 soldiers and 36 ships finally captured it. The French tried to get the fort back in 1711 but failed.
Battles During Second French Control
- Battle of Port Royal (May 1690) - In May 1690, a large group of New England soldiers arrived. The French governor had only 70 soldiers, and the fort was not ready. He quickly surrendered. The New Englanders then looted the town and fort.
- Battle of Port Royal (June 1690) - More soldiers arrived in June 1690. They burned and looted the settlement before leaving.
- Raid on Port Royal (1693) - English ships attacked Port Royal, burning houses and barns.
- Blockade of Port Royal (1704) - In July 1704, Major Benjamin Church blocked Port Royal for 14 days. The fort had just been upgraded, and the defenders were ready. Church eventually left without attacking the fort.
- Siege of Port Royal (June 1707) - In June 1707, Colonel John March tried to capture Port Royal. The French governor successfully defended the fort.
- Siege of Port Royal (August 1707) - In August 1707, a second attack lasted eleven days. The French killed sixteen New Englanders and lost three of their own. This attack also failed.
- Siege of Port Royal (1710) - In September 1710, the British returned with a massive force. They surrounded the fort. The French defenders, about 300 of them, surrendered on October 2. This ended French rule in Acadia.
- Siege of Port Royal (1711) - After a nearby battle, the French tried to recapture the fort but were unsuccessful.
British Control (1713–1854)

The British controlled Fort Anne for 141 years. In 1713, a treaty officially gave a large part of Acadia, including Port Royal, to Great Britain. The British had already been in control since 1710. At this time, the town was renamed Annapolis Royal, after Queen Anne.
During Father Rale's War (1722–1725), Mi'kmaq and Maliseet troops attacked the fort twice. They were not successful in taking the fort, but there were casualties on both sides.
The last big attempt by the French to get Fort Anne back was during King George's War (1744–1748). After three failed tries, the French sent a huge fleet in 1746. This fleet, called the Duc d'Anville expedition, aimed to recapture both Port Royal and Louisbourg. This plan also failed. It was the last time the French tried to take the fort back.
During the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), American privateers attacked the fort twice. They were more interested in stealing things than in taking over the fort.
Even though there was a chance of attacks during the War of 1812, none happened at Fort Anne.
In 1854, a new fort was finished in Halifax. The British soldiers at Fort Anne moved there. The United Kingdom owned Fort Anne until 1883, but it was no longer used for fighting. Most of the fort's remaining buildings were destroyed. Then, in 1917, the Canadian government became interested in the site.
Battles During British Control
- Blockade of Annapolis Royal (1722) - In May 1722, Mi'kmaq and Maliseet troops tried to surround Annapolis Royal. The British took 22 Mi'kmaq as hostages to stop the attack.
- Raid on Annapolis Royal (1724) - In July 1724, 60 Mi'kmaq and Maliseets raided Annapolis Royal. They killed soldiers, wounded others, and scared the town. They also burned houses and took prisoners. The British responded by executing one of the Mi'kmaq hostages.
- Siege of Annapolis Royal (July 1744) - On July 12, 1744, 300 Mi'kmaq warriors attacked Annapolis Royal. They outnumbered the British soldiers. Two British soldiers were captured. The attack lasted four days until more British soldiers arrived.
- Siege of Annapolis Royal (September 1744) - In September 1744, François Dupont Duvivier attacked Annapolis Royal with 200 local Acadians. They fought against 250 soldiers at the fort. The siege lasted a week. When British reinforcements arrived first, Duvivier had to retreat.
- Siege of Annapolis Royal (1745) - In May 1745, Paul Marin de la Malgue led 200 troops and hundreds of Mi'kmaq in another attack. The siege ended quickly when Marin was called away to help defend Louisbourg.
- Siege of Annapolis Royal (1746) - The French surrounded Annapolis Royal for 23 days. They were waiting for ships to help them, but the ships never arrived. They had to retreat. This was the last major French attempt to retake the fort.
- Raid of Annapolis Royal (1778) - On October 2, 1778, British soldiers defeated American privateers who were raiding Annapolis Royal. The British destroyed the privateer ship.
- Raid of Annapolis Royal (1781) - In 1780, the soldiers from Fort Anne were sent to help in South Carolina. On August 29, 1781, two large American privateer ships attacked the undefended town. They looted both the fort and houses. Two town residents were taken hostage but later released.
Fort Anne National Historic Site
In 1917, the Canadian government took over Fort Anne. It was named Fort Anne National Park. Two years later, it became a National Historic Site in 1920.
Fort Anne is often called Canada's "first National Historic Site." This is because it was the first place the government bought for its history that is still managed by Parks Canada today.
What You Can Still See Today
- The remains of the French fort (1702–1708) with its star-shaped walls.
- An underground powder magazine from 1708.
- A well in the parade square and another well.
- Earthworks (mounds of earth used for defense).
- Shoreline cribwork (wooden structures along the water) from the 1740s.
- Queen’s wharf (a dock) from the 1740s.
- A dry-stone retaining wall from 1760.
- The British Officers’ Quarters (built 1797–1799). This building was rebuilt in 1935 and now holds the museum. It has exhibits about the fort's history and old items found in the area.
- A sally-port (a secret exit) from the 1800s.
- An Acadian cemetery.
- A British garrison cemetery.
Important Leaders
- Sir William Alexander (1629–1630)
- Sir George Home (1630–1632)
- John Doucett (1717–1726)
- Lawrence Armstrong
- Alexander Cosby
- Paul Mascarene
- Henry Daniel (military officer)
- John Handfield (1752–1755)
Legacy
On June 28, 1985, Canada Post released a stamp featuring 'Fort Anne, N.S., circa 1763.' This was part of a series called "Forts Across Canada."
See also
- Military history of Nova Scotia
- List of forts
- List of oldest buildings in Canada
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |