Four Commanderies of Han facts for kids
The Four Commanderies of Han (Chinese: 漢四郡; pinyin: Hàn-sìjùn; Korean: 한사군; Hanja: 漢四郡; RR: Han-sagun) were special areas controlled by the ancient Chinese Han dynasty. They were located in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula and a bit of the Liaodong Peninsula. These areas were set up around 108 BC by Emperor Wu of Han after his army defeated a kingdom called Wiman Joseon.
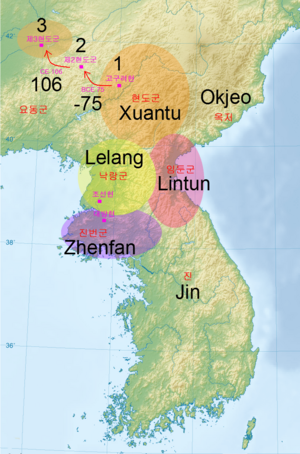
The main goal of these commanderies was to control the people living in the former Gojoseon area. The most important one was the Lelang commandery, near what is now Pyongyang. Some historians see these commanderies as Chinese colonies. While scholars in North Korea disagree, most historians outside North Korea believe Lelang was indeed in the Korean Peninsula. It was a major center for trade and culture between China and the local people for about 400 years.
Chinese officials, soldiers, and traders lived in a special city within Lelang. Their way of ruling greatly changed the local Gojoseon society. Later, a new Korean kingdom called Goguryeo (founded in 37 BCE) began to fight and take over these Chinese areas. By the early 4th century AD, Goguryeo had fully absorbed them into its own territory.
Contents
What Were the Commanderies?
Early Chinese Control
Before the Han dynasty set up the Four Commanderies, there was an earlier Chinese area called Canghai Commandery. It covered parts of the northern Korean peninsula and southern Manchuria. This commandery was created after a local leader named Nan Lü, who was part of Wiman Joseon, rebelled and joined the Han dynasty with many people. However, this early commandery only lasted for two years before it was removed.
The Four Main Commanderies
The Han dynasty established four main commanderies after defeating Gojoseon:
- Lelang Commandery (樂浪郡): This was the largest and most important. It lasted from 108 BC to 313 AD. In 2 AD, it had 25 smaller districts and over 400,000 people.
- Lintun Commandery (臨屯郡): This one was set up in 107 BC but was absorbed into Xuantu by 82 BC.
- Xuantu Commandery (玄菟郡): Also started in 107 BC, it lasted until 319 AD. In 2 AD, it had 3 smaller districts and over 220,000 people.
- Zhenfan Commandery (眞番郡): Established in 107 BC, it was absorbed into Lelang by 82 BC.
Daifang Commandery
Later on, a new commandery called the Daifang Commandery (帶方郡) was created. It was separated from the Lelang Commandery between 204 AD and 210 AD and lasted until 315 AD.
History of the Commanderies
Han Dynasty Rule
When the Han dynasty defeated Gojoseon in 108 BC, they created the Lelang, Lintun, and Zhenfan commanderies. The Xuantu Commandery was added a year later. However, some of these commanderies did not last long. By 82 BC, Lintun and Zhenfan were absorbed into Xuantu and Lelang. Xuantu even moved its main city to Liaodong in 75 BC because of strong resistance from the local people.
These commanderies were managed just like other areas within the Han dynasty. Local Korean groups, like the Jinhan confederacy and Byeonhan confederacy, traded with Lelang and bought goods like mirrors. Over time, a mix of Han Chinese and local Korean cultures developed in Lelang.
Changes in Control
After the Han dynasty started to weaken, a powerful family called the Gongsun family took control of the Liaodong region, which included some of the commanderies.
- Gongsun Du became a powerful leader in 189 AD. He expanded his territory and even fought against the kingdom of Goguryeo. He died in 204 AD.
- His son, Gongsun Kang, took over. In 204 AD, he expanded into Goguryeo's land and created the Daifang Commandery. He also helped the Chinese general Cao Cao by killing some of Cao Cao's enemies who had fled to his territory.
- Gongsun Kang died in 220 AD. His brother, Gongsun Gong, ruled next.
- Later, Gongsun Gong's nephew, Gongsun Yuan, took power in 228 AD. He tried to rule independently, but a powerful Chinese general named Sima Yi invaded in 238 AD and took over his land.
After these events, Goguryeo grew stronger. In 238 AD, Goguryeo even worked with the Chinese state of Cao Wei to defeat the Gongsun family.
Later Chinese Dynasties and Goguryeo's Rise
Goguryeo attacked the Xuantu Commandery in 242 AD. In response, the Chinese state of Cao Wei invaded Goguryeo from 244 to 245 AD. The Wei general Guanqiu Jian attacked Goguryeo's capital and forced its king to flee. This greatly weakened Goguryeo for a while.
After this, the Lelang, Daifang, and Xuantu commanderies were ruled by different Chinese dynasties, including Cao Wei and the Jin dynasty (266–420). However, Goguryeo continued to grow stronger.
Goguryeo Takes Over
The Jin dynasty (266–420) ruled Lelang Commandery until 313 AD. But because of civil wars in China, the Jin dynasty could not properly manage its territories in northern Korea. Local leaders in Liaodong and Lelang broke away from Jin rule.
Goguryeo then attacked and took over the Lelang Commandery in 313 AD. They conquered Daifang Commandery between 314 and 315 AD, and Xuantu Commandery in 319 AD. After the Chinese commanderies fell, Goguryeo welcomed Chinese people who wanted to move there. This helped Goguryeo strengthen its control over the region.
Different Views on History
In North Korea and some parts of South Korea, some scholars disagree about where the Han commanderies were located. They claim that these Chinese areas were actually outside the Korean Peninsula, perhaps in the Liaodong Peninsula in modern-day China.
This idea came partly from how Japanese scholars during colonial times studied the Lelang Commandery. They found many historical items near Pyongyang and said that this Chinese commandery had a big impact on Korean civilization. Before North Korea challenged this, most people agreed that Lelang was established by Emperor Wu of Han after he defeated Gojoseon in 108 BCE.
North Korean scholars say that the Chinese items found, like tombs and jewelry, are actually from Gojoseon or Goguryeo. They argue that if the items look Chinese, they were either brought through trade or were fake. They also suggest there were two Lelangs: one run by the Han dynasty in China, and an "independent Korean state" called Nangnang Kingdom near Pyongyang. They say the traditional view of Lelang was made up by Chinese and Japanese imperialists.
However, most scholars in South Korea, the United States, China, and Japan do not agree with this new theory. Many Korean scholars from the Goryeo and Joseon dynasties believed Lelang was near today's Pyongyang, based on old Korean history books like Samguk Yusa. Some scholars, like Bak Ji-won from the Joseon dynasty, did suggest Lelang was in Liaodong after visiting China. More recently, some historians from North and South Korea have also published research suggesting the Han commanderies were in the Liaodong Peninsula.
Images for kids
-
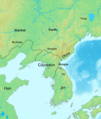
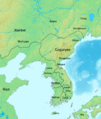
Korea before 108 BC. This shows Wiman Joseon before the Han dynasty defeated it.
-
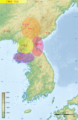
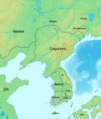
The Han Dynasty defeats Wiman Joseon in 108 BC and sets up the Four Commanderies.
-
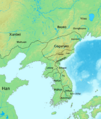
Korea in 315 AD. Goguryeo has taken back the land that used to be Gojoseon's.
See also
- Han conquest of Gojoseon
- Daifang Commandery
- Canghai Commandery
- Wiman Joseon